Mix & Flow
advertisement

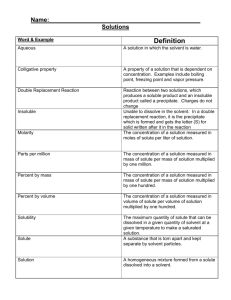
PURE ___COMPOUND____ -Made up of two or More elements in a Fixed Definite Ratio. 1 2 3 4 ___ELEMENT_____ -Made up of one type of atom ex: _OXYGEN GOLD__ MIXTURE TYPE-DEFINITION __MECHANICAL MIXTURE__: can see the different parts _____SOLUTION___: two or more particles but looks like one-clear _________SUSPENSION___:two or more particles the larger one will settle out with time _____COLLOID_____: two or more particles do not settle out—cloudy-tyndal effect EXAMPLE(S) 5 POINTS OF THE PARTICLE THEORY Particle model of Matter) 1 All matter is made up of __ATOMS (PARTICLES)____________ 2 Same particles are found in the same SUBSTANCE__ 3 Particles are _ATTRACTED________ to each other (_STRONGER _______ attraction between particles in a ______SOLID_ state) 4 There are __SPACES____ between particles (_LARGER____ spaces between particles of a _____GAS____________ state) 5 Particles are always ___MOVING___________ (particles move the fastest in a __GAS___________ state) FACTORS AFFECTING SOLUBILITY ARE TYPE OF SOLUTE TYPE OF SOLVENT (WATER, OIL, ALCOHOL) TEMPERATURE PARTICLE THEORY WHY DIFFERENT TYPES OF SOLUTE HAVE DIFFERENT ATTRACTION FORCES TO THE SOLVENT DIFFERENT TYPES OF SOLVENTS HAVE DIFFERENT ATTRACTION FORCES TO THE SOLUTES AS YOU INCREASE TEMPERATURE THE PARTICLES OF THE SOLVENT MOVE FURTHER APART LEAVING MORE ROOM FOR SOLUTE How to Increase Rate of Dissolving INCREASING TEMPERATURE OF SOLUTION STIRRING THE SOLUTION SMALLER PIECES PARTICLE THEORY WHY AS YOU INCREASE THE TEMPERATURE THE PARTICLES START TO MOVE FASTER BUMPING INTO THE SOLUTE PARTICLES FASTER TO DISSOLVE THE SOLUTE SAME AS ABOVE BUT AS YOU STIR THE PARTICLES MOVE FASTER… AS YOU CRUSH THE SOLUTE THE PIECES ARE SMALLER-MORE SURFACE AREA ALLOWING THE SOLUTE TO ATTRACT TO THE SOLVENT PARTICLES FASTER LEARNING OUTCOME #2 STUDY GUIDE: VARIABLES OF A LAB: manipulated, responding, controlled PARTICLE MODEL (5 points used to explain) MATTER CLASSIFIED AS MIXTURES: made up of __2____ or more types of ___MATTER_____ (know examples) Mechanical mixtures: Colloids: Suspensions: Solutions: MATTER CLASSIFIED AS PURE: (know examples used in class) Elements: Compounds MIXTURES CLASSIFIED AS: Heterogeneous mixtures: (_MECHANICAL MIXTURES_, _COLLOIDS_, ___SUSPENSIONS__) Homogeneous mixtures: look like __1______ ( _____SOLUTION_________) PARTS OF A SOLUTION: Solute: Solvent: Soluble vs. insoluble TERMS TO DESCRIBE A SOLUTION Dilute vs. Concentrated solutions Unsaturated vs. Saturated solutions Saturation point Written Concentration of a solution Solubility THREE FACTORS AFFECTING SOLUBILITY OF A SOLUTION (particle theory tod explain) 1. 2. 3. THREE FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF DISSOLVING (particle theory to explain) 1. 2. 3. READING and EXPLAINING SOLUBILTY GRAPHS Classify the following examples into the appropriate category. Milk, mud puddle, pop, clean air, granola cereal, cloud, salt water, pizza, hair gel, tea, coffee, tomato juice, smog, tap water, sandwich, peanut butter, gold jewelry, apple juice Mechanical GRANOLA PIZZA SANDWICH MIXTURES Colloid Suspension MILK HAIR GEL MUD PUDDLE, PEANUT BUTTER TOMATO JUICE, CLOUD SMOG Solution POP, CLEAN AIR, SALT WATER, TEA, COFFEE, TAP WATER, GOLD JEWELRY, APPLE JUICE Name