Class XI Physics
advertisement

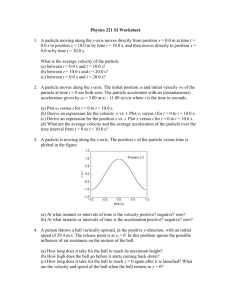
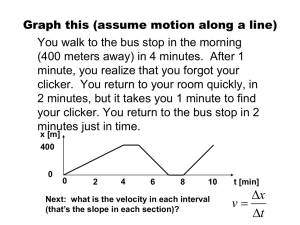
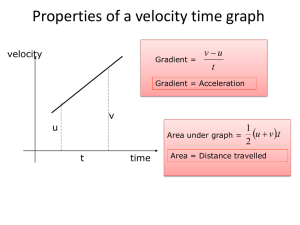
Summer Holiday Homework Session 2013-2014 Name: _____________________ S.No. : 1 Date: _______/ _05_____/ _2013_ Class: XI-A D-II, VasantKunj, New Delhi - 110070 Subject: Physics Topic: Unit1 & Unit 2 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: A: The numerical are based on application of theory content. Attempt them in your physics notebook as practice assignment. B: Do all questions in sequence. Unit-I: Physical World and Measurement 1. Check the correctness of the following equations (i) v2=u2+2aS (ii) K E=1/2 mv2 2. Centripetal force acting on a body moving along a circular path depends on (i) mass of body (m), velocity of the body (v), radius of circular path (r). Using the method of dimensions derive the expression for centripetal force. 3. Rate of flow of liquid through a pipe depends on (i) pressure gradient exist between the ends of pipe (P/l))(ii)radius of the pipe (r)(iii)co-efficient of viscosity of liquid(η). using the method of dimensions derive the expression for Rate of flow of liquid through a pipe. 4. Energy of a body executing SHM depends on (i) mass of the body(m) (ii) amplitude with which the body oscillate(a) (iii)frequency of oscillation(ν) using the method of dimensions derive the expression for centripetal force. 5. Convert one Newton into dyne using the method of dimensions. 6. Assuming that the mass M of the largest stone that can be moved by a flowing river depends upon ‘v’ the velocity, ‘ρ’ the density of water and on ‘g’ the acceleration due to gravity. Using dimensions show that M varies with the sixth power of the velocity of flow. 7. State the no. of significant figures of the following (a) 5.327 104 8. (b) 12.00 (c) 5.07 (d) 9320 (d) 214.213 The radius of a cylinder is 1.250cm and its length is 5.7324cm.Calculate its area and volume to the correct significant figures? 9. What is the difference between angstrom unit and A.U.? 10. What are micron and Fermi? 11. If x = a + bt + ct2, where x is in metres, t in seconds, what is the unit of c? 12. The moon is observed from two diametrically opposite points A and B on earth. The angle subtended at the moon by the two directions of observations is 10 54’. Given the diameter of the earth to be about 1.276 x 107 m. Compute the distance of the moon from the earth. 13. Write the dimensional formulae of the following: Power, pressure, mass density, momentum, resistance, acceleration. THS,VK, Cl.XI Physics, Summer HHW, Topic: Unit1 & 2 Session:2013-14 Page 1 14. Find the dimensions of a and b in the equation F= at + bt2, where F is force and t is time. 15. Specific resistance ρ of a thin circular wire of radius r cm, resistance R ohms and length L is given by Ρ = π r2R/L. If r = 0.26+0.01 cm, R = 30 + 2 ohm and L = 75.00 + 0.01cm, find the percentage error in ρ. 16. If 500g be the unit of mass, 50s the unit of time and acceleration due to gravity 980cms-2 be the unit of acceleration, find what will be the new unit of energy? Unit-II: Kinematics 1. Can a body have zero velocity and finite acceleration? Give one example? 2. A car starting from rest acquires a speed of 25ms-1 in 10 seconds, after which it maintains this speed for 10 seconds. Find (a) the acceleration (b) distance traveled during acceleration (c) total distance traveled? 3. Show that the area under velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the body? 4. A particle moves along x-axis in such a way that its coordinate (x) varies with time t, according to expression x=2-5t+6t.Find the initial velocity of the particle and acceleration x in meter and t in second. 5. A particle is projected at 60º to the horizontal with a kinetic energy K. What is the kinetic energy at the highest point? 6. Which of the following statements is false for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed? (a) the velocity vector is tangent to the circle (b) the acceleration vector is tangent to the circle (c) the acceleration vector points to the centre of the circle (d) the velocity and acceleration vectors are perpendicular to each other 7. The distance traveled by an object along the axes are given by x=2t², y = t² – 4, z = 3 t – 5. What is the initial velocity of the particle? 8. A boy playing o the roof of 10m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 30º the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10m from the ground? 9. If a body travels half of its path in the last second of its fall from rest; find the time and height of its fall? 10. A bullet strikes a uniform plank with a speed of 400ms-1 and comes out with the half the velocity. What would be the velocity if the plank were only half thick? 11. A train passes three points A,B ,C at 24 kmh-1,36 kmh-1,54 kmh-1 respectively with uniform acceleration. If the distance AB=2 km, find the distance BC? 12. A stone thrown vertically up went up 98m and came down. How long it was in air? 13. A man walks on a straight road from his home to market, which is 2.5km away from his home with a speed of 5kmh-1. Finding market closed, he returns and walks back THS,VK, Cl.XI Physics, Summer HHW, Topic: Unit1 & 2 Session:2013-14 Page 2 to home with a speed of 7.5kmh-1. 