Paper Title - Academic Science,International Journal of Computer
Fuzzy Based System for detecting and preventing
Flooding attacks on MANET
Sanjeet Kaur
Computer Sc. and Engg.
MATS University
Raipur,India
Jeet_108@rediffmail.com
Mr. Nilmani Verma
Computer Sc. and Engg.
MATS University
Raipur, India nilmaniv@matsuniversity.ac.in
Abstract—
Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET’s) are formed dynamically by a sovereign system of nodes that are connected via wireless links without any extant infrastructure. In an ad hoc network the nodes can communicate with any other node that resides within its transmission range and for communication with the nodes outside the transmission range the nodes utilize the intermediate nodes to reach to the destination. The nodes in
MANET acts both like host and the router. MANET does not have any clear line of defense and each and every node has to be prepared for the encounters with the antagonist directly or indirectly. Flooding attacks comes under the Denial of Service
(DoS) attacks as the malicious node attempts to send a large no. of fake route request control packets inside the network thus preventing the authenticated nodes from being using the intended services and consuming the whole network resources. In this paper we propose a Technique which uses Fuzzy based system for the detection of the malicious node present inside the network. The schemes uses Fuzzy If-Then rules and the membership functions to define the threshold limit through which it will identify the misbehavior of the nodes present in the network and declares it as a flooder or malicious node . The measurements were taken in the light of throughput, end-to-end delay and Packet delivery ratio. Simulation is done in NS-2.
Keywords—MANET; AODV; RREQ; Flooding Attack; Fuzzy
System, Membership Function. proactive approach which attempts to prevent an attacker from launching attacks through various cryptographic techniques[16].
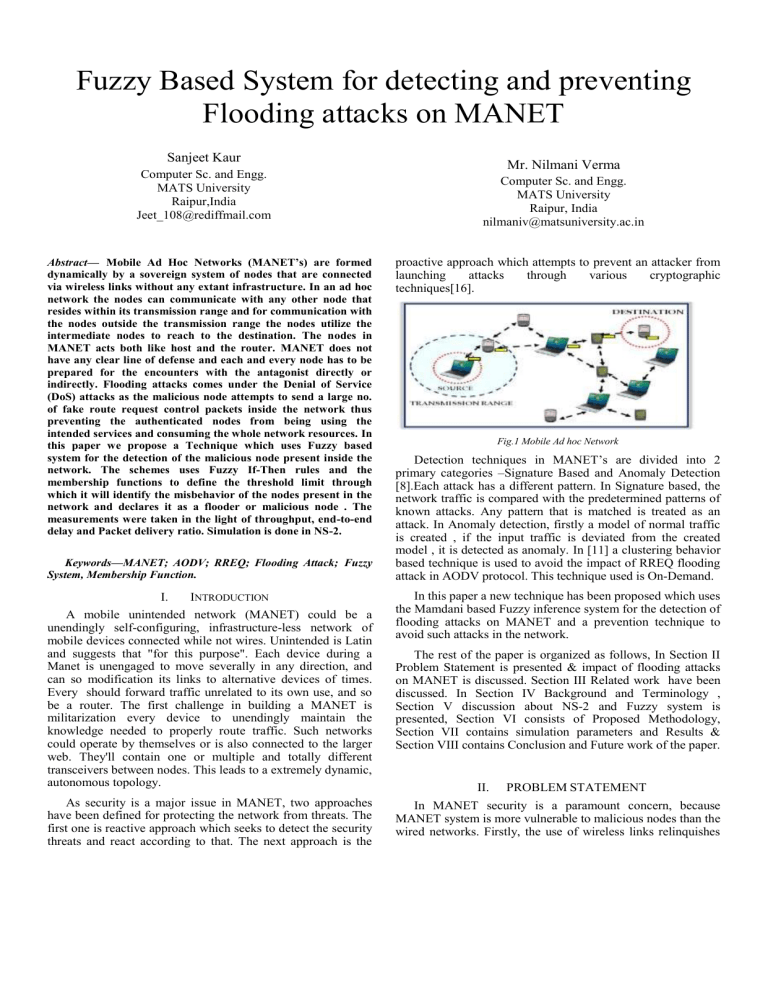
Fig.1 Mobile Ad hoc Network
Detection techniques in MANET’s are divided into 2 primary categories –Signature Based and Anomaly Detection
[8].Each attack has a different pattern. In Signature based, the network traffic is compared with the predetermined patterns of known attacks. Any pattern that is matched is treated as an attack. In Anomaly detection, firstly a model of normal traffic is created , if the input traffic is deviated from the created model , it is detected as anomaly. In [11] a clustering behavior based technique is used to avoid the impact of RREQ flooding attack in AODV protocol. This technique used is On-Demand.
