Carbon Cycle Worksheet
advertisement

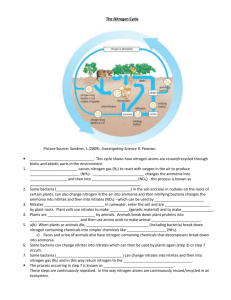
1. What inorganic molecule is carbon normally found in? CO2 2. Name an organic molecule that carbon is found in. GLUCOSE, CARBOHYDRATES, LIPIDS, PROTEINS, DNA Name _________________________ Carbon Cycle Worksheet 3. What molecule do trees get their carbon from? CO2 4. Where do primary consumers get their carbon from? EATING PLANTS 5. What process adds carbon to the atmosphere? CELLULAR RESPIRATION 6. What process removes carbon from the atmosphere? PHOTOSYNTHESIS 7. How does oxygen get into the water? PHOTOSYNTHESIS MOVEMENT OF WATER 8. What do producers produce? GLUCOSE (CARBOHYDRATES) 9. List 3 groups of producers? PLANTS ALGAE SOME BACTERIA 10. What group eats producers? PRIMARY CONSUMERS 11. How does carbon get back into the atmosphere from the food we eat? CELLULAR RESPRATION 12. Where do secondary consumers get their carbon from? PRIMARY CONSUMERS 13. Where does an animal’s or plant’s carbon go when it dies? GROUND 14. Why should the amount of carbon in the atmosphere stay the same? PHOTSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION SHOULD BALANCE EACH OTHER OUT. 15. How is extra carbon getting into the atmosphere today? BURNING FOSSIL FUELS 16. List 3 ways that we could reduce the extra carbon that is getting into the atmosphere. 1. PLANT TREES 2. USE LESS FOSSIL FUELS 3. REMOVE CO2 FROM EMISSIONS 4. CONSERVE ELECTRICITY 5. ELECTRIC CARS In the space below, draw your own version of the carbon cycle. Use arrows to show which way the carbon is going. Label: Producers Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers 1. Why do plants and animals and animals need nitrogen (N)? TO BUILD PROTEIN MOLECULES 2. What molecule in the atmosphere is nitrogen normally found in? Name _________________________ N2 3. What molecule in the ground is nitrogen found when there is no oxygen around? NH3 4. What molecule in the ground is nitrogen found when there is oxygen around? NO3 5. What organic molecule is nitrogen found in? AMINO ACIDS, PROTEINS 6. What are 2 ways that atmospheric nitrogen gets into the ground? NITROGENFIXING BACTERIA LIGHTNING 7. What organisms (living things) do the nitrogen fixation for plants? BACTERIA 8. Why don’t farmers have to put nitrogen fertilizer on soybeans? SOYBEANS ARE LEGUMES; HAVE NITROGEN-FIXING BACTERIA 9. Where do plants get their nitrogen from? THE GROUND (NO3) 10. How do primary consumers get their nitrogen from? EATING PLANT PROTEIN 11. How do secondary consumers get their nitrogen from? EATING ANIMAL PROTEIN 12. What’s another term for a primary consumer? HERBIVORE 13. What’s another term for a secondary consumer? CARNIVORE 14. Where does an animal’s or plant’s nitrogen go when it dies? GROUND AFTER BACTERIA DECOMPOSE THE ORGANISM 15. Who breaks the dead organisms’ body back into inorganic nitrogen? BACTERIA 16. How is extra nitrogen getting into the Bay ecosystem? BURNING FOSSIL FUELS FERTILIZER SEWAGE (ANIMAL OR HUMAN WASTE) DECAY 17. Why is extra Nitrogen (N) in the Chesapeake Bay a problem? 1. EXTRA N CAUSES ALGAE BLOOMS. 2. ALGAE BLOCKS SUNLIGHT FOR SAV PHOTOSYYNTHESIS 3. WHEN ALGAE DIE, BACTERIA USE UP OXYGEN BREAKING IT DOWN (EUTROPHICATION) Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet N In the space below, draw your own version of the nitrogen cycle. Use arrows to show which way the carbon is going. Label: Producers (Plants) Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Decomposers