Here
advertisement

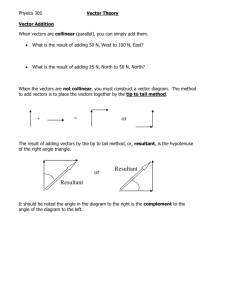
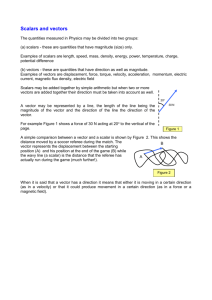
Chapter I: VECTORS IN R2 Mon Wed Thu Feb13 Feb15 Feb16 Feb20 Feb22 Feb23 Feb27 Mar01 Mar02 Mar06 Mar08 Mar09 1.1. Vectors in R2: Basic definitions. The vector and the scalar. Algebra of vectors. Properties of vectors. The magnitude of a vector and its properties. The unit vector in the direction of another vector. 1.2. The Dot Product: Definition and properties of the dot product. 1.3. The Projection of a Vector upon another: 1.4. The Angle between Two Vectors: Basic definitions and conventions. Finding the angle between two vectors. Orthogonal vectors. 1.5. Geometric Representation: The triangle (parallelogram) law. Chapter II: VECTORS IN R3 2.1. R3: The three dimensional coordinate system. The right- hand coordinate system and coordinate axes. The coordinate planes. The ordered triple. The coordinate of a point in R3. The coordinates of points in the coordinate planes and the coordinates of points on the axes. Te projection of a point into a coordinate plane. The distance between two points. The equation of a sphere. The midpoint on a line segment in R3. 2.2. Comparing R, R2 and R3: Points and sets in the three systems. The interpretations of equations and inequalities in the three systems. The concepts of a region and a surface. 2.3. Vectors in R3: 2.3.1. Vectors in R3: Basic definitions. The vector and the scalar. Algebra of vectors. Properties of vectors. The magnitude of a vector and its properties. The unit vector in 1 the direction of a given vector. Mar13 Mar15 Mar16 Mar20 Mar22 Exam1 Mar23 2.3.2. The Dot Product: Definition and properties of the dot product. 2.3.3. The Projection of a Vector upon another 2.3.4. The Angle between Two Vectors: Basic definitions and conventions. Finding the angle between two vectors. Orthogonal vectors. 2.4. Direction Numbers: The set of direction angles and the set of direction cosines for a vector. Sets of direction numbers for a vector. 2.5. Straight Lines In R3: The two sets of direction angles and the two sets of direction cosines for a straight line. Sets of direction numbers for a straight line. Parallel and perpendicular lines. Parametric representations for a straight line. Symmetric equations for a straight line. 2.6. Cross Product: Properties of the cross product. 2.7. The Plane: The general equation of the plane. Parallel and perpendicular planes. A normal to a plane. 2.8. Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates: Cylindrical and spherical representations of a point. Transforming equations from rectangular coordinates to cylindrical and spherical coordinate and visa versa. First Examination: Mar 22 2 Mar27 Mar29 Mar30 Apr03 Apr05 Apr06 Apr10 Apr12 Apr13 Apr17 Apr19 Apr20 Apr24 Apr26 Apr27 May01 May03 Exam2 May04 Chapter IV: FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 4.1.1. Basic Concepts: The domain of a function of two variables. Algebra of functions of two variables. 4.1.2. Level Curves 4.2. Limit of a Function of Two Variables: Equivalent definitions of a function of two variables. Algebra of limits. 4.3. Continuity of a Function of Two Variables: The domain of a function of two variables. Algebra of functions of several variables. 4.4. Partial Derivatives: Rules for partial differentiation. Clairout’s Theorem. Geometric Interpretation. 4.5. The Differential: Differentiability of a function of two variables. 4.6. The Chain Rule 4.7. Directional Derivatives: The gradient. The directional derivative. 4.8. Tangent Planes 4.9. Extrema: Local maximum and minimum. Absolute extremun. Boundary extremum. Test for local extrema. 4.10. Constrained Extrema: Lagrange’s theorem. Lagrange’s multipliers and theorem for a function constrained by more than one condition. Second Examination: May 3 3 May08 May10 May11 May15 May17 May18 Chapter V: MULTIPLE INTEGRALS 5.1. Iterated Integrals 5.2. Double Integral: Definition and properties of double integral. Using symmetry to evaluate some double integrals. 5.3. Double integral in Polar Coordinates 5.4. Triple Integral: Definition and properties of triple integral. 5.5. Triple integral in Cylindrical Coordinates 5.6. Triple integral in Spherical Coordinates 4 Page 5 Evaluation First Examination: 17% Second Examination: 17% Quizzes: 10% Final Examination: 40% Project: 10% Assignments 06% Office Hours Sunday & Wednesday: Lecture 4 : 11.00 - 12.00 5