7th Math Ecofriendly
advertisement
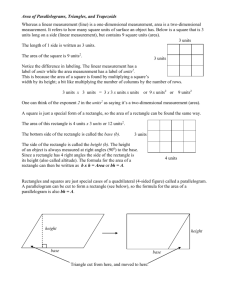
Unit Title: Eco-Friendly Days 1-10 Algebra Lesson Plan Grade: 7th 2013-2014 School Year Lesson Title: Invertebrates and their living spaces STRANDS Area of Plane and Composite Figures Volume of prisms, pyramids, cones, cylinders, and spheres Summary of the task, challenge, investigation, career-related scenario, problem, or community link. LESSON OVERVIEW Students will be reviewing area equations for squares, rectangles, triangles, trapezoids, and circles as well as calculating volume for different geometric solids This should be a review from previous grades and a preview for geometry. Students will also be finding the area of composite figures by extending area equations. Their project days will allow them to stake off square meter samples and remove the ground cover to a certain depth(volume). After counting the invertebrates in the one meter square samples, they will convert units and predict the number of invertebrates that are in an acre of ground cover. Hook for the week unit or supplemental resources used throughout the week. (PBL scenarios, video clips, websites, literature) MOTIVATOR Students will watch a short video clip about invertebrates and how sometimes small and seemingly insignificant creatures can make a necessary impact on the eco-system. DAY Objectives Materials & Resources Instructional Procedures Differentiated Instruction Assessment (I can….) 1 I can define volume and find the volume of a prism and cylinder. earthworm Essential Question: Paper How can I define volume and find the volume of a prism and cylinder? Pencil iPad Presentation Graphing calculator Geometric Solids Manipulatives Soup cans Empty paper box Activating Strategy: Tell students that you want to send 20 paper boxes full of a certain soup can to a needy region somewhere outside the US. What is the most soup cans possible that they should collect without going over the limit of the 20 boxes. Teaching Strategy: Define Volume for the students. Lead a demonstration to help students discover how to find volume of a prism. Start with a plane figure, such as a square, and then add more squares on top. Lead students to the formula for the volume of prism: Area of the Base times Height. Use geometric manipulative solids to help students picture the flat versions of the shapes. Work some example problems to calculate area as an entire class, then some partner work time, and finally individual work time. Students will continue to practice this skill with a short homework assignment. Intervention and Enrichment can be achieved through varying the difficulty of problems during the individual work time, heterogeneous grouping, and questioning during the activity. Short homework assignment Intervention and enrichment can be achieved by various problems of pyramid and cone volumes. Informal observation during the lesson In-Class work Exit Ticket Summarizing Strategy: Discuss how area, if filled up a certain height, creates volume. Remind students that the capital “B” in the volume formulas causes the prism and the cylinder formulas to coincide. 2 I can find the volume of a pyramid and cone. Paper, pencil Essential Question: How can I find the volume of a pyramid and cone? Ipad Calculator Geometric Solids manipulatives Activating Strategy: Have a pyramid and a prism and a cone and cylinder that have the same bases. Ask the students how many pyramids they think can fit in the prism or cones in the cylinder? Student Presentations Short homework assignment Dry rice or beans or sand ruler . Teaching Strategy: Demonstrate to students how volume of a cone relates to volume of a cylinder. Fill up the cone with rice, beans or sand. Pour into the cylinder. You should be able to do this 3 times. Have students discuss the proportional differences and how this impacts the calculation of the volume of a cylinder. Lead a brief presentation on volume of pyramids and cones. The volume is one-third the volume of a cylinder. After placing the cone inside the cylinder, place the pyramid inside the prism and ask what proportion of the prism that the pyramid is? Practice finding the volume of pyramids and cones as a whole class, then in small groups, and finally allow the students some time for individual practice. Summarizing Strategy: Discuss volume again but in terms of its rapidly decreasing as it approaches a vertex of no dimension and what effect this has on the proportional variance of volume from a stated base. 3 I can find the volume of a composite figure. Paper, pencil Essential Question: Ipad How can I find the volume of a composite figure? Composite Figure digital images Activating Strategy: Draw a cone on the board with an attached hemisphere. Ask the class if a can were full and the can had the same radius and height as the cone, which could contain the most substance? Or same? Teaching Strategy: Define volume of a sphere for the students. Lead a discussion that a hemisphere is exactly one half of the sphere volume. Remind students that a cylinder with the same radius and height as a cone has three times the capacity(volume). Summarizing Strategy: Discuss with students other possible composite figures that might be difficult to compare volume just by their “looks”. 