In this paper a new technique has been proposed which uses the Mamdani based Fuzzy inference system for the detection of flooding attacks on MANET and a prevention technique to avoid such attacks in the network.
I.
I NTRODUCTION
A mobile unintended network (MANET) could be a unendingly self-configuring, infrastructure-less network of mobile devices connected while not wires. Unintended is Latin and suggests that "for this purpose". Each device during a
Manet is unengaged to move severally in any direction, and can so modification its links to alternative devices of times.
Every should forward traffic unrelated to its own use, and so be a router. The first challenge in building a MANET is militarization every device to unendingly maintain the knowledge needed to properly route traffic. Such networks could operate by themselves or is also connected to the larger web. They'll contain one or multiple and totally different transceivers between nodes. This leads to a extremely dynamic, autonomous topology.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows, In Section II
Problem Statement is presented & impact of flooding attacks on MANET is discussed. Section III Related work have been discussed. In Section IV Background and Terminology ,
Section V discussion about NS-2 and Fuzzy system is presented, Section VI consists of Proposed Methodology,
Section VII contains simulation parameters and Results &
Section VIII contains Conclusion and Future work of the paper.
As security is a major issue in MANET, two approaches have been defined for protecting the network from threats. The first one is reactive approach which seeks to detect the security threats and react according to that. The next approach is the
II.
PROBLEM STATEMENT
In MANET security is a paramount concern, because
MANET system is more vulnerable to malicious nodes than the wired networks. Firstly, the use of wireless links relinquishes
the network influenced to attacks ranging from passive eavesdropping to active interference. Secondly the mobile nodes are capable of roaming independently as they are autonomous units, this means that if the nodes have improper physical protection they are more receptive of being captured, compromised and hijacked. Thirdly, decision making is sometimes decentralized in mobile computing environment and some of the wireless networking algorithms entrust on the cooperative participation of all the nodes and the framework.
In mobile ad hoc network there is a mutual trust between the sender and the receiver in the network due to which any malicious node can enter into the network and affect the network resources. The affected resources may be the battery and the bandwidth. The malicious nodes can also cause damage to the network through leaking secret information, contaminating the message and node impersonation.
III.
RELATED WORK
Fatemeh Barani and Sajjad Gerami et, al [2013] proposed a technique named ManetSVM for detection of flooding, black hole, neighbor, rushing, and wormhole attacks have been evaluated with regards to the efficiency of ManetSVM. In this paper, author tends to plan a dynamic approach supported oneclass support vector machine, known as ManetSVM, for anomaly detection in MANETs. Our approach has 3 main phases: initial coaching, updating, and detection. Within the initial training section, a model is generated exploitation the
OCSVM algorithm to explain the traditional area. Within the detection section, the generated model is employed to discover abnormal input traffic. In the change section, the model is updated supported network topology changes. The NS2 machine was accustomed conduct the simulation study in
MANETs and a few attacks on AODV routing protocol.
ManetSVM may be a quick approach with high accuracy that's appropriate for mobile ad-hoc networks. Two measures of detection rate (DR) and warning rate (FAR) square measure used for our experiments and analysis of the planned approach.
Author tends to compare the performance of ManetSVM with three different dynamic approaches. The results incontestible that ManetSVM will increase the common detection rate by a minimum of 0.53% and 8.39% and therefore the average warning rate by a minimum of 6.61% and 3.74% that of DCAD and WPCA. Within the different experiment, the impact of various lengths of the time window on the performance of
ManetSVM was evaluated. The shortcoming of this technique is that SVM uses binary classifiers, so there is a constraint on the classifiers being used[8].
Fatehmeh Barani et, al [2014] proposed a hybrid approach for dynamic intrusion detection using Genetic Algorithm and
Artificial Immune System called GAAIS. GAAIS is in a position to adapting itself to topology changes victimization 2 change methods: partial and total. Each normal feature vector extracted from network traffic is represented by a hyper sphere with fix radius. a group of spherical detector is generated victimization Niche MGA rule for covering the non self area.
