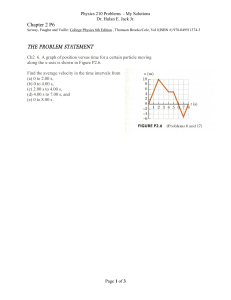
DSlabs by: Prof. J. Chen 2015.12.21 LabHelloWorld LabArrayList
advertisement

DSlabs
by: Prof. J. Chen
2015.12.21
LabHelloWorld
LabArrayList
LabArrayList&LinkedList
LabRedBlackTree
LabTreeSet
LabCompare4DS
LabGraph
Instructions on the Labs:
The grading is based on READABILITY.
Develop labs in 3 abstraction levels: 1) system #### 2) class **** 3) method ---For each method, do 1) header, 2) pseudo-code, and 3) code.
LabHelloWorld
Use Eclipse to write a main() in class Main that prints:
Hello world! My name is 張一二.
/*###################################################################
LabArrayList
By: 張一二 2015.10.09
Insert ("add" in ArrayList) one million randomly-generated grades from 0 to 100 to anArrayList.
Then, search for the max grade in the list, and record the search time.
If there are multiple answers, return one at the highest index.
###################################################################*/
Use following names:
aGrade
- a grade to be inserted to an ArrayList.
anArrayList - an ArrayList object to hold an inserted grade.
maxGrade - the max grade in anArrayList.
endTime - ending time of the search.
searchTime - endTime minus startTime.
startTime - start time of the search.
/***************************************************
class Main
anArrayList is an object of Java ArrayList class
public main() calls the two methods below.
private prepareGrades () returns nothing
private searchMaxGrade () returns nothing
******************************************************/
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
main() {construct anArrayList. It calls prepareGrades() and searchMaxGrade (). }
Time estimate: O(n)
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------prepareGrades () puts all the grades in anArrayList
Time estimate: O(n)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ /*
loop for one million times
1.use Java Random class to randomly generate aGrade (int from 0 to 100)
2.insert aGrade into anArrayList
end loop
*/
/* Put prepareGrades() code here */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------searchMaxGrade () looks for max grade in anArrayList
Example result:
The max grade is 100 and the search time is 28 milliseconds for ArrayList.
Time estimate: O(n)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
1. record startTime.
2. let the first grade be maxGrade
3. loop for one million times
if next grade >= maxGrade then let it be maxGrade
end loop
4. record endTime.
5. get searchTime.
6. print maxGrade and searchTime
/* Put searchMaxGrade () code here */
LabArrayList&LinkedList
Add “LinkedList” version to the previous lab.
/***************************************************
class Main
anArrayList is an object of Java ArrayList class
aLinkedList is an object of Java LinkedList class
public main()
private prepareGradesInArrayList () returns anArrayList
private prepareGradesInLinkedList () returns aLinkedList
private searchMaxGrade (whichDS) returns nothing
******************************************************/
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------main()
1. call prepareGradesInArrayList ()
2. call prepareGradesInLinkedList ()
3. call searchMaxGrade (1)
4. call searchMaxGrade (2)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------prepareGradesInArrayList () puts all the grades in anArrayList
returns: anArrayList, which is an object of ArrayList class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------prepareGradesInLinkedList () puts all the grades in aLinkedList
returns: aLinkedList, which is an object of LinkedList class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------searchMaxGrade (whichDS) looks for the max grade.
parameter: “whichDS” means which data structure (DS) is searched.
Note: 1 means ArrayList, and 2 means LinkedList.
Example result:
If ArrayList:
The max grade is 100 and the search time is XX milliseconds for ArrayList.
If LinkedList:
The max grade is 100 and the search time is XX milliseconds for LinkedList.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
LabRedBlackTree
Study the class notes of Chap. 12, p. 26 to develop the red-black tree (RBT) insert()
specified below:
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------Red black tree (RBT) insert() puts an element into the RBT.
----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
RBT.Entry RBTinsert (anElement)
In this method, you need binary search tree (BST) insert() (see class note Chap.
10, p.36).
You also need “rotation” method (see pp. 67-82 of Chap. 10 class note).
Turn in 2 classes:
1) Main class with main ()
2) RBT class with 7 methods:
RBT() constructor,
RBTinsert (),
BSTinsert(),
rotateRight(),
rotateLeft(),
recolor(x)
inOrder () (See class note Chap. 9, p.71).
Be sure to have readable headers for each class and method.
You can paste design sketches in class notes to improve its readability.
Most importantly, give big O time estimate for each method.
