IB-SL Review – Electrostatics & Electricity 1. Which of the following
advertisement
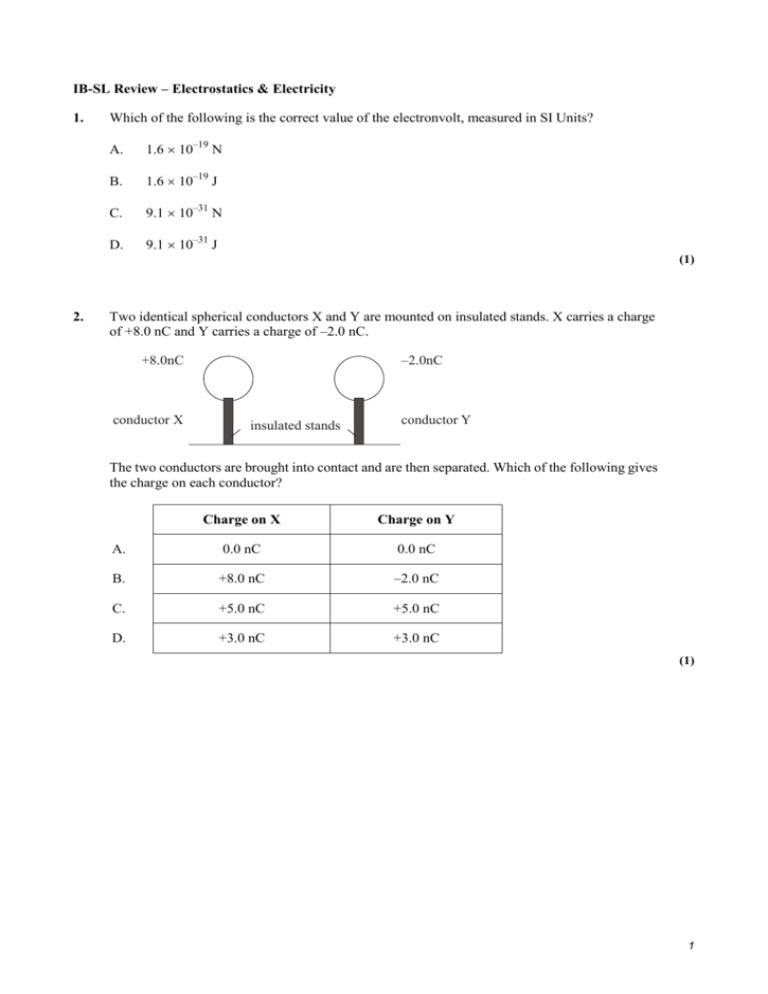
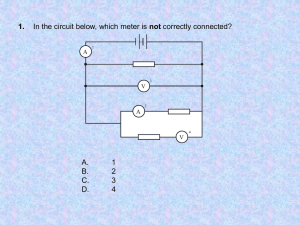
IB-SL Review – Electrostatics & Electricity 1. Which of the following is the correct value of the electronvolt, measured in SI Units? A. 1.6 10–19 N B. 1.6 10–19 J C. 9.1 10–31 N D. 9.1 10–31 J (1) 2. Two identical spherical conductors X and Y are mounted on insulated stands. X carries a charge of +8.0 nC and Y carries a charge of –2.0 nC. –2.0nC +8.0nC conductor X insulated stands conductor Y The two conductors are brought into contact and are then separated. Which of the following gives the charge on each conductor? Charge on X Charge on Y A. 0.0 nC 0.0 nC B. +8.0 nC –2.0 nC C. +5.0 nC +5.0 nC D. +3.0 nC +3.0 nC (1) 1 3. A positively charged rod is brought close to an earthed sphere S, as shown below. S The earth connection to the sphere is removed and then the charged rod is removed. The sphere S is found to be negatively charged. Which one of the following describes the material of S and the movement of charge between S and earth? Material of S Movement of charge A. conductor negative charge moves from earth to S B. insulator negative charge moves from earth to S C. conductor positive charge moves from S to earth D. insulator positive charge moves from S to earth (1) 4. A battery is connected to a resistor as shown below. energy transferred E B energy transferred E R The battery transfers energy EB when charge Q passes completely around the circuit and the resistor transfers energy ER. The emf of the battery is equal to A. ER . Q B. EB . Q C. EB ER . Q D. EB ER . Q (1) 2 5. The graph below shows the variation with potential difference V of the current I in an electrical component. I 0 0 V0 V Which one of the following is a correct statement about the resistance of the component? A. For potential differences greater than V0, the resistance is constant. B. For potential differences greater than V0, the resistance decreases with increasing potential difference. C. The variation of current with potential difference is linear and so Ohm’s law is obeyed. D. For potential differences less than V0, the resistance is zero. (1) 6. The resistors in each of the circuits shown below each have the same resistance. circuit P circuit Q circuit S Which of the following gives the circuits in order of increasing total resistance? A. P Q S B. Q P S C. S Q P D. P S Q (1) 3 7. X and Y are two identical conducting spheres separated by a distance d. X has a charge +6 μC and Y has a charge –2 μC. The electric force between them is + F (ie attractive). The spheres are touched together and are then returned to their original separation d. The force between them now is A. +F. B. –F. C. F . 3 D. F . 