the categories below for mixtures and classify the above examples into the following two categories. _HOMOGENEOUS______is a mixture where the components that make up the mixture are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture. Appears to look like one substance. Ex: POP, CLEAN AIR, SALT WATER, TEA, COFFEE, TAP WATER, GOLD JEWELRY, APPLE JUICE ___HETEROGENEOUS__:is a mixture where the components of the mixture are not uniform or have localized regions with different properties. Ex: GRANOLA PIZZA SANDWICH GRANOLA PIZZA SANDWICH MUD PUDDLE, TOMATO JUICE, SMOG Classify the following examples into the appropriate category. Oxygen, sugar, salt, baking soda, hydrogen, neon, gold, distilled water (H2O) PURE MATTER Elements Compounds OXYGEN HYDREGEN NEON GOLD SUGAR, SALT, BAKING SODA, DISTILLED WATER What is the difference between soluble and insoluble? Solution SOLUTE SOLVENT Does the dissolving To make a glass of lemonade you dissolved sugar and lemon juice into water. The solute(s) is/are __SUGAR, LEMON JUICE__ and the solvent(s) is/are _WATER____ Is dissolved A dilute solution has _______LITTLE__ solute dissolved into the _SOLVENT____ A concentrated solution has __LOTS_____ of __SOLUTE_______ dissolved into the __SOLVENT_______ A solution that can still dissolve more solute is called an __UNSATURATED_____ solution. A solution that cannot dissolve anymore solute is called a _____SATURATED________ solution. If you write the amount of solute dissolved into a certain amount of solvent you would have written the ____CONCNETRATION__________________ of the solution. If 33g of solute is dissolved into 50g of water what is the concentration of the solution? _____33g/50g OF WATER___________________ What is meant by the solubility of a solution?__ THE MAXIMUN AMOUNT OF SOLUTE THAT CAN DISSOLVE IN A CERTAIN AMOUNT OF SOLVENT AT A CERTAIN TEMPERATURE TO MAKE A SATURATED SOLUTION ___________________________________________ Sam had 135mL of water in which he put 23g of sugar and then heated it to 37˚C. What is the solubility of Sam’s solution? ___23g/135Ml @ 37 ˚C ______________ Convert Sam’s solution and compare to Sally’s solution of 17.1g/100mL @ 37˚C. 23 = X 135 100 135X = 23X100 135X = 2300 135X = 2300 135 135 X = 17.0g/100mL @ 37 ˚C Which substance is more soluble at 60˚C? KNO3 What is the solubility of NaCl at 0˚C? GAS If you had 100g of each solute at 80˚C which substance would be saturated? NaCl How much solute of KNO3 is needed to make a saturated solution at 0˚C? 18g Draw what the solubility of the gas CO2 on the graph. What is the connection to thermal pollution? AS TEMPERATURE INCREASES THE SOLUBILITY OF GASES DECREASES LEAVING LESS DISSOLVED OXYGEN IN THE WATER FOR FISHFISH WILL LEAVE AREA OR DIE OUT. Sam heard that water was called the _UNIVERSAL____ solvent, because he was told that it dissolves many types of solute. To test this statement he took six different solutes and tried to dissolve them into 100mL of water. He then did the same but used vegetable oil and alcohol as the solvent. The manipulated variable in this lab was ___SOLVENT TYPE__________________ The responding variable in this lab was _AMOUNT OF SOLUTE DISSOLVED_______ List two controlled variables Sam should have used _100mL of SOLVENT, TYPE OF SOLUTES, TEMPERATURE OF SOLVENT _____