An overview:
advertisement

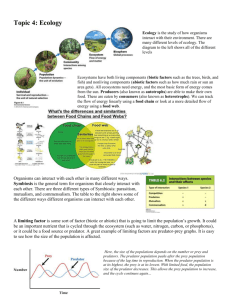
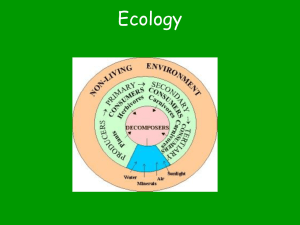
TEST -All of Ch. 7 and 8 (Unit 4) from our new textbook and small nuggets from chapter 1 and 2 (Unit 1). -Specific Heat Capacity -Humidity Pg. 20, 50, 51, 58 read but don’t do Here is an over view of MOST of the concepts we covered. Crossed out are concepts we did not focus on. Other concepts from Ch 7 and 8 maybe also be important. An overview: 1. You will have to know the meaning of the following ecology terms and provide examples for each. a. ecosystem b. producers c. primary consumers d. secondary consumers e. tertiary consumers f. trophic levels g. detritivores h. decomposers i. pyramid of numbers j. biomass k. pyramid of biomass l. pyramis of energy flow m. carrying capacity n. competition intra/inter specific o. population density p. biotic factors q. abiotic factors r. eutrophication s. keystone species 2. You must be able to draw food chains and food webs. 3. You must know the formula and process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 4. You must be able to explain the carbon cycle and the nitrogen cycle. You must be able to describe all the different steps of the nitrogen cycle. You must be able to explain the influence of humans on those cycles. Questions to work on: 1. Matching definitions a. Ecosystem b. Carrying capacity c. Productivity d. Biological magnification e. Biotic f. A biotic g. Eutrophication h. Biodiversity i. Sustainability j. Succession k. Pioneer organisms l. Primary succession m. Climax community 1. Non-living part of the environment 2. Variety of living organisms that inhabit Earth 3. The accumulation of toxic substances in the bodies of organisms 4. Living part of the environment 5. Maximum number of organisms in a population that can survive 6. Measure of an individual's or a population's impact on the environment 7. The buildup of nutrients in an aquatic ecosystem 8. All the interactive parts of a biological community and its environment 9. The replacement of existing species by more recently arriving species 10. Ability to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs 11. Lichen 12. Amount of p1ant growth in a given area within a given period of time 13. Destruction of a shared resource by individual greed 14. Last stage of succession in which communities of organisms are most complex 15. Begins in an area of bare rock 2. Explain how the following factors can affect the size of a population: a. Intra specific competition and inter specific competition b. Density dependent and density independent factors 3. Why can't a population of organisms grow indefinitely? Why have the levels of carbon dioxide steadily increased since the mid-ninetieth century? How is acid precipitation produced? Why is it bad to clear a tropical rainforest for agriculture? 4. a. Why is nitrogen important for living organisms? b. Describe the three main forms into which we can find nitrogen in the nitrogen cycle. c. Why are bacteria important in tile nitrogen cycle? d. How do the following organisms obtain the nitrogen necessary for them: producers and consumers? e. Describe the three main phases of the nitrogen cycle. f. Describe two effects of the imbalance between the amount of nitrogen produced and the amount used. 5. In the following population of an ecosystem, form three food chains: (Clover, lizard, falcon, worm bacteria grasshopper, snake, mouse, ant, mushroom, rabbit, centipede, mole, robin, butterfly., and crow) 6. From the above population, divide the organisms into the following columns: producers Herbivores primary consumer carnivores secondary consumer decomposers top carnivore detritivore 7. Use DDT as an example to demonstrate the process of bioaccumulation. Explain how organisms far from the original source of DDT can become toxic. Explain what the relationship between the concentration of DDT and the position of the organism in the pyramid is. Discuss two, possible reasons why the crops sprayed with DDT for several years found that the populations of insect pests rebounded. 8. a. Show the relationships between the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. b. Why must there always be a supply of radiant energy to the ecosystems? 9. a. Draw a pattern for the three types of pyramids studied in class. b. Indicate what they represent. c. Show which ones can be inverted. d. Indicate how the position of an organism in the pyramid may determine its mass and population size. 10. Draw a sketch of the carbon cycle. Include four uses of CO2 and four sources of CO2. Show how it is a closed system. Describe two effects of the imbalance between the amount of carbon produced and the amount used. 11. Why is it more effective for humans to consume vegetable products than animal products?