Instructions on LabRedBlackTree
Follow the design below:
main ()
1. call RBT() to construct an empty red-black tree called “t”
2. call t.RBTinsert (anElement) 4 times to insert 3, 1, 4, and 2 to “t”
3. call recursive inOrder() to traverse “t” to print out:
1 black 2 red 3 black 4 black
The pseudo-code above can be coded as below:
inOrder ( new RBT() .RBTinsert(3) .RBTinsert(1) .RBTinsert(4) .RBTinsert(2) );
public class RBT
//red-black trees (RBT)
private static final boolean RED
= false;
private static final boolean BLACK =true;
public class Entry <E> { fill in here the code of class Entry shown below}
public inOrder ()
public RBT () {Entry <Integer> t=null; return t;}
public RBTinsert ()
private recolor(x) {if color of x is red, recolor it to black; else to red end if}
private rotateRight();
private rotateLeft();
private BSTinsert(); //binary search trees (BST) insert
end of class RBT
protected static class Entry<E>
{
protected E
element;
protected Entry<E> left
= null, right = null, parent;
protected boolean color;
protected Entry (E element,
Entry<E> parent)
{this.element = element; this.parent = parent; color = RED;}
} // end of class Entry
LabTreeSet
First, you import the two utilities below:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
and you construct an empty TreeSet called “t”. Then, you call “add” of TreeSet class 4
times to insert 3, 1, 4, and 2 to “t”, respectively. Last, you construct an iterator to
traverse “t” to print out:
1 2 3 4
LabCompare4DS
Use 4 data structures (4DS) below:
0) “ArrayList”,
1) “LinkedList”,
2) “TreeMap”,
3) “HashMap”
to store a big data set of one million elements with ID from 0 to 999,999.
In a list, an element contains a grade.
In a map, a mapping contains both ID (as key) and grade (as value).
Use Java Random class to obtain a grade so you do not need to prepare a big input
text file. Then, do run-time analysis on the 4 data structures (DS).
You will see some data structure is slower than others!
/****************************************************
LAB Compare 4 DS
By 張一二 2015.12.18
隨機產生一百萬筆 aGrade 資料 每筆資料分別存入下列四種資料結構 (DS):
0) anArrayList,
aLinkedList,
2) aTreeMap,
3) aHashMap
1)
Example result:
請輸入ID 400000 (red means user input)
ID: 400000
Grade: 91
各資料結構搜尋時間:
ArrayList
80 milliseconds
LinkedList
92 milliseconds
TreeMap
8 milliseconds
HashMap
2 milliseconds
*****************************************************/
class Main
static int[4]
grades
// hold aGrade of an ID for 4 data structures.
static double[4] searchTimes // hold the searchTime using 4 data structures, respectively
main() {
1.
construct 4 empty data structures: 0) anArrayList, 1) aLinkedList, 2) aTreeMap, and
3) aHashMap with n= 1000000, m=1250000 (load factor: 1000000/1250000 = 0.8)
2.
for ID from 0 upto 999,999
1.
randomly generate aGrade with range 0..100
2.
store aGrade into 0) anArrayList and 1) aLinkedList
3.
store ID (as key) and aGrade (as value) into 2) aTreeMap and 3) aHashMap
end for
3.
for DSindex from 0 upto 3 (for each of 4 DS, data structures)
call search (DSindex, 400000)
end for
4.
prompt for ID and print result
} // end main()
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------search() looks for the grade of the given ID stored in 4 data structures.
It also records the search time for each.
Parameters: DSindex
ID
specifies which of the 4 data structures (0 to 3)
specifies the student ID to search
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
private void search (int DSindex, int ID)
1.get startTime by system clock
2.case (DSindex)
0: from anArrayList get aGrade of ID
1: from aLinkedList
do the same
2: from aTreeMap
do the same
3: from aHashMap
do the same
3.get endTime by system clock
4.searchTime is endTime minus startTime
5.store searchTime into searchTimes[DSindex]
6.store aGrade into grades[DSindex]
end of search()
end of class Main
LabGraph
To model the graph below, use 1) TreeMap and 2) HashMap versions, respectively.
Your code should pass these 3 acceptance test cases:
Test case 1:
我是張一二 將告知您兩地最短哩程 (Tree 版)
請輸入出發地 Karen (Red means user input)
請輸入目的地 Don
From Karen to Don it is 7.4 km
Test case 2:
我是張一二
將告知您兩地最短哩程 (Tree 版)
請輸入出發地 Mark
請輸入目的地 Karen
From Mark to Karen 抱歉 兩地無路可達
Test case 3:
我是張一二 將告知您兩地最短哩程 (Hash 版)
請輸入出發地 Karen
請輸入目的地 Tara
From Karen to Tara it is 18.3 km
The design sketch for the “TreeMapVersion” and its data structure are:
The design sketch for the “HashMapVersion” and its data structure are:
Hint 1: read the input text file like this (note its alphabetical order):
Courtney Don 20.0
Courtney Tara 15.0
Karen Courtney 14.2
………………………
Hint 2: use the Dijkstra algorithm (Ch. 15. class note pp. 77-91) to find the shortest
path in a network.
Hint 3: You need to write two separate programs:
“TreeMapVersion” and “HashMapVersion”
with the methods like “buildTreeMap()”, “buildHashMap()”, “findShortestPath()”
and class “UI”.