Genetics Practice Problems: Mendelian & Incomplete Dominance
advertisement

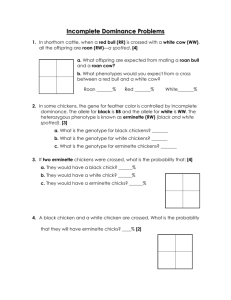
Name: _________________________________________ Period: _____ Date: __________ Genetics Practice Problems 1. In pea plants, tall (T) is dominant to dwarf (t). Show the cross between a heterozygous tall and a dwarf homozygous plant. Use the Punnett square to predict the % Phenotype and Genotype of the offspring. % Genotype % Phenotype Homozygous = _____ Tall = _____ Heterozygous = ______ Dwarf = _____ 2. Show the cross between two heterozygous (Tt) tall plants. Use the Punnett square to predict the % Phenotype and Genotype of the offspring. % Genotype % Phenotype Homozygous = _____ Tall = _____ Heterozygous = ______ Dwarf = _____ 3. In pea plants, green pods are dominant to yellow pods. Show the cross between a homozygous yellow pod plant (gg) and a hybrid green pod plant (Gg)? Use the Punnett square to predict the % Phenotype and Genotype of the offspring. % Genotype % Phenotype Homozygous = _____ Green = _____ Heterozygous = ______ Yellow = _____ 4. If two green pod plants (Gg) are crossed what are the expected phenotypes of the offspring and genotypes of the offspring? Use the Punnett square to predict the % Phenotype and Genotype of the offspring. % Genotype % Phenotype Homozygous = _____ Green = _____ Heterozygous = ______ Yellow = _____ 5. In humans, tongue rolling is a dominant trait; those with the recessive condition cannot roll their tongues? If two people one is a hybrid (Rr) to roll tongue and one is a pure recessive (rr) to roll tongue what percent of the offspring could roll there tongue? % can roll tongue __________ 6. In purple people eaters, one-horn is dominant (H) and no horns are recessive (h). Use the Punnet Square showing the cross of a purple people eater that is hybrid for horns (Hh) with a purple people eater that does not have horns (hh). Summarize the genotypes & phenotypes of the possible offspring % Genotype % Phenotype Homozygous = _____ Horn = _____ Heterozygous = _____ No Horn = _____ Incomplete Dominance Problems 7. In shorthorn cattle, when a red bull (RR) is crossed with a white cow (WW), all the offspring are roan (RW)—a spotted, [4] a. What offspring are expected from mating a roan bull and a roan cow? b. What phenotypes would you expect from a cross between a red bull and a white cow? Roan _______% Red _______% White_______% 8. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by incomplete dominance. The allele for black is BB and the allele for white is WW. The heterozygous phenotype is known as erminette (RW) (black and white spotted). [3] a. What is the genotype for black chickens? _______ b. What is the genotype for white chickens? _______ c. What is the genotype for erminette chickens? _______ 9. If two erminette chickens were crossed, what is the probability that: [4] a. They would have a black chick? ______% b. They would have a white chick? ______% c. They would have a erminette chicks? ______% 10. A black chicken and a white chicken are crossed. What is the probability that they will have erminette chicks? ____% [2] 11. In snapdragons, flower color is controlled by incomplete dominance. The two alleles are red (RR)and white (WW). The heterozygous genotype is expressed as pink (RW). [4] a. A pink-flowered plant (RW) is crossed with a whiteflowered plant (WW). What is the probability of producing pink-flowered plant? _______% red-flowered plant? _______% white-flowered plant? _______% 12. In Andalusian fowls, black individuals (BB) and white individuals (WW) are homozygous. A homozygous black bird is crossed with a homozygous white bird. The offspring are all bluish-gray. Show the cross as well as the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents and offspring. [4] a. Phenotype Black ______% White _____% Bluish-gray ______% b. Genotype BB _______% WW _______% RW _______% 13. What results if two bluish-gray individual are crossed? Show the cross as well as the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents and offspring. [4] a. Phenotype Black ______% White _____% Bluish-gray ______% b. Genotype BB _______% WW _______% RW _______%