ANNEX– Literature review Table S1. Keywords used in search
advertisement
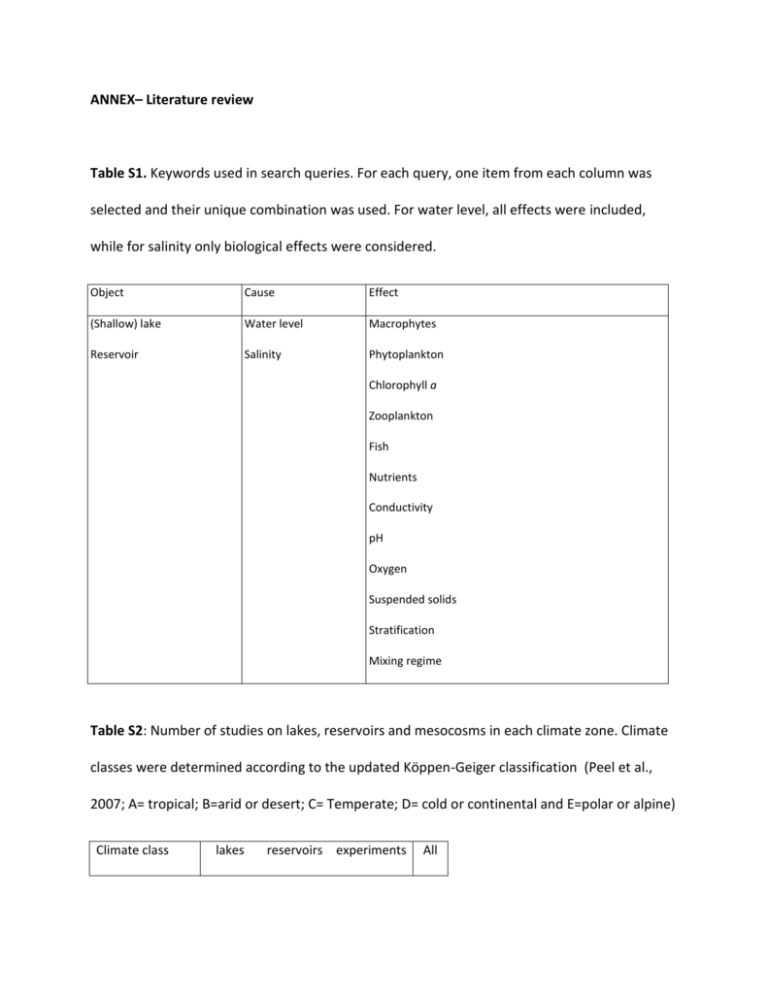
ANNEX– Literature review Table S1. Keywords used in search queries. For each query, one item from each column was selected and their unique combination was used. For water level, all effects were included, while for salinity only biological effects were considered. Object Cause Effect (Shallow) lake Water level Macrophytes Reservoir Salinity Phytoplankton Chlorophyll a Zooplankton Fish Nutrients Conductivity pH Oxygen Suspended solids Stratification Mixing regime Table S2: Number of studies on lakes, reservoirs and mesocosms in each climate zone. Climate classes were determined according to the updated Köppen-Geiger classification (Peel et al., 2007; A= tropical; B=arid or desert; C= Temperate; D= cold or continental and E=polar or alpine) Climate class lakes reservoirs experiments All A 6 6 0 12 B 6 2 2 10 C 49 15 6 70 D 23 2 1 26 E 1 0 0 1 Total 85 25 9 119 Table S3: Literature survey using Web of Science and a number of key word combinations. The single impacts cannot fully exclude synergistic or antagonistic effects due to potential multiple stressors (e.g. phytoplankton increase due to water level reduction can be masked by a concomitant increase in nutrient levels due to intensified anthropogenic impacts). Water body Cause shallow Water lake level Effects Phytoplankton increase Change in phytoplankton community reduction Bacterioplankton increase (climate) Change in zooplankton community Zooplankton increase Zooplankton decrease Macrophyte increase References 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 8,9,10,11 1 12 5,13 14 15,16,17,10,11,12,18,19,20, 21,22,23,24 Macrophyte decrease 4,7 Change in macroinvertebrate community 25 Fish increase 12 Fish decrease 19 Fish spawn earlier 26 Oxygen decrease 27 Water transparency decrease Water transparency increase Conductivity increase Salinity increase DIN increase NO3 decrease 2,4,14,28 10 5 23 23,29 20 TP increase 23,29 TP decrease 28 SRP increase 20 TN decrease 28 Internal loading 23,29 Water Phytoplankton decrease 30,31 level Cyanobacteria increase reduction (other) Macrophyte increase level 33,34,30,31,35 Change in macrophyte community 36,37,38 Reed bed increase 37,38,39 Fish reproduction decrease 40 Periphyton increase 45 Oxygen decrease 43 Water transparency increase Water 32 33,34 Conductivity increase 44 TP increase 42 SRP increase 41 TN increase 42 Phytoplankton decrease 46,8,47 Macrophyte increase 46 increase Oxygen increase 27 (climate) SRP decrease 48 Change in phytoplankton community 49 Phytoplankton decrease 49 Water level increase (other) Salinity Change in phytoplankton community increase Change in zooplankton community 50,51 52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60, 61,62,63,64,65,66 Zooplankton decrease Zooplankton increase 55,69 Change in macrophyte community 52,70 Change in macroinvertebrate community Macroinvertebrate decrease Change in fish community deep lake 52,56,67,68,60,66,62 52,55,71,61,63,64 71 52,61 Macrobenthos decrease 72 Phytoplankton increase 73 level Macrophyte decrease 74 reduction Water mixing ceasing 75 Water (climate) Water level Phytoplankton increase 76,77 Macrophyte decrease 78 Reed bed increase 78 Macroinvertebrate decrease 78 Fish community change 78 Fish reproduction decrease 79 Nutrients increase 76 DIN decrease 78 Salinity increase 78 Phytoplankton increase 80 Zooplankton decrease 80 increase Fish increase 80 (other) TP decrease 80 NH4 decrease 80 Change in zooplankton composition 81 reduction (other) Water level Salinity increase shallow reservoir Water level Phytoplankton increase 82 Macrophyte decrease 82 reduction (climate) deep Water reservoir level reduction (climate) Phytoplankton increase Change in