Patient presents with wrist or hand symptoms
advertisement

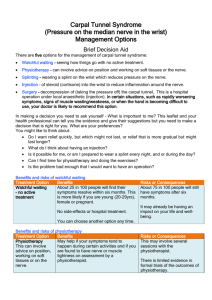
Rotherham Hand Pathway Patient presents with wrist or hand symptoms Confirm diagnosis (see attached notes) Secondary Care Please refer the following directly to Secondary Care History of or suspected malignancy, investigate and refer as appropriate. Consider red flags of unexplained weight loss, night pain and high inflammatory markers. Primary Care Acute wrist or hand injury Dupuytren’s contracture Suspected inflammatory condition, investigate and refer to Rheumatology Acute tendon rupture or severe carpal tunnel syndrome, urgent referral to Orthopaedic Surgeon Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Tendinopathies Investigations X-rays are indicated to exclude fracture including scaphoid and wrist views. Investigations Investigations Investigations NOT indicated NOT indicated NCT to be considered if positive CTS history but negative examination findings Management Consider analgesia or /NSAIDs/ splints Management Consider analgesia and NSAIDs Suspected fracture, dislocation or infection, refer to A&E Hand/wrist OA Injection NOT indicated Referral If no improvement after 2 weeks of conservative management, refer to MSK Physiotherapy Service. Dupuytren’s contracture as described: Refer to Orthopaedic Surgeon. www.patient.co.uk Injection NOT indicated Referral Any contracture at PIP joint or at MCP joint over 30 degrees, or significant limitation of lifestyle, refer to Orthopaedic Surgeon, otherwise reassure and monitor. www.nhs.uk/con ditions/dupuytre ns-contracture Injection therapy can be considered if no improvement after 4/52 of conservative management Management Advise patient on provision of a wrist splint for up to 8 weeks. Investigations NOT indicated Management Consider analgesia Injection therapy can be considered if no improvement after 4/52 of conservative management Referral NOT indicated If no response to one injection refer to MSK CATS Referral Referral If no response to one injection refer to MSK CATS. Consider referrals to social support www.cks.nhs.uk If severe symptoms affecting function or neurological deficit: refer immediately for surgical opinion www.cks.nhs.uk Investigations NOT indicated Injection If unresponsive refer to MSK CATS. Ganglions or finger cysts If symptoms recur after a second injection, refer to Orthopaedic Surgeons www.medicine net.com Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Investigations NOT indicated Management Review pain management. Consider referral to pain clinic Injection Injection NOT indicated NOT indicated Referral Referral If painful, recurrent or affecting function, refer to MSK CATS Refer urgently to MSK CATS. www.netdoctor. co.uk Consider referrals to social support services and / or psychologist Acute hand and wrist injury X-rays are only indicated to exclude fracture including wrist and scaphoid views. Consider NSAID’s and analgesia. Advise patient regarding initial relative rest, encouraging gentle, pain free movement, ice, elevation, use of support/splint/bandage intermittently. – See PRICE guidelines. If no improvement after 2 weeks, refer to MSK Physiotherapy service. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (Previously known as Sudeck’s Atrophy) Patient will present with shiny, red skin which is hypersensitive to touch and temperature. There will be associated with swelling, abnormal sweating of the skin and nail and hair changes. Patient may present not using the hand. Symptoms can be associated with surgery or minor injury. In later stages symptoms may involve the contralateral limb. Review pain management. Imaging and blood tests are not indicated. Consider referrals: to psychologist or social support services, to social services for a home assessment as required and / or to pain clinic. Urgently refer to MSK CATS. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Patient presents with: Paraesthesia / pain affecting thumb, index and middle finger. Typically at night, but can occur during the daytime. Late signs will include objective sensory change in median nerve distribution, weakness of thumb abduction and thenar eminence wasting. Positive provocative tests: Phalen’s test, Durkins compression test and Tinel’s sign. Exclude nerve root involvement from cervical spine. Reassure patient that most cases resolve within 6/12. Do not refer for imaging. Do not inject. Do not provide diuretics. Provide wrist splints at night for up to 8 weeks, if unresponsive refer to MSK CATS. If symptoms are severe with sensory blunting, wasting and weakness, in line with median nerve involvement at the wrist, refer for urgent hand surgeon opinion. Dupuytren’s Contracture Patient presents with nodules or thickening in palm or digits + / - flexion contracture of digits. No investigations are indicated. If there is there a fixed flexion deformity more than 30 degrees at MCP, any flexion contracture at an IP joint, or significant functional loss, refer to hand surgeon for routine appointment. If not, advise patient re-benign nature of condition and how to monitor deformity. Ganglions / finger cysts Patient presents with a mobile, fluid-containing mass, usually attached to a tendon sheath or connected with an underlying joint, located distal to the distal palmar crease. Reassure patient that most ganglia/ cysts resolve spontaneously. If condition is recurrent, painful or affecting function: refer to MSK CATS. Insidious wrist pain Patient presents with wrist pain and inflammation. Area will be hot and swollen with limited movement and usually marked functional loss. Blood tests are indicated: inflammatory markers for infection and urate levels for gout. If septic arthritis refer urgently to on-call orthopaedics. If RA refer to rheumatology. OA hand and wrist Patient presents with pain, swelling of wrist or hand joint. Advise patient on use of a wrist splint (if required), to use intermittently with advice to rest the hand, but to maintain gentle, functional movement. Advise on use of ice treatment. Review medications and consider prescription of Paracetamol, topical NSAIDS and Capsaicin. If ineffective, oral NSAIDS can be prescribed. Consider referral to social services for home assessment if required. Medical imaging / blood tests are not indicated. If no improvement after 4 weeks, injection therapy can be considered. If no response, (i.e. Symptomatic relief for over 2 months) to one injection, refer to MSK CATS. Trigger digit (Stenosing flexor tendinopathy) / Dequervain’s tendinopathy Local pain on use and palpation of the tendon(s) involved. Condition occurs due to degeneration and overuse. Advise relative rest from repetitive hand use / gripping activities and consider prescription of NSAIDS/ gel. Splinting and imaging are not advised. If no improvement after 4 weeks from onset consider steroid injection therapy. If no response, (i.e. Symptomatic relief for over 2 months) to one injection, or if patient requires more than 2 injections over time to manage condition: refer to hand surgeon. Author: rachel.lewis@rotherham.nhs.uk