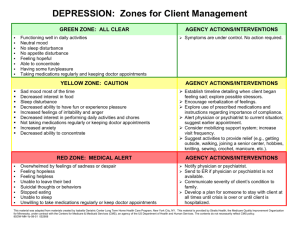
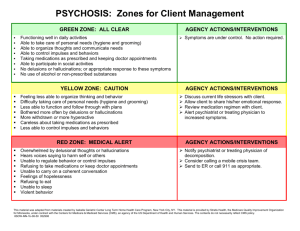
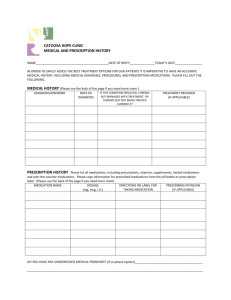
PERSON handout - Austin Community College
advertisement

P Need: Psychosocial E Need: Elimination History – demographic information – ethnicity, religion, age sex, marital status. View of self – self-esteem, internal vs. external locus of control Sexuality Perception of stress and ways of coping Beliefs and attitudes about illness Family assessment – support systems Home and community assessment (The data will be used to help the patient cope with illness/hospitalization, find effective teaching methods, and plan for discharge.) Current Status – includes a mental status exam (part of which will be learned this semester) Degree of reality orientation – orientation to time, place, and person; memory – remote and recent General observations of intelligence, behavior, speech, mood or affect, ability to understand and follow directions, attention span, etc. P-Need Medications – ie. Psychotropic, Tranquilizers, etc. History of urinary, renal, or bowel problems. Patterns of elimination, e.g., has daily BM, wakes up several times a night to urinate, has difficulty starting stream. Past illness or surgery. Use of laxatives or other aids to elimination. Current Status – pattern, method (bedpan, toilet), difficulty with urination, number of days since last BM. Use of foley catheter. Description of urine or BM. Physical assessment of abdomen Relevant laboratory tests – BUN, Creatinine, Xrays, CT scan E-Need Medications ie., Laxatives, Urinary antispasmodics Diagnostic test – Colonscopy, Barium enema, Cystoscopy Therapeutic interventions Fluid intake and output for a 24 hour period R Need: Rest, Regulatory, Reproductive S Need: Safety Rest, sleep, activity, comfort Description of rest/restful activity Normal sleep pattern Changes in sleep pattern Aids used in sleep Usual pattern of daily activity Exercise, types, amount, frequency Aids in ambulation Medications associated with activity Pain – onset, progression, duration, character, location, course, aggravating or relieving factors Treatment to relieve pain (history or current) NOTE: this area also includes regulatory mechanisms, i.e., the neurological and endocrine systems Neurological exam: level of consciousness speech problems perceptual problems emotional problems PERLA motor deficits – movement of extremities sensory deficits – vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch Endocrine system – evaluation for the function of pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, pancreas, and adrenals NOTE: is the patient diabetic? Current status – see preceding list Diagnostics Therapeutic interventions Assessment of reproductive function Usual physical environment-stairs, equipment, pollution (the elderly sometimes function well in familiar environment and appear disoriented in the hospital) Hygiene Skin – usual care, condition Medications (not included elsewhere); over-thecounter; allergies; immunizations; antibiotics Emotional environment prior hospital experience present attitude toward hospital need for privacy strength of nurse patient relationship Physical environment in hospital Risk factors for infection Risk for fall O Need: Oxygenation N Need: Nutrition History of cardiac or respiratory problems Occupational or environmental hazards (other risk factors) Physical assessment of chest, skin, pulses, blood pressure, breathing patterns, temperature, exercise tolerance Diagnostic tests – EKG, electrolytes, CPK, LDH, SGOT, Hg, Hct Therapeutic interventions O-Need Medications – Cardiac glycosides, Calcium channel blockers, Beta blockers, Antihistamines, Antitussives Family history of ulcers, Ca, colitis, diabetes Patient, history – GI diseases, diabetes, “gas,” belching, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, pain, difficulty eating, swallowing, or digesting food, weight gain or loss Height / Weight General appearance Diet patterns Food restrictions; allergies; tolerances; special diet Food preferences Fluid intake Care and condition of teeth N-Need Medications Nutritional and abdominal assessment Laboratory and diagnostic tests Therapeutic interventions