Spherical detectors are used for detective work anomaly in network traffic. The performance of GAAIS is evaluated for detective work many kinds of routing attacks simulated using the NS2 machine, like Flooding, Black hole, Neighbor,
Rushing, and Worm hole. Performance of this approach has been evaluated by multiple experiments for detection of some routing attacks like Flooding, Black hole, Neighbors, Rushing and Worm hole.
Meenakshi Patel, Sanjay Sharma and Divya sharan et, al
[2013] proposed a detection and prevention scheme for flooding attacks using SVM. In this methodology ab initio collect the behavior of each node then mistreatment of this knowledge to seek out out the flooded malicious node. For this collected behavior of each node pass the support vector machine and check this to threshold limit if the node cross the edge limit they're discover as a malicious node through the
SVM.
Author has used this method for bar. SVM are put in on some node for sleuthing malicious node once detection this node broadcast acknowledgement message to all or any then all nodes update their routing table and delete the entries of malicious node. If the nodes modification the threshold limit for this method it'll notice by the opposite node. In this theme we tend to outline a standard profile of node victimization its communication activity to alternative nodes (like PDER, CO,
PMIR) if any node deviate from their regular profile that means the node is abnormal and additional use this bar mechanism can go for stop such sort of activities.
In this paper author has got to discuss a Flooding attack and there have an effect on of the network. Flooding is another kind of attack launched victimization routing request. During this paper author has got proposed an answer for locating and interference of Flooding attacks. The methodology is straightforward and quick and that it can be implement on the planned theme victimization NS-3 machine. In future this technique can implement to find different kind of attacks [2].
One of the major drawback of this technique is that SVM constraints on the number of classifiers, and once the kernel function is defined it cannot be changed in SVM, and SVM are not having real time implementation. This leads us to propose a new scheme based on Fuzzy system as these systems are easy to build because of their human intuitive rules. And have real time implementation.
IV.
BACKGROUND AND TERMINOLOGY
A.
Flooding Attacks
Flooding attacks can be categorized as Denial-of-Service
(DoS) attacks. In this attack , a malicious node takes the advantage of the route discovery phase of the AODV routing protocol. The malicious node aims to consume the network resources by sending a large number of fake route request
(RREQ) packets to the non-existent destinations in the network. Since the destination does not exist in the network so there will be no node to send the route reply (RREP) packet and all the nodes keep on flooding the network with RREQ packets because of this new routes can no longer be added and the network is unable to transmit the data packets.
Thus it leads to the congestion in the network and the route table overflows in the intermediate nodes so that the nodes are
not able to receive new RREQ packets, resulting in DoS attacks.
Fig. 2 Flooding attack
B.
AODV routing Protocol
Ad-hoc on-demand Distance Vector routing protocol uses on-demand route discovery technique to ensure loop free, single path, hop by hop distance vector routing. AODV operates in 2 sub phases. Route discovery section is initiated by a supply node not having valid route to a destination node to that it desires to send knowledge. Route maintenance section for handling dynamic topology in Edouard Manet changes as the node moves or once some error persists. When a node desires to send knowledge to some destination it floods Route
Request (RREQ) messages to any or all its neighbouring nodes. associate degree intermediate node receiving RREQ updates its routing table with reverse route entry to the supply node if
RREQ is exclusive. Source id and broadcast id determines individuality of a RREQ packet. associate degree intermediate node will more rebroadcasts RREQ to its neighbors or unicasts
RREP message back to the supply node if it already has unexpired route to it destination in its routing table otherwise destination node replies.
In AODV, a node will receive multiple RREP messages for one route discovery message sent however it maintains just one entry per destination in its routing table. associate degree intermediate node invariably forwards initial RREP message received when creating entry for forward path towards destination in its routing table and second RREP for a specific
RREQ is employed for updating table and forwarded providing
RREP has higher destination sequence variety for the destination o hop count is smaller just in case of same destination sequence variety otherwise RREPs area unit suppressed. Higher sequence variety ensures underclassman route. HELLO messages area unit changed for maintaining neighborhood property.
AODV works on 2 phases to work out a route they're as follows:
Route Discovery Phase:
In the route breakthrough part, a node disseminates some kind of RREQ thought once the concept determines it wants a path to a resort area and does not have one available in its direction-finding table. The perennial process connected with
RREQ package at intermediate nodes is prevented just by checking for the creator informatics address and RREQ
IDENTITY combine. If the node is not the supposed destination, then the reverse route for the supply node is either designed or updated also because the RREQ package is extra broadcasted. A node generates a RREP if it's itself this destination of the packet or it offers a vigorous and valid path to the holiday spot. The RREP package is unicast back on the creator node on the reverse journey. once an honest intermediate node receives the RREP thought, it first creates or maybe updates forwards route access in their route table before forwarding the concept to their next mount the supply node.