phytoplankton community 85,77,86 87,84 Macrophyte decrease 88 Change in macrophyte community 89 TP increase 83,84 DIN increase 84 Break up stratification 77 Internal loading 77 Water Phytoplankton increase 90 level Cyanobacteria decrease 91 reduction (other) Change in zooplankton community Macrophyte increase 91,92,93 33 Macrophyte decrease 100 Change in macrophyte community 101 Fish reproduction decrease 96,97,98 Change in fish community 99 Fish pelagic species decrease 99 Macro-invertebrate increase 94 Change in macro-invertebrate community 95 Nutrients increase 95 TP increase 92,102 Chlorophyll a increase 92 Water transparency decrease 92 Water transparency increase 33 Longer stratification 103 Water Phytoplankton increase 104 Change in phytoplankton community 105 Change in zooplankton community 105 level increase (other) Experiment al setup Water level reduction (climate) Macrophyte increase 105,106,107,108 Increase in bacteria, HNF and ciliates 114 Salinity Change in phytoplankton community 111,112 increase Change in zooplankton community 111,113 Zooplankton decrease Change in macrophyte community Macrophyte decrease 1 109 110,111 111 Kisand, V. & T. Nõges, 2004. Abiotic and biotic factors regulating dynamics of bacterioplankton in a large shallow lake. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 50: 51–62. 2 Nõges, T., P. Nõges & A. C. Cardoso, 2010a. Review of published climate change adaptation and mitigation measures related with water. Scientific and Technical Research Series EUR 24682 EN, Joint Research Centre. Publications Office of the European Union. Luxembourg, 127 pp. http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/111111111/15801 3 Ndungu, J., B. C. Monger, D. C. M. Augustijn, S. J. M. H. Hulscher, N. Kitaka & J. M. Mathooko, 2013. Evaluation of spatio-temporal variations in chlorophyll-a in Lake Naivasha, Kenya: remote-sensing approach. International Journal of Remote Sensing 34: 8142–8155. 4 Loverde-Oliveira, S. M., V. L. M. Huszar, N. Mazzeo & M. Scheffer, 2009. Hydrology-driven regime shifts in a shallow tropical lake. Ecosystems 12: 807–819. 5 Chaparro, G., M. C. Marinone, R. J. Lombardo, M. R. Schiaffino, A. de Souza Guimarães & I. O’Farrell, 2011. Zooplankton succession during extraordinary drought–flood cycles: A case study in a South American floodplain lake. Limnologica – Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 41: 371–381. 6 O’Farrell, I., I. Izaguirre, G. Chaparro, F. Unrein, R. Sinistro, H. Pizarro, P. Rodríguez, P. Tezanos Pinto, R. Lombard & G. Tell, 2011. Water level as the main driver of the alternation between a free- floating plant and a phytoplankton dominated state: a long-term study in a floodplain lake. Aquatic Sciences 73: 275–287. 7 Barone, R., G. Castelli & L. Naselli-Flores, 2010. Red sky at night cyanobacteria delight: the role of climate in structuring phytoplankton assemblage in a shallow, Mediterranean lake (Biviere di Gela, southeastern Sicily). Hydrobiologia 639: 43–53. 8 Nõges, T., P. Nõges & R. Laugaste, 2003. Water level as the mediator between climate change and phytoplankton composition in a large shallow temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 506-509: 257–263. 9 Nõges, P., U. Mischke, R. Laugaste & A. G. Solimini, 2010b. Analysis of changes over 44 years in the phytoplankton of Lake Võrtsjärv (Estonia): the effect of nutrients, climate and the investigator on phytoplankton-based water quality indices. Hydrobiologia 646: 33–48. 10 Nõges, P., L. Tuvikene, T. Nõges & A. Kisand, 1999. Primary production, sedimentation and resuspension in large shallow Lake Võrtsjärv. Aquatic Sciences 61: 168–182 11 Nõges, T. & P. Nõges, 1999. The effect of extreme water level decrease on hydrochemistry and phytoplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 408-409: 277–283. 