CLASS COPY – Please do NOT write on this paper. Return this
advertisement

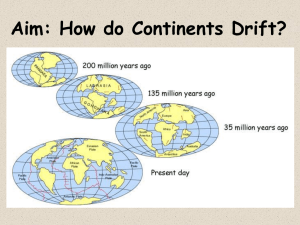
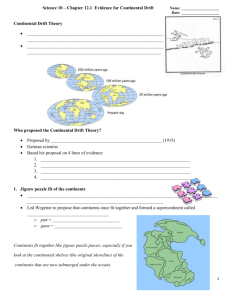
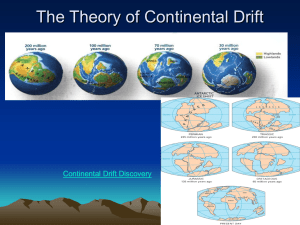
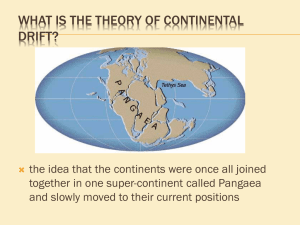
CLASS COPY – Please do NOT write on this paper. Return this sheet at the end of the class period. READING 5: Digging Deeper: Development of the Plate Tectonics Theory [ EarthComm Book pages G110-68-G72 ] Directions: Read the tasks presented below for each section of the article. This will give you a reason for your reading. Then read the corresponding section of the article in your textbook. Record your responses in your science notebook, being sure to include a title, date, and any other information you need to make a helpful entry. Remember – you will be allowed to use your science notebook on the unit test. Development of the Plate Tectonics Theory 1. Edward Suess explained the Earth’s origins in the 1800s. a. According to him, how were the mountains formed? b. According to him, how can you explain the same fossils on separate continents? c. How were land bridges supposedly formed and lost? 2. Alfred Wegener challenged the ideas of the contraction theory in his hypothesis of continental drift. a. What was the observation of the Alps he used as evidence? b. What effect did the discovery of radioactive heat have on supporting or disproving his theory? 3. What was Wegener’s evidence for the supercontinent of Pangea? 4. After World War II as scientists mapped the ocean floor they originally found evidence to support continental drift, but eventually it led to the theory of plate tectonics. What was the big difference between the two? 5. To identify continents before Pangea we have to look at old continental crust. a. What do the Urals and Appalachians show? b. What do rocks and fossils show? c. What is the Wilson cycle? Paleomagnetism 6. What is believed to cause the Earth’s magnetic field? 7. Why are there no longitude lines on the map of Pangea? CLASS COPY – Please do NOT write on this paper. Return this sheet at the end of the class period. Development of the Plate Tectonics Theory 8. Edward Suess explained the Earth’s origins in the 1800s. a. According to him, how were the mountains formed? As the Earth cooled and shriveled ridges formed like a dried apple b. According to him, how can you explain the same fossils on separate continents? Land bridges allowed migration, but they have since sunk. c. How were land bridges supposedly formed and lost? They rise and fall as the Earth cools and shrinks 9. Alfred Wegener challenged the ideas of the contraction theory in his hypothesis of continental drift. a. What was the observation of the Alps he used as evidence? The layers of rock are folded like in a collision. b. What effect did the discovery of radioactive heat have on supporting or disproving his theory? The radioactive heat shows the Earth isn’t really cooling, but rather the surface is subject to convection from below. 10. What was Wegener’s evidence for the supercontinent of Pangea? Fossils, matching rocks and minerals, cuts in mountain ranges such as the Appalachians. 11. After World War II as scientists mapped the ocean floor they originally found evidence to support continental drift, but eventually it led to the theory of plate tectonics. What was the big difference between the two? In PT the sea floor spreads and subducts, where in the drift theory the continents randomly plow their way through the crust. 12. To identify continents before Pangea we have to look at old continental crust. a. What do the Urals and Appalachians show? Old compression line b. What do rocks and fossils show? Old matchups c. What is the Wilson cycle? Cycle of forming and reforming super-continents Paleomagnetism 13. What is believed to cause the Earth’s magnetic field? Outer core flowing over the inner core 14. Why are there no longitude lines on the map of Pangea? Evidence shows latitude of past fossils but not their longitude CLASS COPY – Please do NOT write on this paper. Return this sheet at the end of the class period. Contraction Who proposed it? Describe continental movement Explain the same fossils on different continents Explain Mountain folds Seuss None horizontally Land bridges allowed migration but have long since sunk to the ocean floor Contraction of the cooling surface like an apple drying Rise and fall vertically as the Earth cools Continental Drift Wegener Continents plow through ocean basins Continents were together in Pangea Continents collide and bend the rock layers Plate Tectonics Everyone Sea floor spreading and subduction, propelled by convection Continents were together in Pangea Continents collide and bend the rock layers CLASS COPY – Please do NOT write on this paper. Return this sheet at the end of the class period. Contraction Who proposed it? Describe continental movement Explain the same fossils on different continents Explain Mountain folds Seuss None horizontally Land bridges allowed migration but have long since sunk to the ocean floor Contraction of the cooling surface like an apple drying Rise and fall vertically as the Earth cools Continental Drift Wegener Continents plow through ocean basins Continents were together in Pangea Continents collide and bend the rock layers Plate Tectonics Everyone Sea floor spreading and subduction, propelled by convection Continents were together in Pangea Continents collide and bend the rock layers