Route Maintenance Step:
In this route Maintenance part, a node starts a path error
(RERR) idea, if the thought detects an internet link break for ensuing hop of an energetic path in their routing table or the thought gets some form of information package destined into a node that terribly straightforward have an active route and it isn't trying any near repairing. Upon deed the RERR message the origin node either tries a decent route throughout its direction-finding table or perhaps reinitiates path discovery course of action.
V.
N S -2 N ETWORK S IMULATOR AND FUZZY SYSTEM
NS version two (ns-2) was initiated supported a refactoring by Steve McCanne. Use of Tcl was replaced by MIT's Object
Tcl (OTcl), associate object-oriented non-standard speech Tcl.
The core of ns-2 is additionally written in C++, however the
C++ simulation objects are coupled to shadow objects in OTcl and variables may be coupled between each language realms.
Simulation scripts are written within the OTcl language, associate extension of the Tcl scripting language.
Fuzzy abstract thought is that the method of formulating the mapping from a given input to associate output victimization formal logic. The mapping then provides a basis from that selections may be created, or patterns discerned. The method of fuzzy abstract thought involves all of the items that square measure delineates in Membership Functions, Logical
Operations, and If-Then Rules. The point of symbolic logic is to map associate degree input area to associate degree output area, and therefore the primary mechanism for doing this is often a listing of if-then statements known as rules.
The basic structure of Fuuzy consists of 3 conceptual components:
A.
Membership Functions:
A membership function (MF) may be a curve that defines however every purpose within the input house is mapped to a membership price (or degree of membership) between zero and one
.
B.
Logical Operations:
The most necessary issue to appreciate concerning fuzzy logical reasoning is that the undeniable fact that it's a superset of normal Boolean logic. In alternative words, if you retain the fuzzy values at their extremes of one (completely true), and zero (completely false), customary logical operations can hold.
C.
If-Then Rules:
A single fuzzy if-then rule assumes the shape ,
if x could be A then y is B where, A and B are unit linguistic values outlined by fuzzy sets on the ranges (universes of discourse) X and Y, severally.
The if-part of the rule "x is A" is termed the antecedent or premise, whereas the then-part of the rule "y is B" is termed the resultant or conclusion.
Mamdani Fuzzy Inference System:
Mamdani's fuzzy abstract thought technique is that the most typically seen fuzzy methodology. Mamdani's technique was among the primary management systems engineered victimisation fuzzy pure mathematics. It had been planned in
1975 by Ebrahim Mamdani as a trial to manage a externalcombustion engine and boiler combination by synthesizing a group of linguistic control rules obtained from intimate with human operators. Mamdani's effort was supported Lotfi
Zadeh's 1973 paper on fuzzy algorithms for advanced systems and call processes. though the abstract thought method represented within the next few sections differs somewhat from the ways represented within the original paper, the fundamental plan is far constant.
Mamdani-type abstract thought, as outlined for the tool cabinet, expects the output membership functions to be fuzzy sets. When the aggregation method, there's a fuzzy set for every output variable that desires defuzzification.
VI.
PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
As MANET has some vulnerabilities owing to that it's extremely vulnerable to security threats likewise as routing attacks. The planned intrusion detection system uses formal logic as a result of formal logic is ready to handle the uncertainity and provides the selections supported assumptions and unsure values. The planned work is being enforced in NS-2 that ends up in increase the performance of network. The information is analyzed by MATLAB fuzzy tool case.
The work has been divided into 2 phases:
PHASE-1: Consists of Fuzzy based prevention system which consists of set of Fuzzy rules.
Fig.3 Fuzzy based Detection System(Phase-1)
Steps to be followed:
1) A network topology is constructed which defines the logical connection between the nodes participating in the
MANET.
2) The communication between these nodes is possible by using some roouting protocol, here in this proposed methodology we have used AODV routing protocol .
3) The next step is to pass this network to a Fuzzy Based
System, which consists of a set of fuzzy rules which will prevent the entry of any malicious nodes inside the network before communication and once detected it prevents the whole network from being affected by that node.