12 Havens, K., T. East & J. Beaver, 2007. Zooplankton response to extreme drought in a large subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 589: 187–198. 13 Palijan, G. & A. Galir, 2012. Change in metazooplankton abundance in response to flood dynamics and the trophic relations in Danubian floodplain lake (Kopačk rit, Croatia). Polish Journal of Ecology 60: 777–787. 14 G.-Tóth, L., L. Parpala, C. Balogh, I. Tátrai & E. Baranyai, 2011. Zooplankton community response to enhanced turbulence generated by water-level decrease in Lake Balaton, the largest shallow lake in Central Europe. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 2211–2222. 15 Havens, K. E., B. Sharfstein, M. A. Brady, T. L. East, M. C. Harwell, R. P. Maki & A. J. Rodusky, 2004. Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical lake in Florida, USA. Aquatic Botany 78: 67–82. 16 Beklioğlu, M., G. Altinayar & C. O. Tan, 2006. Water level control over submerged macrophyte development in five shallow lakes of Mediterranean Turkey. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 166: 535–556. 17 Blindow, I., 1993. Long-term pattern of alternative stable states in two shallow eutrophic lakes. Freshwater Biology 30: 159–167. 18 Tan, C. O. & M. Beklioğlu, 2005. Catastrophic-like shifts in shallow Turkish lakes: a modeling approach. Ecological Modelling 183: 425–434. 19 Mazzeo, N., L. Rodriguez-Gallego, C. Kruk, M. Meerhoff, J. Gorga, G. Lacerot, F. Quintans, M. Louriero, D. Larrea & F. Garcia-Rodriguez, 2003. Effects of Egeria densa plant beds on a shallow lake without piscivorous fish. Hydrobiologia 506-509: 591–602. 20 Mäemets, H., L. Freiberg, M. Haldna & T. Möls, 2006. Inter-annual variability of Potamogeton perfoliatus stands. Aquatic Botany 85: 177–183. 21 Van Geest, G. J., H. Wolters, F. C. J. M. Roozen, H. Coops, R. M. M. Roijackers, A. D. Buijse & M. Scheffer, 2005. Water-level fluctuations affect macrophyte richness in floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia 539: 239–248. 22 Beklioğlu, M., S. Romo, I. Kagalou, X. Quintana & E. Becares, 2007. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 584: 317–326. 23 Beklioğlu, M. & C. O. Tan, 2008. Restoration of shallow Mediterranean lake by biomanipulation complicated by drought. Archiv für Hydrobiologie – Fundamental and Applied Limnology 171: 105– 118. 24 Liira, J., T. Feldmann, H. Mäemets & U. Peterson, 2010. Two decades of macrophytes expansion on the shores of a large shallow northern temperate lake – A retrospective series of satellite images. Aquatic Botany 93: 207–215. 25 Muskó, I. B., C. Balogh, Á. P. Tóth, É. Varga & G. Lakatos, 2007. Differential response of invasive malacostracan species to lake level fluctuations. Hydrobiologia 590: 65–74. 26 Nõges, P. & A. Järvet, 2005. Climate driven changes in the spawning of roach (Rutilus rutilus (L.)) and bream (Abramis brama (L.)) in the Estonian part of the Narva River basin. Boreal Environment Research 10: 45–55. 27 Moncayo-Estrada, R., C. Escalera-Gallardo & O. T. Lind, 2011. Spatial patterns of zooplanktivore Chirostoma species (Atherinopsidae) during water-level fluctuation in the shallow tropical Lake Chapala, Mexico: seasonal and interannual analysis. Neotropical Ichthyology 9: 815–824. 28 Skinner, D., R. Oliver, K. Aldridge & J. Brookes, 2014. Extreme water level decline effects sediment distribution and composition in Lake Alexandrina, South Australia. Limnology 15:117-126. 29 Özen, A., B. Karapinar, I. Kucuk, E. Jeppesen & M. Beklioğlu, 2010. Drought-induced changes in nutrient concentrations and retention in two shallow Mediterranean lakes subjected to different degrees of management. Hydrobiologia 646: 61–72. 30 Kong, X.-Z., S. E. Jørgensen, W. He, N. Qin & F.