31. Find out the average speed the person? From the velocity-time graph of uniform accelerated motion deduce the equations of motion in(i) Velocity and time (ii) distance and time 14. (iii) distance and velocity. A body moving with uniform acceleration describes 20 m in 2nd and 30 m in 4th second of its motion. Describe the distance moved by it in 6th second. 15. A particle is thrown vertically upwards with the velocity of 19.6 m/s .Find a. the velocity and acceleration of the particle at the highest point. b. how high a particle will rise? c. time taken for rising to the highest point. d. time taken for falling from the highest point of projection. e. its velocity, when it comes back to the point of projection. 14. A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 3m. After striking the ground it rises to height of 2 m . If it remains in contact with the ground for 0.01s, find the average acceleration during this time. 15. A particle is moving along x- axis. The position of the particle at any instant is given by X = a + bt2. Where, a = 6m and b = 3.5 m/s2. T is measured in seconds. Find (i) the velocity of the particle at t = 0s and t = 3s. (ii) the average velocity between t = 3s and t = 6s. 16. The velocity of a particle is given by the equation, v = 2t2 + 5 cm/s. Find (i) the change in velocity of the particle during the time interval between t1 = 2s and t2 = 4s (ii) the average acceleration during the same interval and (iii) the instantaneous acceleration at t2 = 4s. 17. On a foggy day two drivers spot each other when they are just 80 m apart. They are travelling at 72 km/h and 60 km/h, respectively. Both of them applied brakes retarding their cars at the rate of 5 m/s2.Determine whether they avert collision or not. 18. A tennis ball is dropped on the floor from a height of 4m. It rebounds to a height of 3m. If the ball was in contact with the floor for 0.01 s, what was its average acceleration during contact? 19. A ball is thrown upwards with an initial velocity of 100 m/s. After how much time will it return? Draw velocity – time graph for the ball and find from the graph (i) the maximum height attained by the ball and (ii) height of the ball after 15 s. Take g = 10 m/s2. 20. A car, starting from rest, accelerates at the rate f through a distance s, then continues at constant speed for some time t and then decelerates at the rate f/2 to come to rest. If the total distance is 5 s, then prove that s = ½ ft2. 21. The position coordinate of a moving particle is given by x = 6 + 18t + 9t2 (x in metres and THS,VK, Cl.XI t in seconds). What is its velocity at t = 2 sec? Physics, Summer HHW, Topic: Unit1 & 2 Session:2013-14 Page 3 22. Derive kinematic equations of motion for uniformly accelerated motion by Calculus method. Investigatory Projects- Physics (2013-14) As per C.B.S.E. guidelines, all students have to prepare one Investigatory Project carrying 3 marks. All students are therefore, advised to prepare one Investigatory Project on any one of the following topics or any other topic of their choice based on concept of physics after consulting the teacher during the summer vacation. POINTERS FOR MAKING PROJECT REPORT The material should be placed and bound in the following order: 1. Top Sheet of transparent plastic –The top page of your report should carry the following information in printed form or handwritten in neat block letters: Title of Project: Name of Student: Roll Number: Date of submission: 2. Aim of Project 3. Apparatus required 4. Principle/theory 5. construction with labeled diagram, 6. Working 7. Observations 8. calculations, 9. Result/ Conclusions 10. Applications, 11. Graphs if any, 12. References/bibliography 13. Back cover of plastic: may be opaque or transparent THS,VK, Cl.XI Physics, Summer HHW, Topic: Unit1 & 2 Session:2013-14 Page 4 List of Investigatory Projects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. To demonstrate that a centripetal force is necessary for moving a body with a uniform speed along a circle, and that the magnitude of this force increases with increase in angular speed. To demonstrate inter-conversion of potential and kinetic energy. To demonstrate conservation of linear momentum. To demonstrate the law of moments. To demonstrate the effect of angle of launch on range of a projectile. To demonstrate that the moment of inertia of a rod changes with the change of position of a pair of equal weights attached to the rod. To study variation of volume of a gas with its pressure at constant temperature using a doctors’ syringe. To demonstrate Bernoulli's theorem with simple illustrations To demonstrate free oscillations of different vibrating systems. To demonstrate resonance with a set of coupled pendulums. To demonstrate longitudinal and transverse waves. To demonstrate resonance using an open pipe. Note: Complete the practical file, activity file and the investigatory project and submit the same within one week after re opening of school i.e.by 7th of July.2013. Name of Teacher: R.K.Sharma THS,VK, Cl.XI Physics, Summer HHW, Topic: Unit1 & 2 Session:2013-14 Page 5