Progressive Mathematics Initiative www.njctl.org Mathematics
advertisement

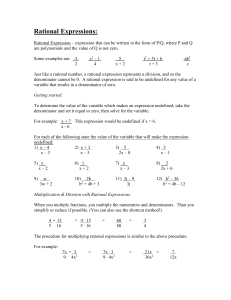
Progressive Mathematics Initiative www.njctl.org Mathematics Curriculum Unit Plan # 4 Title: Rational Expressions and Equations Subject: Algebra 2 Length of Time: 2 weeks Unit Summary: The unit covers what a rational expression is and how to simplify it. The unit covers adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing rational equations. Solving rational equations, variation and graphing of rational equations will also be covered. Learning Targets Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Arithmetic with Polynomials and Rational Expressions Cluster: Rewrite rational expressions Standard#: Standard: A-APR.6 Rewrite simple rational expressions in different forms. A-APR.7 Understand that rational expressions form a system analogous to the rational numbers, closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by a nonzero rational expression; add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions. Conceptual Category: Algebra Domain: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Cluster: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and explain the reasoning Standard#: Standard: Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers A-REI.1 asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable, and give examples showing A-REI.2 how extraneous solutions may arise. Conceptual Category: Functions Domain: Interpreting Functions Cluster: Analyze functions using different representations F-IF.7 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated cases Unit Essential Question: Unit Enduring Understandings: How are rational functions and their graphs similar Denominator cannot equal zero to linear functions? How are they different? Zeros of the denominators create discontinuities at those points for the function at those values. To add or subtract rationals, need common denominators. To solve a variation problem, need to find constant of variation first. Solving a rational equation yields possible solutions, substitute to check for extraneous solutions. Unit Objectives: Students will be able to simplify rational expressions. Students will be able to add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Students will be able to solve variation problems. Students will be able to graph rational equations, identify asymptotes and removable discontinuities. Students will be able to solve rational equations and identify solutions as feasible or extraneous. Evidence of Learning Formative Assessments: SMART Response questions used throughout the unit. 3 Quizzes Summative Assessment: Unit Test Lesson Plans Topics Timeframe (days) Topic #1: Variation Topic #2: Simplifying Rational Expressions Quiz 1: Variation & Simplifying Rational Expressions Topic #3: Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Topic #4: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions Quiz 2: Operations with Rational Expressions Topic #5: Solving Rational Equations Topic #6: Applications of Rational Equations Topic #7: Graphing Rational Equations Quiz 4: Solving & Graphing Rational Equations Topic #8: Review and Unit Test Curriculum Resources: www.njctl.org/courses/math/algebra2/ 1 0.5 0.5 1 1.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 1.5 0.5 2