-L. Xu, 2013. Predicting the restoration effects by a structural dynamic approach in Lake Chaohu, China. Ecological Modelling 266: 73–85. 31 Blindow, I., 1992. Long- and short-term dynamics of submerged macrophytes in two shallow eutrophic lakes. Freshwater Biology 28: 15–27. 32 Frisk, T., H. Kaipainen, O. Malve & M. Möls, 1999. Modelling phytoplankton dynamics of the eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv, Estonia. Hydrobiologia 414: 59–69. 33 Bachmann, R. W., M. V Hoyer, C. Fernandez & D. E. Canfield, 2003. An alternative to proposed phopshorus TMDLs for the management of Lake Okeechobee. Lake and Reservoir Management 19: 251–264. 34 Havens, K. E., D. Fox, S. Gornak & C. Hanlon, 2005. Aquatic vegetation and largemouth bass population responses to water-level variations in Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Hydrobiologia 539: 225–237. 35 Mcgowan, S., P. R. Leavitt & R. I. Hall, 2005. A whole-lake experiment to determine the effects of winter droughts on shallow lakes. Ecosystems 8: 694–708. 36 Egertson, C. J., J. A. Kopaska & J. A. Downing, 2004. A century of change in macrophyte abundance and composition in response to agricultural eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 524: 145–156. 37 Papastergiadou, E. S., A. Retalis, P. Kalliris & T. Georgiadis, 2007. Land use changes and associated environmental impacts on the Mediterranean shallow Lake Stymfalia, Greece. Hydrobiologia 584: 361–372. 38 Papastergiadou, E., A. Retalis, A. Apostolakis & T. Georgiadis, 2008. Environmental monitoring of spatio-temporal changes using remote sensing and GIS in a Mediterranean wetland of Northern Greece. Water Resources Management 22: 579–594 39 Papastergiadou, E., I. Kagalou, K. Stefanidis, A. Retalis & I. Leonardos, 2010. Effects of anthropogenic influences on the trophic state, land uses and aquatic vegetation in a shallow Mediterranean lake: Implications for restoration. Water Resources Management 24: 415–435. 40 Paulovits, G., G. Borbely, L. Toth & N. Kovats, 2007. Effects of water level fluctuation on reproduction and spawning habits of fish species in Lake Balaton. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal 6: 467–471. 41 Mitraki, C., T. L. Crisman & G. Zalidis, 2004. Lake Koronia, Greece: Shift from autotrophy to heterotrophy with cultural eutrophication and progressive water-level reduction. Limnologica 34: 110– 116. 42 Lind, O. T., L. O. Dávalos-Lind, T. H. Chrzanowski & J. G. Limón, 1994. Inorganic turbidity and the failure of fishery models. Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie Akademie Verlag, Berlin 79: 7–16. 43 Cott, P. A., P. K. Sibley, W. M. Somers, M. R. Lilly & A. M. Gordon, 2008. A review of water level fluctuations on aquatic biota with an emphasis on fishes in ice-covered lakes 1. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 44: 343–359. 44 Padisák, J. & M. T. Dokulil, 1994. Meroplankton dynamics in a saline, turbulent shallow lake (Neusiedlersee, Austria and Hungary). Hydrobiologia 289: 23–42. 45 Albay, M. & R. Akcaalan, 2003. Comparative study of periphyton colonisation on common reed (Phragmites australis) and artificial substrate in a shallow lake, Manyas, Turkey. Hydrobiologia 506509: 531–540. 46 Mihaljević, M., D. Špoljarić, F. Stević, V. Cvijanović & B. Hackenberger Kutuzović, 2010. The influence of extreme floods from the River Danube in 2006 on phytoplankton communities in a floodplain lake: Shift to a clear state. Limnologica 40: 260–268. 47 Nõges, T., 2004. Reflection of the changes of the North Atlantic Oscillation Index and the Gulf Stream Position Index in the hydrology and phytoplankton of Võrtsjärv, a large, shallow lake in. Boreal Environment Research 9: 401–407. 48 Kangur, K., T. Möls, A. Milius & R. Laugaste, 2003. Phytoplankton response to changed nutrient level in Lake Peipsi (Estonia) in 1992–2001. Hydrobiologia 506: 265–272. 