3 (1) 8. In the circuit below, the battery has negligible internal resistance. Lamps L, M and N which have different resistance are connected as shown. L M N Which one of the following is always true? A. Lamps L and N have the same current through them. B. Lamps L and M have the same current through them. C. Lamps L and N have the same potential difference across them. D. Lamps L and M have the same potential difference across them. (1) 9. A conductor of constant resistance dissipates 6.0 W of power when the potential difference across it is 12 V. The power that will be dissipated in this conductor when the potential difference across it is 24 V is A. 6.0 W. B. 12 W. C. 24 W. D. 48 W. (1) 4 10. An electron and a proton are accelerated from rest through potential differences of the same magnitude. After acceleration the speed of the electron is ve and the speed of the proton is vp. Which of the following is the best estimate for the ratio A. 2000 B. 2000 vp ? ve 1 2000 C. D. 1 2000 (1) 11. A resistor of resistance 1.0 is connected in series with a battery. The current in the circuit is 2.0 A. The resistor is now replaced by a resistor of resistance of 4.0 . The current in this circuit is 1.0 A. A 2.0 A 1.0 4.0 The best estimate for the internal resistance of the battery is A. 1.0 . B. 2.0 . 4.0 . C. D. 5.0 . (1) 12. The graphs below are the current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of three electrical components P, Q and R. component P component Q I 0 component R I 0 0 V 0 I V 0 0 V Which component(s) has (have) constant resistance? A. P only B. R only C. P and Q only D. P and R only (1) 5 13. The graph below shows the variation with current I of the potential difference V across a filament lamp. V / volts 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 I / mA The resistance of the lamp when I = 1.5 mA is A. 950 . 400 . B. C. 0.95 . D. 0.40 . (1) 14. A voltmeter of resistance 50 k is connected in a circuit as shown in the diagram below. e.m.f. = 12V V 50k R 10k The emf of the battery is 12 V and the resistance of the resistor is 10 k. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. The reading of the voltmeter is A. 0.0 V. B. 2.0 V. C. 10 V. D. 12 V. (1) 6 15. A metal conductor is negatively charged. It is connected to earth using a metal wire, as illustrated below. negatively-charged conductor wire earth What is the movement of charge as the conductor is earthed? A. Positive charge moves from earth to the conductor. B. Negative charge moves to earth from the conductor. C. Negative charge moves from the conductor and positive charge moves from earth. D. Positive charge from the wire moves to the conductor and negative charge moves to earth. (1) 16. Which graph best represents the relationship between the current I and the voltage V of a filament lamp. A. 0 0 C. B. V 0 0 0 0 I D. V I V I V 0 0 I (1) 7 IB-SL Review – Electrostatics & Electricity 1. B 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. B 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. C 10. C 11. B 12. A 13. B 14. C 15. B 16. C 8