Dear colleagues, - Industrial Engineering Department EMU-DAU
advertisement
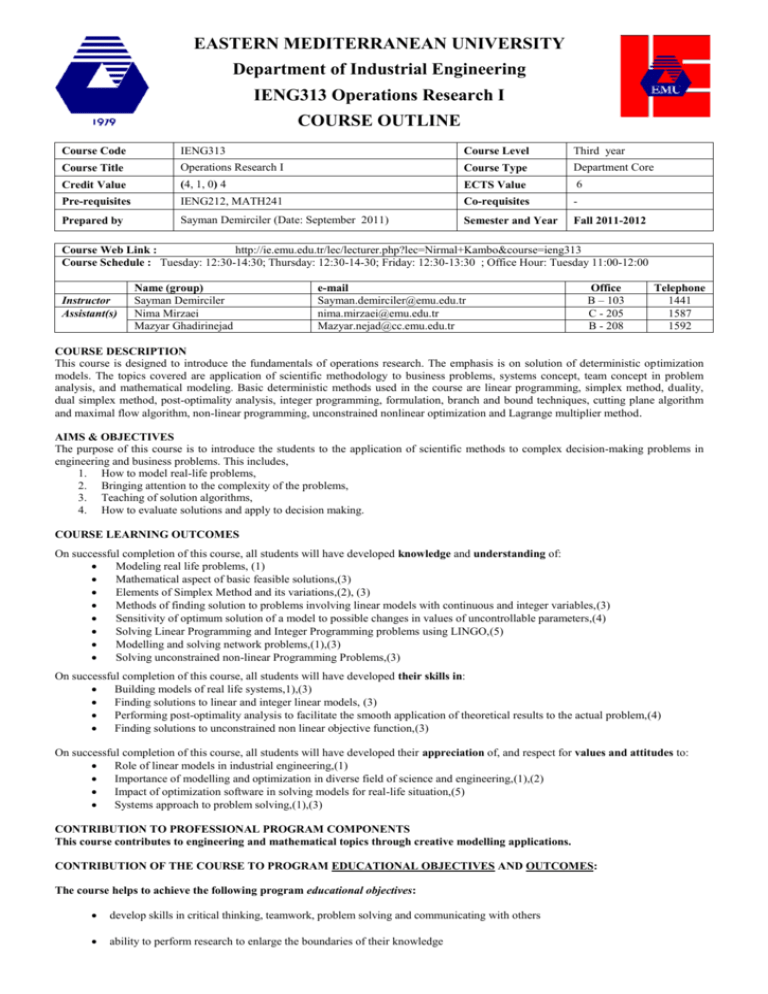
EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial Engineering IENG313 Operations Research I COURSE OUTLINE Course Code IENG313 Course Level Third year Course Title Operations Research I Course Type Department Core Credit Value (4, 1, 0) 4 ECTS Value 6 Pre-requisites IENG212, MATH241 Co-requisites - Prepared by Sayman Demirciler (Date: September 2011) Semester and Year Fall 2011-2012 Course Web Link : http://ie.emu.edu.tr/lec/lecturer.php?lec=Nirmal+Kambo&course=ieng313 Course Schedule : Tuesday: 12:30-14:30; Thursday: 12:30-14-30; Friday: 12:30-13:30 ; Office Hour: Tuesday 11:00-12:00 Instructor Assistant(s) Name (group) Sayman Demirciler Nima Mirzaei Mazyar Ghadirinejad e-mail Sayman.demirciler@emu.edu.tr nima.mirzaei@emu.edu.tr Mazyar.nejad@cc.emu.edu.tr Office B – 103 C - 205 B - 208 Telephone 1441 1587 1592 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to introduce the fundamentals of operations research. The emphasis is on solution of deterministic optimization models. The topics covered are application of scientific methodology to business problems, systems concept, team concept in problem analysis, and mathematical modeling. Basic deterministic methods used in the course are linear programming, simplex method, duality, dual simplex method, post-optimality analysis, integer programming, formulation, branch and bound techniques, cutting plane algorithm and maximal flow algorithm, non-linear programming, unconstrained nonlinear optimization and Lagrange multiplier method . AIMS & OBJECTIVES The purpose of this course is to introduce the students to the application of scientific methods to complex decision-making problems in engineering and business problems. This includes, 1. How to model real-life problems, 2. Bringing attention to the complexity of the problems, 3. Teaching of solution algorithms, 4. How to evaluate solutions and apply to decision making. COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES On successful completion of this course, all students will have developed knowledge and understanding of: Modeling real life problems, (1) Mathematical aspect of basic feasible solutions,(3) Elements of Simplex Method and its variations,(2), (3) Methods of finding solution to problems involving linear models with continuous and integer variables,(3) Sensitivity of optimum solution of a model to possible changes in values of uncontrollable parameters,(4) Solving Linear Programming and Integer Programming problems using LINGO,(5) Modelling and solving network problems,(1),(3) Solving unconstrained non-linear Programming Problems,(3) On successful completion of this course, all students will have developed their skills in: Building models of real life systems,1),(3) Finding solutions to linear and integer linear models, (3) Performing post-optimality analysis to facilitate the smooth application of theoretical results to the actual problem,(4) Finding solutions to unconstrained non linear objective function,(3) On successful completion of this course, all students will have developed their appreciation of, and respect for values and attitudes to: Role of linear models in industrial engineering,(1) Importance of modelling and optimization in diverse field of science and engineering,(1),(2) Impact of optimization software in solving models for real-life situation,(5) Systems approach to problem solving,(1),(3) CONTRIBUTION TO PROFESSIONAL PROGRAM COMPONENTS This course contributes to engineering and mathematical topics through creative modelling applications. CONTRIBUTION OF THE COURSE TO PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND OUTCOMES: The course helps to achieve the following program educational objectives: develop skills in critical thinking, teamwork, problem solving and communicating with others ability to perform research to enlarge the boundaries of their knowledge The course makes significant contributions to the following program outcomes: an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice. TEXTBOOK/S Winston , Wayne L., “Operations Research : Applications and Algorithms” 4th edition, Duxbury Press 2004. REFERENCES (available at EMU Library) Taha Hamdy A, “Operations Research”, 7th international edition, Prentice Hall 2003. Hillier, F.S.; Lieberman , G.J., “Introduction to Operations Research”, 9th international edition, McGraw Hill 2009. METHOD OF ASSESSMENT All Examinations will be based on lectures, discussions, textbook and assigned work. To enter a formal examination, a student has to present her/his EMU student Identification card to the invigilator. Quizzes: There will be several quizzes designed to test familiarity and basic understanding of various topics. There will be no quiz makeups. Midterm Exams: The midterm exam I will be held in the week designated by the university administration. It will cover all of the material up to the date of examination. Final Exam: The final exam will cover the whole course material. In form it will be a longer version of the midterm exam. Make-up Exams: Make-up examinations will only be offered to students who provided adequate documentation for the reason of their absence within four working days at the latest after the examination date. One final exam type make-up exam will be offered after the final exams for the missed midterm and/or final exam. University regulations apply for graduate make-ups. Any objection to the grade or mark should be made latest within a week following its announcement. Grading Policy: Class Participation Quizzes Midterm Exam Case study & Lab Final Exam 5% 20 % 25 % 20 % 30% COURSE CONTENT (WEEKLY TEACHING PLAN) Week 1-2 2-4 5-6 7-8 9-10 11-12 13-14 Date Topics Introduction to OR, Formulation of LP problem Graphical Solution, Simplex Algorithms, Special Cases Duality, Dual Simplex method and Sensitivity Analysis Transportation, Assignment and Transshipment Problems Simple Network, Minimal Spanning Tree Algorithm, Dijkstra’s Algorithm and Maximal Flow Algorithm Integer Programming, Branch and Bound Algorithm, Cutting Plane Algorithm Nonlinear Programming, Unconstrained Optimization and Langrange Multiplier Method LEARNING/TEACHING METHODS This is a basic course which prepares the students for several allied courses in the future. Teaching will enable the students to understand the techniques of OR and problem formulation. To get a hands on experience, lectures will be suppliemented by tutorials and lab sessions. ATTENDANCE Attendance will be taken every lecture hour. Note that university regulations allow the instructor to give a grade of NG to a student whose absenteeism is more than 25% of the total lecture hours or who do not complete sufficient work. ACADEMIC HONESTY - PLAGIARISM Cheating is copying from others or providing information, written or oral, to others. Plagiarism is copying without acknowledgement from other people’s work. According to university by laws cheating and plagiarism are serious offences punishable with disciplinary action ranging from simple failure from the exam or project, to more serious action (letter of official warning suspension from the University for up to One Semester). Disciplinary action is written in student records and may appear in student transcripts. PLEASE KEEP THIS COURSE OUTLINE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE AS IT CONTAINS IMPORTANT INFORMATION