49 Beshkova, М. B., R. K. Kalchev, V. Vasilev & R. L. Tsvetkova, 2008. Changes of the phytoplankton abundance and structure in the biosphere reserve Srebarna (Northeastern Bulgaria) in relation to some environmental variables. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 2: 165–175. 50 Fazio, A. & I. O’Farrell, 2005. Phytoplankton and water quality in a shallow lake: A response to secondary salinization (Argentina). Wetlands 25: 531–541. 51 Ballot, A., K. Kotut, E. Novelo & L. Krienitz, 2009. Changes of phytoplankton communities in Lakes Naivasha and Oloidien, examples of degradation and salinization of lakes in the Kenyan Rift Valley. Hydrobiologia 632: 359–363. 52 Jensen, E., S. Brucet, M. Meerhoff, L. Nathansen & E. Jeppesen, 2010. Community structure and diel migration of zooplankton in shallow brackish lakes: role of salinity and predators. Hydrobiologia 646: 215–229. 53 Northcote, T. G. & K. J. Hall, 2009. Salinity regulation of zooplanktonic abundance and vertical distribution in two saline meromictic lakes in south central British Columbia. Hydrobiologia 638: 121– 136. 54 Blinn, D. W., S. A. Halse, A. M. Pinder, R. J. Shiel & J. M. Mcrae, 2004. Diatom and micro-invertebrate communities and environmental determinants in the western Australian wheatbelt : a response to salinization. Hydrobiologia 528: 229–248. 55 Brucet, S., D. Boix, X. D. Quintana, E. Jensen, L. W. Nathansen, C. Trochine, M. Meerhoff, S. Gascón & E. Jeppesen, 2010. Factors influencing zooplankton size structure at contrasting temperatures in coastal shallow lakes: Implications for effects of climate change. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1697–1711. 56 Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, A. R. Pedersen, K. Jürgens, A. Strzelczak, T. L. Lauridsen & L. S. Johansson, 2007. Salinity induced regime shift in shallow brackish lagoons. Ecosystems 10: 47–57. 57 Echaniz, S. A., A. M. Vignatti, S. J. de Paggi, J. C. Paggi & A. Pilati, 2006. Zooplankton seasonal abundance of South American saline shallow lakes. International Review of Hydrobiology 91: 86–100. 58 Golubkov, S., R. Kemp, M. Golubkov, E. Balushkina, L. Litvinchuk & Y. Gubelit, 2007. Biodiversity and the functioning of hypersaline lake ecosystems from Crimea Peninsula (Black Sea). Fundamental and Applied Limnology – Archiv für Hydrobiologie 169: 79–87. 59 De Los Ríos, P. & G. Gajardo, 2010. A null model to explain zooplankton species associations in saline lakes of the South American Altiplano (14-27°S). Crustaceana 83: 769–777. 60 Brucet, S., D. Boix, S. Gascón, J. Sala, X. D. Quintana, A. Badosa, M. Søndergaard, T. L. Lauridsen & E. Jeppesen, 2009. Species richness of crustacean zooplankton and trophic structure of brackish lagoons in contrasting climate zones: north temperate Denmark and Mediterranean Catalonia (Spain). Ecography 32: 692–702. 61 Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, E. Kanstrup, B. Petersen, R. B. Eriksen, M. Hammershøj, E. Mortensen, J. P. Jensen & A. Have, 1994. Does the impact of nutrients on the biological structure and function of brackish and fresh-water lakes differ? Hydrobiologia 275: 15–30. 62 Green, A. J., C. Fuentes, E. Moreno-Ostos & S. L. Rodrigues da Silva, 2005. Factors influencing cladoceran abundance and species richness in brackish lakes in Eastern Spain. Annales de Limnologie – International Journal of Limnology 41: 73–81. 63 Boix, D., S. Gascón, J. Sala, A. Badosa, S. Brucet, R. López-Flores, M. Martinoy, J. Gifre & X. D. Quintana, 2008. Patterns of composition and species richness of crustaceans and aquatic insects along environmental gradients in Mediterranean water bodies. Hydrobiologia 597: 53–69. 