4 Essential Question: Intervention and enrichment can be achieved by varying the type of figures for the area activity as well as heterogeneous grouping and questioning during the activity.. Informal observation during the lesson Student Presentations Short homework assignment Project – Refer to Unit Plan Watershed Health Essential Question: 5 Project – Refer to Unit Plan Watershed Health 6 I can define area and find the area of a Paper Essential Questions: EQ: How can I define area and find the area of a square, rectangle, Enrichment: Formative: Pencil and triangle. How can I derive the formula through visual proof for the area of a parallelogram. Short Exit ticket square, rectangle, and triangle. iPad I can derive the formula through visual proof for the area of a parallelogram. Graphing calculator Presentation Area of triangles discovery activity. Activating Strategy: Tell the students they can suggest to paint the room any color they’d like. The group that can find the area of the room to the closest square foot gets to have their color suggested for painting during summer break.. Teaching Strategy: How did you find the area of the wall? Have a short teacher led discussion over the definition of area and common units used to express area. Also review the equations for finding the area of a square and rectangle. Try some examples as a whole class, some small group work, and finally some individual work. This should lead into the parallelogram area formula discovery activity. Give all students some Parallelograms. Then, have them create a rectangle out of the parallelogram by cutting a triangle from one end and moving it to the other. Lead students to the formula that the area of a parallelogram is the same as the area of a rectangle. Finish with a short presentation on the area of a parallelogram. Include parallelograms that are not “right side up” and introduce the concept of height in a parallelogram. Summarizing Strategy: Exit Ticket - Put a parallelogram, rectangle, and square on the board. Have the students find the area of each, they should be close, and have them put them in order from smallest to largest. 7 Essential Question: homework assignment Remediation: Have students write out steps for finding area of triangle and rectangle Summative: Survey student classwork IEE Project Day: Refer to Unit Plan 8 I can find the area of a trapezoid and triangle. I can derive the area formulas for a trapezoid and triangle through a visual proof. I can find the area of a circle. Paper, pencil Essential Question: EQ: How can I find the area of a trapezoid and parallelogram? How Ipad can I derive the area formulas for a trapezoid and triangle through a visual proof? How can I find the area of a circle? Ruler Grid sheets Activating Strategy: Put a big triangle on the board and have students discuss at table groups how to find the area of a triangle. Also, draw a large square and rectangle with a diagonal in each. Have students share the results of the discussion. Teaching Strategy: Lead a quick review over the homework on the area of a parallelogram, square, and rectangle from the previous day. Have students write examples on the board or have them share through airplay. Pass out the grid sheets. Give students a picture of a triangle or trapezoid. Ask them to use another shape of equal size to construct a parallelogram or rectangle. Then ask them to find the area of the larger shape and describe how the two are related. At the end of the activity have students share results and then introduce the area formulas for trapezoids and triangles. Have students practice a few examples. End the lesson with a short presentation on the area of a circle. Introduce the basic vocabulary of diameter, radius, and pi. Work some examples as an entire class. Some should have radius given and some diameter. Have students practice some examples. Enrichment: Formative: Short homework assignment Exit ticket Remediation: Have students write out steps for finding area of trapezoid and parallelogram Summative: Survey student classwork Summarizing Strategy: Exit Ticket - Put a parallelogram, rectangle, square, triangle, and trapezoid on the board. Have the students find the area of each, they should be close, and have them put them in order from largest to smallest. 9 I can find the area of a composite figure. Paper, pencil Essential Question: EQ: How can I find the area of a composite figure. Ipad Grid paper Activating Strategy: Draw a picture of a football field with two semi-circles attached on each end whose diameters are the same as the width of the field. Ask the students to find the area and also as simple as possible or is it that simple? Let them argue for a minute then tell them to show you on paper or Ipad. Teaching Strategy: Finish the field problem with presentations of students or with instruction. Work one example of a composite area problem as an entire class. Show the students how to break the image into shapes that are known. Next, pass out challenge problems that ask students to find the area of a composite figure. Each group will get a different problem. After each group has had time to complete the problem, they will the present how to find the area to the entire class. Summarizing Strategy: Present students with the composite area problem they will face during the project day to find the cross sectional area of a planter. Lead the students through one example problem. 10 Essential Question: Enrichment: Formative: Short homework assignment Exit ticket Remediation: Unit squares Different unit squares Summative: Give test on areas and volume on next regular scheduled class Project Day: Refer to Unit Plan STANDARDS Identify what you want to teach. Reference State, Common Core, ACT College Readiness Standards and/or State Competencies. 7.G.6 - Solve real world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms. G-MG1 - Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder). G-MG.2 - Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot) G-GMD.3 - Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems