Mechanical Energy Conservation Worksheet
advertisement

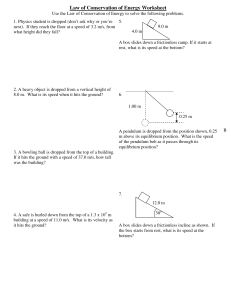
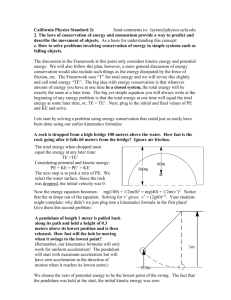
6.3/6.4 – Mechanical Energy and the Law of the Conservation of Energy 1. A heavy object is dropped and reaches the floor at a speed of 3.2 m/s. From what height was it dropped? 2. A heavy object is dropped from a vertical height of 8.0 m above the ground. What is the speed of this object as it hits the ground? 3. A heavy object is dropped from the top of a building. If this object hits the ground with a speed of 37.0 m/s, how tall was the building? 4. A heavy object is thrown vertically down from the top of a 1.3 × 102 m building at a speed of 11.0 m/s. What is its velocity as it hits the ground? 5. A heavy box slides down a frictionless incline as shown in the diagram. If the box starts from rest at the top of the incline, what is its speed at the bottom? 6. A heavy box slides down a frictionless incline 12.0 m as shown in the diagram. If the box starts from rest at the top of the incline, what is its speed at the bottom? Incline is 30o from horizontal. 7. A roller coaster car starts from rest at point A. What is the speed of this car at point B if the track is frictionless? 8. A roller coaster car starts from rest at point A. What is the speed of this car at point C if the track is frictionless? 9. A student is running at a speed of 3.5 m/s and grabs a long rope that is hanging vertically from a tree. How high can the student swing? 10. A pendulum is 1.20 m long. What is the speed of the pendulum bob when it passes through its equilibrium position if it is pulled aside until it makes a 25.0° angle to the vertical? (HINT: Is it possible to determine the vertical drop of the pendulum bob and then use the law of conservation of mechanical energy?) 11. A pendulum is dropped from a position 0.25 m above the equilibrium position as shown in the diagram. What is the speed of the pendulum bob as it passes through the equilibrium position? 12. A 2.5 kg object is dropped from a height of 10.0 m above the ground. Calculate the speed of the object as it hits the ground. 13. An archer exerts an average horizontal force of 12 N on his bow-arrow system by pulling the string back 0.30 m. If the arrow has a mass of 0.45 kg, and at the target is 5.0 m away, what is the horizontal speed of the arrow as it hits the target? 14. A 1.0 kg box slides without friction around the loop-the-loop apparatus as shown in the diagram. If the object starts from rest at point A, and the radius of the loop is 0.75 m, what is the speed of the box at point B? 15. A 0.20 kg mass vibrates at the end of a horizontal spring (k = 0.800 N/m) along a frictionless surface. The kinetic energy at the equilibrium position is 3.00 × 10-3 J. a) What is the speed of the object at the equilibrium position? b) The formula for elastic potential energy is Ep 12 kx2 (k = spring constant, x = displacement). What is the maxima displacement? c) What is the total mechanical energy when the mass is halfway between the end position and the equilibrium position? 16. A 0.40 kg pendulum bob is swinging back and forth in simple harmonic motion as shown in the diagram. When the pendulum bob is at position A, its gravitational potential energy is 0.20 J relative to position B. a) What is the vertical displacement, h, as described in the diagram? b) What is the kinetic of the bob at position B? c) What is the mechanical energy of the bob when it is halfway between B and C? d) What is the speed of the bob at position B? 17. The following chart is taken from observations of a pendulum at different positions. Solutions: 1. –0.52 m 2. 13 m/s 3. –69.8 m 4. 52m/s 5. 8.9m/s 6. 10.8 m/s 7. 7.7 m/s 8. 13 m/s 9. 0.62m 10. 1.49 m/s 11. 2.2 m/s 12. 14 m/s 13. 4.0 m/s 14. 6.3 m/s 15. a) 0.173 m/s b) 8.66 × 10–2 m c) 3.00 × 10-3 J. 16. a) 5.1 × 10-2 m b) 0.20 J c) 0.20 J d) 1.0 m/s 17. 1) 0 J, 0.736 J, 0.736 J 2) 0.245 J, 0.492 J, 0.736 J 3) 0.491 J, 0.245 J, 0.736 J