64 Verschuren, D., J. Tibby, K. Sabbe & N. Roberts, 2000. Effects of depth, salinity, and substrate on the invertebrate community of a fluctuating tropical lake. Ecology 81: 164–182. 65 Boronat, L., M. R. Miracle & X. Armengol, 2001. Cladoceran assemblages in a mineralization gradient. Hydrobiologia 442: 75–88. 66 Schallenberg, M., J. H. Catherine & C. W. Burns, 2003. Consequences of climate-induced salinity increases on zooplankton abundance and diversity in coastal lakes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 251: 181–189. 67 Amsinck, S. L., E. Jeppesen & F. Landkildehus, 2005. Relationships between environmental variables and zooplankton subfossils in the surface sediments of 36 shallow coastal brackish lakes with special emphasis on the role of fish. Journal of Paleolimnology 33: 39–51. 68 De los Ríos, P., 2005. Richness and distribution of zooplanktonic crustacean species in Chilean Andes mountains and Southern Patagonia shallow ponds. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 14: 817– 822. 69 Echaniz, S. A. & A. M. Vignatti, 2011. Seasonal variation and influence of turbidity and salinity on the zooplankton of a saline lake in central Argentina. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research 39: 306–315. 70 Wollheim, W. M. & J. R. Lovvorn, 1995. Salinity effects on macroinvertebrate assemblages and waterbird food webs in shallow lakes of the Wyoming High Plains. Hydrobiologia 310: 207–223. 71 Brucet, S., D. Boix, L. W. Nathansen, X. D. Quintana, E. Jensen, D. Balayla, M. Meerhoff & E. Jeppesen, 2012. Effects of temperature, salinity and fish in structuring the macroinvertebrate community in shallow lakes: implications for effects of climate change. PloS one 7: 1–11. 72 Sereda, J., M. Bogard, J. Hudson, D. Helps & T. Dessouki, 2011. Climate warming and the onset of salinization: Rapid changes in the limnology of two northern plains lakes. Limnologica Elsevier 41: 1– 9. 73 Bouvy, M., S. M. Nascimento, R. J. R. Molica, A. Ferreira, V. Huszar & S. M. F. O. Azevedo, 2003. Limnological features in Tapacura reservoir (northeast Brazil) during a severe drought. Hydrobiologia 493: 115–130. 74 Bresciani, M., R. Bolpagni, F. Braga, A. Oggioni & C. Giardino, 2012. Retrospective assessment of macrophytic communities in southern Lake Garda (Italy) from in situ and MIVIS (Multispectral Infrared and Visible Imaging Spectrometer) data. Journal of Limnology 71: 180–190. 75 Sahoo, G. B., S. G. Schladow, J. E. Reuter, R. Coats, M. Dettinger, J. Riverson, B. Wolfe & M. CostaCabral, 2013. The response of Lake Tahoe to climate change. Climatic Change 116: 71–95. 76 Hambright, K. D., T. Zohary, W. Eckert, S. S. Schwartz, L. Claire, K. R. Laird, P. R. Leavitt & C. L. Schelske, 2008. Exploitation and destabilization of a warm, freshwater ecosystem through engineered hydrological change. Ecological Applications 18: 1591–1603. 77 Naselli-Flores, L., 2003. Man-made lakes in Mediterranean semi-arid climate: the strange case of Dr Deep Lake and Mr Shallow Lake. Hydrobiologia 506-509: 13–21. 78 Stefanidis, K. & E. Papastergiadou, 2013. Effects of a long term water level reduction on the ecology and water quality in an eastern Mediterranean lake. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 411: 1–14. 79 Yamamoto, T., Y. Kohmatsu & M. Yuma, 2006. Effects of summer drawdown on cyprinid fish larvae in Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology 7: 75–82. 80 Zohary, T. & I. Ostrovsky, 2011. Ecological impacts of excessive water level fluctuations in stratified freshwater lake. Inland Waters 1: 47–59. 81 Rumes, B., H. Eggermont & D. Verschuren, 2011. Distribution and faunal richness of Cladocera in western Uganda crater lakes. Hydrobiologia 676: 39–56. 82 Thomas, S., P. Cecchi, D. Corbin & J. Lemoalle, 2000. The different primary producers in a small African tropical reservoir during a drought: temporal changes and interactions. Freshwater Biology 45: 43–56. 