Humid Subtropical Climate: Locations, Weather, and Biomes
advertisement

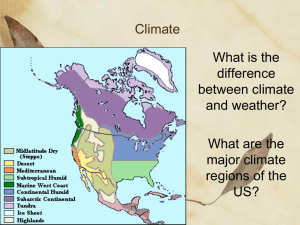
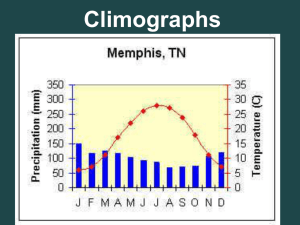
Humid Subtropical Climate Type Where is it Usually Located? The Humid Subtropical climate is found on the east coast of continents between 20o and 40o north and south of the equator. The southeast United States is a good example of this climate. Florida has a Humid Subtropical climate. It is noteworthy that the Mediterranean climate occupies the western sides of the continents, whereas the humid subtropical climate is located on the eastern sides. Since in the Northern Hemisphere land masses are more extensive in the middle latitudes than those in the Southern Hemisphere, this climate covers much larger areas in the Northern Hemisphere. The subtropical humid climate is developed in the following regions: Southeastern United States of America, eastern Asia, particularly China, south of the Hwang Ho River, eastern and central South America (in Paraguay, Southern Brazil, Uruguay, and northeastern Argentina), east coasts of South Africa and Australia. Locations- United States What Seasons Does it Have? Temperatures usually stay high (above 70) throughout the year, but cool down for a few months, so there are really only 2 seasons here: summer and winter. However, the winter season is not a cold winter. Summer season lasts longer, since Humid Subtropical areas are somewhat near the equator. What are the Temperatures Like? Humid Subtropical climate is known for hot humid summers and mild winters. During the summer the average temperature is between 70 and 80 degrees. The coldest month usually averages 45-50 degrees. Since Humid Subtropical is found between 20o and 40o latitude, they receive direct sunlight for a large part of the year. How Much Precipitation Does it Receive? Most Humid Subtropical areas receive about 48 inches of rain each year. The rain falls throughout the year. The regularly high temperatures evaporate water, which causes humidity and precipitation. The high humidity in this region makes summer temperatures feel even hotter. Humid Subtropical areas usually experience strong storms such as tornadoes and hurricanes. What Kinds of Vegetation (Plants) Does it Have? The natural vegetation found in Humid Subtropical areas are mainly evergreen trees, bushes, and shrubs. These are not the hardy evergreen trees like pine and spruce. Most of these evergreens are more delicate. The reason many plants here are evergreens is because of the long months of warmth and regular rain. These plants have adapted to the regular climate conditions. Many broad-leaf evergreens such as palm trees and ferns are found here. Many plants can be farmed here since the growing season is sometimes 8 months long. What Kind of Animals Does it Usually Have? Humid Subtropical supports many types of mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. Alligators, deer, and panthers can be found in the US. Brazil's subtropical area has the capybara, which is the world’s largest rodent. INDUSTRIES Industrial Crops Tobacco and cotton grow well in the humid subtropical climate. Deciduous and evergreen trees also grow quickly in the humid subtropics. Both managed tree plantations and logging of wild forests are a major economic activity in this climate zone. Pine tree products like pitch, tar and turpentine are produced in these areas. Jute and sisal, raised for fiber, also grow in humid subtropical environments. Biofuel crops like sugar cane and subtropical jatropha are rising in importance in the humid subtropics. Tourism The humid subtropics can be a winter haven for those from cooler climates, providing warm weather without the oppressive heat of the tropics. In areas with a waterfront, mountains or scenery, the humid subtropics are ripe for tourism since they are open for travel year round. Examples of tourist destinations in humid subtropic regions include Florida in the United States, Buenos Aires in Argentina and Rio de Janeiro in Brazil. Population Centers From Agra in India to Shanghai in China to Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, many of the largest cities in the world are based in humid subtropical regions. According to the authors of "Demography: A Treatise in Population," "in the early 1960s, Jozef Staszewski showed that the highest demographic densities (on average, 60 persons per square kilometer) were found in humid temperate climates and humid subtropical climates." Port cities in this climate zone, like Venice and Buenos Aires, also benefit from being ice-free year round. Other industries in these cities depend on available natural resources, industrial development and infrastructures.