Objectives

Midterm Study Guide 8
th
Grade Science
Blue Book Motions, Forces, and Energy
Chapter 1
Vocabulary
Motion
Reference Point
International System of Units
Meter
Speed
Average Speed
Instantaneous Speed
Velocity
Rise
Run
Slope
Plate
Plate Tectonics
Acceleration
Deceleration
Circular Motion
Initial Speed
Final Speed
Objectives
Determine when an object is in motion
Calculate an objects speed and velocity
Demonstrate how to graph motion
Describe how the theory of plate tectonics explains the movement of earth’s landmasses
Calculate the speed at which earths plates move
Describe the motion of an object as it accelerates
Calculate acceleration
Describe what graphs are used to analyze the motion of an accelerating object
1
Chapter 2
Vocabulary
Force
Newton
Net force
Unbalanced forces
Balanced forces
Friction
Static Friction
Sliding Friction
Fluid Friction
Gravity
Mass
Weight
Free Fall
Air Resistance
Terminal Velocity
Inertia
Momentum
Law of conservation of momentum
Satellite
Centripetal force
Objectives
Describe what a force is
Explain how balanced and unbalanced forces are related to an objects motion
Describe friction and identify factors that determine the friction forces between two objects
Identify the factors that affect the gravitational force between two objects
Explain why objects accelerate during free fall
State Newtons first law of motion
State Newtons second law of motion
State Newtons third law of motion
Explain how an objects momentum is determined
State the law of conservation of motion
Explain how a rocket lifts off the ground
Describe the forces that keep a satellite in motion
2
Chapter 3
Vocabulary
Force
Area
Pressure
Pascal
Fluid
Barometer
Buoyant force
Archimedes principle
Density
Pascal’s principle
Hydraulic system
Bernoulli’s principle
Lift
Objectives
Explain what pressure depends on
Explain how fluids exert pressure
Describe how fluid pressure changes with elevation and depth
Describe the effect of the buoyant force
Explain how the density of an object determines whether it sinks or floats
State Pascal’s principles and recognize its applications
Explain how a hydraulic system multiplies force
Use Bernoulli’s principle to explain how fluid pressure is related to the motion of the fluid
List some application of Bernoulli’s principle
3
Chapter 4
Vocabulary
Work
Joule
Power
Machine
Input force
Output force
Input work
Output work
Mechanical advantage
Efficiency
Inclined plane
Wedge
Screw
Lever
Fulcrum
Wheel and axle
Pulley
Compound machine
Objectives
Identify when work is done on an object
Calculate the work done on an object
Explain how machines make work easier
Calculate the mechanical advantage of a machine
Calculate the efficiency of a machine
Describe the 6 kinds of simple machines and their uses
Calculate the ideal mechanical advantage of each type of simple machine
Describe compound machines
4
Chapter 5
Vocabulary
Energy
Kinetic energy
Potential energy
Gravitational potential energy
Elastic potential energy
Mechanical energy
Thermal energy
Electrical energy
Chemical energy
Nuclear energy
Electromagnetic energy
Energy transformation
Law of conservation of energy
Matter
Fossil fuel
Combustion
Objectives
Describe how energy, work and power are related
Name and describe the two basic kinds of energy
Explain how an objects mechanical energy is determined
Name some forms of energy associated with the particles that make up objects
Describe how different forms of energy are related
Name common energy transformations
State the law of conservation of energy
Identify the source of the energy stored in fossil fuels
Describe how energy is transformed when fossil fuels are used
5
Chapter 6
Vocabulary
Temperature
Fahrenheit scale
Celsius scale
Kelvin scale
Absolute zero
Heat
Specific heat
Conductor
Convection
Convection current
Radiation
Conductor
Insulator
State
Change of state
Melting
Freezing
Evaporation
Boiling
Condensation
Thermal expansion
Heat engine
External combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
Refrigerant
Objectives
Name the three common temperature scale
Describe how thermal energy is related to temperature and heat
Explain the significance of a high specific heat
Describe the three forms of heat transfer
Identify the direction in which heat moves
Describe the differences between conductors and insulators
Name the 3 states of matter
Identify the causes of changes of state
6
Describe what happens to a substance as its thermal energy increase
Describe how heat engines use thermal energy
Describe how refrigerators keep things cold
Formulas
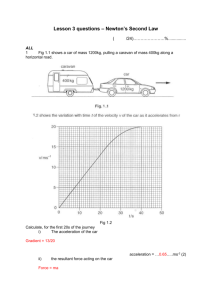
Speed=distance/time
Velocity=distance/time in a given direction
Acceleration=final velocity-starting velocity/time
Density=mass/volume
Momentum=mass X velocity
Work=force X distance
Power=work/time
Acceleration=force/mass (Newtons second law)
9.8m/s/s is rate at which objects accelerate to earth
Mass=density X volume
Volume=mass /density
Area=length x width
Volume of a cube= length X width X height
Mechanical advantage of the 6 simple machines
7
Green Book Cells and Heredity
Chapter 1
Vocabulary
Cell
Microscope
Cell theory
Organelle
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosome
Golgi body
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Lysosome
Element
Compound
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
Amino acid
Enzyme
Nucleic acid
DNA
RNA
Selective permeability
Diffusion
Osmosis
Passive transport
Active transport
8
Objectives
Tell what cells are
Explain how the invention of the microscope contributed to scientist understanding of living things
State the cell theory
Describe how microscopes produce magnified images
Identify the role of the cell wall and the cell membrane in the cell
Describe the functions of the cell organelles
Explain how cells are organized in many –celled organisms
Tell how bacterial cells differ from plant and animal cells
Define element and compounds
Identify the four main kinds of organic compounds in living things
Explain how water is important to the function of cells
Describe how most small molecules cross the cell membrane
Explain why osmosis is important to cells
Tell the difference between passive transport and active transport
9