83 Dalu, T., Z. Thackeray, R. Leuci, B. Clegg, L. D. Chari & T. Nhiwatiwa, 2013. First results on bathymetry, stratification and physicochemical limnology of a small tropical African reservoir (Malilangwe, Zimbabwe). Water SA 39: 119–130. 84 Naselli-Flores, L. & R. Barone, 2005. Water-level fluctuations in Mediterranean reservoirs: Setting a dewatering threshold as a management tool to improve water quality. Hydrobiologia 548: 85–99. 85 Khaliullina, L. Y., V. A. Yakovlev & I. I. Khaliullin, 2009. Seasonal and year-to-year dynamics of phytoplankton in connection with the level regime of the Kuibyshev Reservoir. Water Resources 36: 459–465. 86 Arfi, R., 2005. Seasonal ecological changes and water level variations in the Sélingué Reservoir (Mali, West Africa). Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 30: 432–441. 87 Xiao, L.-J., T. Wang, R. Hu, B.-P. Han, S. Wang, X. Qian & J. Padisák, 2011. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups regulated by monsoonal hydrology in a large canyon-shaped reservoir. Water Research 45: 5099–5109. 88 Thomaz, S. M., T. A. Pagioro, L. M. Bini & K. J. Murphy, 2006. Effect of reservoir drawdown on biomass of three species of aquatic macrophytes in a large sub-tropical reservoir (Itaipu, Brazil). Hydrobiologia 570: 53–59. 89 Boschilia, S. M., E. F. De Oliveira & A. Schwarzbold, 2012. The immediate and long-term effects of water drawdown on macrophyte assemblages in a large subtropical reservoir. Freshwater Biology 57: 2641–2651. 90 Naselli-Flores, L., R. Barone, I. Chorus & R. Kurmayer, 2007. Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in reservoirs under a semiarid Mediterranean climate: The magnification of a problem. Environmental Toxicology 22: 399–404. 91 Valdespino-Castillo, P.M., M. Merino-Ibara, J. Jimenez-Contreras, F.S. Castillo-Sandoval & J.A. Ramirez-Zierold, 2014. Community metabolism in a deep (stratified) tropical reservoir during a period of high water-level fluctuations. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 186: 6505–6520. 92 Geraldes, A. M. & M.-J. Boavida, 2007. Zooplankton assemblages in two reservoirs: one subjected to accentuated water level fluctuations, the other with more stable water levels. Aquatic Ecology 41: 273–284. 93 Naselli-Flores, L. & R. Barone, 1997. Importance of water-level fluctuation on population dynamics of cladocerans in a hypertrophic reservoir (Lake Arancio, south-west Sicily, Italy). Hydrobiologia 360: 223–232. 94 Furey, P. C., R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2006. Littoral benthic macroinvertebrates under contrasting drawdown in a reservoir and a natural lake. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 19–31. 95 Ambelu, A., K. Lock & P. L. M. Goethals, 2013. Hydrological and anthropogenic influence in the Gilgel Gibe I reservoir (Ethiopia) on macroinvertebrate assemblages. Lake and Reservoir Management 29: 143–150. 96 Ozen, O. & R. L. Noble, 2005. Relationship between largemouth bass recruitment and water level dynamics in a Puerto Rico reservoir. Lake and Reservoir Management 21: 89–95. 97 Sutela, T., A. Mutenia & E. Salonen, 2002. Relationship between annual variation in reservoir conditions and year-class strength of peled (Coregonus peled) and whitefish (C. lavaretus). Hydrobiologia 185: 213–221. 98 Clark, M. E., K. A. Rose, J. A. Chandler, T. J. Richter, D. J. Orth & W. Van Winkle, 2008. Water-level fluctuation effects on centrarchid reproductive success in reservoirs: A modeling analysis. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 28: 1138–1156. 99 Piet, G. J., 1998. Impact of environmental perturbation on a tropical fish community. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 55: 1842–1853. 