12.6 Measuring the Critical Angle
advertisement

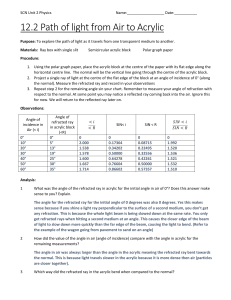
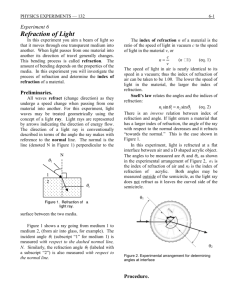
SCN Unit 2 Physics Name:__________________ Date:___________ 12.6 Measuring the Critical Angle Purpose: To explore the critical angle of acrylic Materials: Ray box with single slit Semicircular acrylic block Polar graph paper Procedure: 1. Using the polar graph paper, place the acrylic block at the centre of the paper with its flat edge along the horizontal centre line. The normal will be the vertical line going through the centre of the acrylic block (origin). 2. Project a single ray of light through the curved part of the semicircle so that the incident ray goes through the origin and the refracted ray comes out the flat edge of the block. Position the ray box so that you produce a refracted angle in air that is larger than the angle of incidence in the acrylic block. 3. Slowly move the ray box to increase the angle of incidence in the acrylic block. Eventually the refracted ray leaving the block will disappear. Measure the angle of incidence at this point and record it Observations: Critical angle of acrylic ____41°______ Analysis: 1 The accepted value for the critical angles for acrylic is 42.2. How does your answer compare? Our answer of 41 degrees is very comparable to the accepted value of 42.2. Our value is only 1.2 degrees off. 2 What sources of error could account for any differences between your measured value and the accepted value? This error could be due to measurement errors when measuring the angle. The ray box sends out a fairly wide beam of light, a thinner beam would be more accurate. It was also hard to see the refracted rays when they were close to the medium division line. It is also difficult to determine exactly when the light switches from going along the medium line to when it internally reflects. Another error could be that the light might not have been shone exactly at the origin, and the semicircular piece of acrylic could have been slightly off it’s position. 3 Did partial reflection and refraction still occur when light was travelling more slowly in the first medium than in the second? Explain. Yes partial reflection and refraction still occur when light was is travelling more slowly in the first medium than the second but only in the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle. Conclusion: As the angle of incidence was increased, the moved further and further away from the normal until it ran along the two mediums (acrylic and air). At this point the angle of incidence was approximately 41 degrees. This measurement is very close to the accepted values for the critical anlge of acrylic, which is 42.2. This could be off due to measurement errors and difficulty in determining the exact point that the ray internally reflected. SCN Unit 2 Physics Name:__________________ Date:___________