4) The Fuzzy Based Prevention System identifies the nodes in the network to be Authenticated node or Flooded node. If the node is Authenticated based on the defined parameters & threshold limit , the node is allowed to go through the route selector and participate in communication.
5) Otherwise if the node is malicious or flooded node it is reported to the sender for taking appropriate action.
PHASE-2: Consists of Fuzzy based system which includes a set of Fuzzy rules which will detect the node to be an Intruder or Non-Intruder.
Fig.4 Fuzzy based Detection System(Phase-2)
Steps to be followed:
1) First step is to construct a MANET simulation with attack using NS-2.
2) This simulation will generate some trace files which consists of all the information about the network.
3) The next step is the preprocessing of Trace files which perform the data cleaning that is it extracts the required file from the generated trace files.
4) Next these extracted files are saved as a sample input network behavior file.
5) This sample input network behavior file is fed into the
Fuzzy Based System, which matches the input nodes with the sample and based upon this matching concludes that input node to be an Intruder or Non-Intruder.
Fuzzy inference components:
This paper used Mamdani type fuzzy inference system. This system used the three input parameters i.e. Total no. of roes in the trace file, total no. of packets sent by the node, total no. of packets received by the node and output parameters are With attack and without attack, the input parameters are responsible to check the behavior of the
node and based on that behavior it is concluded that which node is Intruder node. For the good performance, the membership functions are presented below:
1.
Average End-to-End Delay(Seconds)
Fig.5 Input Membership Functions
Fig.6 Output Membership Functions
Fuzzy Rules:
1. If input1 is TOTAL then output1 is WOATTACK
2. If input1 is SEND then output1 is WOATTACK
3. If input1 is RECEIVE then output1 is WOATTACK
4. If input1 is not TOTAL then output1 is ATTACK
5. If input1 is not SEND then output1 is ATTACK
6. If input1 is not RECEIVE then output1 is ATTACK
Prevention Technique :
We will use this technique for prevention. Fuzzy system will be installed on some node for detecting malicious node, after detection this node will broadcast acknowledgement message to all, and then all nodes update their routing table and delete the entries of malicious node. In this scheme we define a normal profile of simulation using its trace file entries generated from the simulation using NS-2, if any of the trace file deviate from their regular entries (such as total no. of rows, max no. of packets sent and max no. of packets received by a node) that means the file is abnormal and further use this prevention mechanism will take to stop such type of activities.
VII.
SIMULATION PARAMETERS & RESULTS
Simulation Parameters
Simulator
Routing Protocol
Number of Nodes
Number of Attackers
Transmission Range
NS-2.35
AODV
50,70 or 120
1,2
250m
Simulation Time
Movement Model
Packet Size
Traffic
Terrine area
20 Secs
Random way point
1500 bytes
Constant Bit Rate (CBR)
1000 m
2
End to End Delay vs No. of Nodes
2.5
2
3.5
3
1.5
1
0.5
0
50
2.
Throughput(KBPS)
70
No. of Nodes
120
Flooded AODV
Normal AODV
Throughput vs No. of Nodes
40
30
60
50
20
10
Flooded AODV
Normal AODV
0
50 70
No. of Nodes
3.
Packet Delivery Ratio(%)
PDR vs No. of Nodes
100
90
60
50
80
70
40
30
20
10
0
50 70
No. of Nodes
120
120
Flooded AODV
Normal AODV
VIII.
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
Flooding attack is one of the major security challenges for
MANETs. The proposed solution can be applied to protect the network from security threats by applying Fuzzy based system to detect the malicious nodes causing flooding in the network and protect the network from being flooded with fake packets which consumes all the network’s bandwidth and resources. It is concluded that the fuzzy systems are very easy to build. The inference rules built are taken from human intuitions and are used to describe the behavior of the system. Fuzzy logical thinking systems are with success applied in fields like automatic management, knowledge classification, call analysis, professional systems, and laptop vision. due to its multidisciplinary nature, fuzzy logical thinking systems square measure related to variety of names, like fuzzy-rule-based systems, fuzzy professional systems, fuzzy modeling, fuzzy associative memory, mathematical logic controllers, and easily
(and ambiguously) fuzzy systems.
In future, the proposed methodology identify other malicious attacks such as Worm Hole, Sink Hole & Black Hole attack and also compare their performances metrics with other routing protocol such as DSDV, DSR & TORA.
