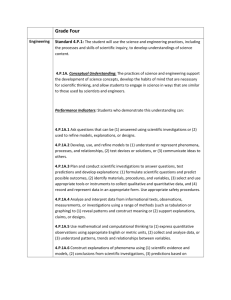
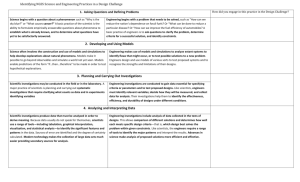
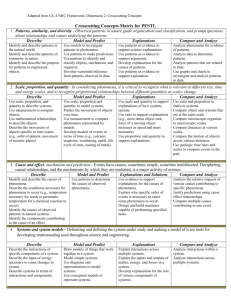
Practices for PESTL
advertisement
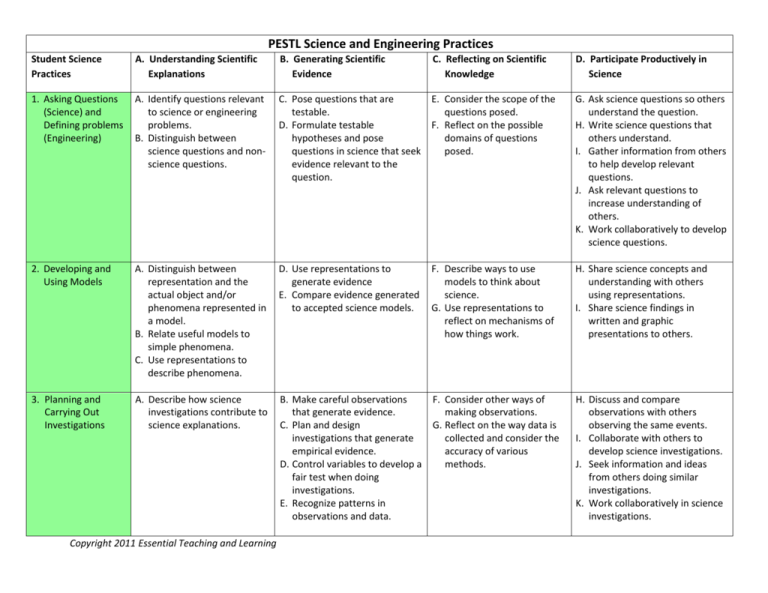
PESTL Science and Engineering Practices Student Science Practices A. Understanding Scientific Explanations B. Generating Scientific Evidence 1. Asking Questions (Science) and Defining problems (Engineering) A. Identify questions relevant to science or engineering problems. B. Distinguish between science questions and nonscience questions. C. Pose questions that are E. Consider the scope of the testable. questions posed. D. Formulate testable F. Reflect on the possible hypotheses and pose domains of questions questions in science that seek posed. evidence relevant to the question. G. Ask science questions so others understand the question. H. Write science questions that others understand. I. Gather information from others to help develop relevant questions. J. Ask relevant questions to increase understanding of others. K. Work collaboratively to develop science questions. 2. Developing and Using Models A. Distinguish between representation and the actual object and/or phenomena represented in a model. B. Relate useful models to simple phenomena. C. Use representations to describe phenomena. D. Use representations to generate evidence E. Compare evidence generated to accepted science models. F. Describe ways to use models to think about science. G. Use representations to reflect on mechanisms of how things work. H. Share science concepts and understanding with others using representations. I. Share science findings in written and graphic presentations to others. 3. Planning and Carrying Out Investigations A. Describe how science investigations contribute to science explanations. B. Make careful observations that generate evidence. C. Plan and design investigations that generate empirical evidence. D. Control variables to develop a fair test when doing investigations. E. Recognize patterns in observations and data. F. Consider other ways of making observations. G. Reflect on the way data is collected and consider the accuracy of various methods. H. Discuss and compare observations with others observing the same events. I. Collaborate with others to develop science investigations. J. Seek information and ideas from others doing similar investigations. K. Work collaboratively in science investigations. Copyright 2011 Essential Teaching and Learning C. Reflecting on Scientific Knowledge D. Participate Productively in Science 4. Analyzing and Interpreting Data A. Compare data to make sense of and explain phenomena. B. Compare data and use comparisons as evidence. C. Reflect on the data in light of others’ data about similar investigations. D. Analyze and share findings. 5. Using Mathematics A. Compare data and Computational quantitatively. Thinking B. Use mathematics to compare explanations and understand scale. C. Make and use measurements as evidence. D. Compare evidence from measurements. E. Reflect on the accuracy of measurements. F. Use averages and graphs to compare data. G. Share findings and data using tables, charts, and graphs. 6. Constructing A. Explain science Explanations phenomena. (Science) and B. Compare multiple Designing Solutions explanations of the same (Engineering) science phenomena. C. Explain science observations using evidence. D. Design a solution to a problem and use evidence to compare the advantages of the design to other solutions. E. Compare two or more science explanations for an observation. F. Evaluate multiple explanations used to explain science phenomena. G. Share explanations with others. H. Work collaboratively to construct science explanations and design solutions. 7. Engaging in Argument from Evidence A. Describe the role of evidence in science explanations. B. Relate the role of science explanation to science arguments. C. Use evidence to support ideas. D. Use evidence to generate or support explanations. E. Use evidence to support arguments about science explanations and phenomena. F. Compare types of evidence. G. Determine the best evidence for a specific argument. H. Listen to others’ explanations. I. Share the sources of information used to support arguments. 8. Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information A. Read and understand science information. B. Read and understand science information from multiple sources. C. Describe information gathered from multiple sources. D. Use appropriate terminology and descriptions. E. Gather and share information using many forms of communication. F. Identify multiple sources of information. G. Compare science information from multiple sources. H. Share science information with others through written, oral, and multi-media reports. Copyright 2011 Essential Teaching and Learning