100 Furey, P. C., R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2004. Water level drawdown affects physical and biogeochemical properties of littoral sediments of a reservoir and a natural lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 20: 280–295. 101 Papastergiadou, E. & D. Babalonas, 1992. Ecological studies on aquatic macrophytes of a dam lake – Lake Kerkini, Greece. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 2: 187–206. 102 Sánchez-Carrillo, S., L. C. Alatorre, R. Sánchez-Andrés & J. Garatuza-Payán, 2007. Eutrophication and sedimentation patterns in complete exploitation of water resources scenarios: an example from Northwestern semi-arid Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 132: 377–393. 103 Nowlin, W. H., J.-M. Davies, R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2004. Effects of water level fluctuation and short-term climate variation on thermal and stratification regimes of a British Columbia reservoir and lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 20: 91–109. 104 Komarkova, J., O. Komarek & J. Hejzlar, 2003. Evaluation of the long term monitoring of phytoplankton assemblages in a canyon-shape reservoir using multivariate statistical methods. Hydrobiologia 504: 143–157. 105 Romo, S., M. R. Miracle, M.-J. Villena, J. Rueda, C. Ferriol & E. Vicente, 2004. Mesocosm experiments on nutrient and fish effects on shallow lake food webs in a Mediterranean climate. Freshwater Biology 49: 1593–1607. 106 Özkan, K., E. Jeppesen, L. S. Johansson & M. Beklioğlu, 2010. The response of periphyton and submerged macrophytes to nitrogen and phosphorus loading in shallow warm lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Freshwater Biology 55: 463–465. 107 Bucak, T., E. Saraoğlu, E. E. Levi, Ü. N. Tavşanoğlu, A. I. Çakıroğlu, E. Jeppesen & M. Beklioğlu, 2012. The influence of water level on macrophyte growth and trophic interactions in eutrophic Mediterranean shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment with and without fish. Freshwater Biology 57: 1631–1642. 108 Bécares, E., J. Gomá, M. Fernández-Aláez, C. Fernández-Aláez, S. Romo, M. Miracle, A. StåhlDelbanco, L.-A. Hansson, M. Gyllström, W. Van de Bund, E. Van Donk, T. Kairesalo, J. Hietala, D. Stephen, D. Balayla & B. Moss, 2008. Effects of nutrients and fish on periphyton and plant biomass across a European latitudinal gradient. Aquatic Ecology 42: 561–574. 109 Bezirci, G., S. B. Akkas, K. Rinke, F. Yildirim, Z. Kalaylioglu, F. Severcan & M. Beklioğlu, 2012. Impacts of salinity and fish-exuded kairomone on the survival and macromolecular profile of Daphnia pulex. Ecotoxicology 21: 601–614. 110 Brock, M. A., D. L. Nielsen & K. Crossle, 2005. Changes in biotic communities developing from freshwater wetland sediments under experimental salinity and water regimes. Freshwater Biology 50: 1376–1390. 111 Barker, T., K. Hatton, M. O’Connor, L. Connor, L. Bagnell & B. Moss, 2008. Control of ecosystem state in a shallow, brackish lake : implications for the conservation of stonewort communities. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: 221–240. 112 Flöder, S. & C. W. Burns, 2004. Phytoplankton diversity of shallow tidal lakes: Influence of periodic salinity changes on diversity and species number of a natural assemblage. Journal of Phycology 40: 54–61. 113 Stephen, D., B. Moss & G. Phillips, 1998. The relative importance of top-down and bottom-up control of phytoplankton in a shallow macrophyte-dominated lake. Freshwater Biology 39: 699–713. 114 Özen, A., T. Bucak, Ü. N. Tavşanoğlu, A.I. Çakıroğlu, E.E. Levi, J. Coppens, E. Jeppsen & M. Beklioğlu, 2014. Water level and fish-mediated cascading effects on the microbial community in eutrophic warm shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 740: 25–35.