R EFERENCES
[1] Mohammed M. Ibrahim, Nayera Sadek and Mohammed El-
Banna,”Prevention of Flooding Attack in Wireless Ad-hoc AODV-based networks using Real-time Host Intrusion Detection” ,Proceedings of
IEEE 2009.
[2] Meenakshi Patel, Sanjay Sharma and Divya Sharan , “Detection and
Prevention of Flooding Attack Using SVM” , IEEE 2013
(CSNT)International Conference on Communication Systems and
Network Technologies.
[3]
Neha Arya, “Improvement in Security Measures in MANET”,
International Journal of Electronics and communication Technology
(IJECT) Vol.6 Issue 1,SPL-2, Jan-March 2015.
[4]
J.S.R.Jang, C.T.Sun & E.Mizutani, “Neuro-Fuzzy & Soft Computing –
A computational Approach to learning & Machine Intelligence”, in 1st
Edition, Prentice Hall of India, 1997.
[5] Alka Chaudhary, Vivekanand Tiwari and Anil Kumar,”A Novel
Intrusion detection System for Ad Hoc Flooding Attack using Fuzzy
Logic in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks” ,IEEE International Conference on
Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering(ICRAIE-2014),May
09-11,2014,Jaipur, India.
[6] Alokparna Bandyopadhyay, Satyanarayan Vuppala & Prasenjit
Choudhary,”A Simulation Analysis of Flooding Attack in MANET using NS-3”, Wireless communication, Vehicular Technology,
Information Theory & Aerospace & Electronics System, February 28
2011- March 3 2011.
[7]
Dhruvi Marsonia and Prof. Hardik Patel, “A Review Paper on Network
Layer attacks in MANETs”, IJSRD- International Journal for Scientific
Research & Development Vol.1,Issue 9,2013.
[8] Fatemeh Barani and Sajjad Gerami ,” ManetSVM: Dynamic Anomaly
Detection using Oneclass Support Vector Machine in MANETs” ,
Proceedings of Information Security and Cryptology(ISCISC)2013
IEEE 10TH International Conference Aug 2013.
[9] K. Kavitha and S. Ranjitha Kumari ,”Particle Swarm Optimization for
Adaptive Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection System using Fuzzy
Controller”, International Journal of Computer Trends and
Technology(IJCTT) – volume 4 Issue 10 – October 2013.
[10]
Fatehmeh Barani , ”A Hybrid Approach for Dynamic Intrusion
Detection in Ad Hoc Networks using Genetic Algorithm and Artificial
Immune System”, Proceedings of IEEE , international Conference on
Intelligent Systems (ICIS) , Pages 1-6 April-2014
[11] Taranpreet Kaur, Amanjot Singh Toor and Krishan Kumar Saluja ,”
Defending MANETs against Flooding Attacks for Military Applications under Group Mobility”, Proceedings of 2014 RAECS VIET Panjab
University Chandigarh, 06 - 08 March, 2014 IEEE.
[12] Kashif Laeeq ,” RFAP, A Preventive Measure against Route Request
Flooding Attack in MANETS”, Proceedings of Multitopic Conference
(INMIC), Dec 2012 IEEE 15th International Conference.
[13] Mohammed M. Ibrahim, Nayera Sadek and Mohammed El-
Banna,”Prevention of Flooding Attack in Wireless Ad-hoc AODV-based networks using Real-time Host Intrusion Detection” ,Proceedings of
IEEE 2009.
[14] Sarah Ahmed & S.M. Nirkhi , ” A Fuzzy Approach for Forensic
Analysis of DDOS Attacks in MANET” , International Conference on
Computer Science and Information Technology, 10th, March 2013,
Hyderabad.
[15] P.Yi, Z.Dai, S.Zhang & Y.Zhang, “A New Routing attack in Mobile Ad hoc Networks", International Journl of Information Technology, Vol.11, pp 83-94, 2005.
[16] Mohamed A. Abdelshafy and Peter J.B King,” Analysis of Security
Attacks on AODV Routing”, Proceedings of Internet Technology and
Secured Transactions (ICITST) Dec 2013 IEEE,8th International
Conference.
[17] Bhuvaneshwari K and Dr. A.Francis Saviour Devaraj, “PDS- A Profile based Detection Scheme for flooding attack in AODV based MANET”,
International Journal of Security ,Privacy and Trust
Management(IJSPTM) vol 2,No.3,June 2013.





