Plants
advertisement

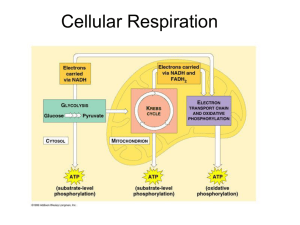
Ch. 9 Answers: Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Review Sheet 1. Write the chemical equation for cellular respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O 6CO2 + 12H2O + 40ATP’S GLUCOSE OXYGEN WATER CARBON DIOXIDE WATER ENERGY 2. Identify the reactants needed for cellular respiration. GLUCOSE, OXYGEN, WATER 3. Identify the products of cellular respiration. CARBON DIOXIDE, WATER, 40 ATP 4. What group of special protein molecules catalyzes the reactions that take place during cellular respiration? ENZYMES 5. Where in the cell does cellular respiration occur? Name the organelle. MITOCHONDRIA 6. Label the parts of the mitochondria. outer membrane, inner membrane, cristae (folds on the inner membrane), fluid matrix 7. Where do we get glucose from? FOODS WE EAT 8. What gas combines with glucose in order for glucose to break down? Hint: We breathe this gas in. OXYGEN 9. Where does the pyruvic acid formed in glycolysis come from? THE SPLITTING OF GLUCOSE 10. What type of organisms carry out glycolysis? ALL ORGANISMS (BACTERIA/PROKARYOTES, PROTISTS, FUNGI, PLANTS, ANIMALS) 11. What type of organisms carry out cellular respiration? FUNGI, PROTISTS, PLANTS, ANIMALS (ALL HAVE MITOCHONDRIA) 12. Are these organisms in #11 prokaryotes or eukaryotes? EUKARYOTES 13. What does cellular respiration produce for our cells? ENERGY/40 ATP’S 14. Where is the energy in glucose stored? IN THE CHEMICAL BONDS OF THE GLUCOSE MOLECULE 15. What do humans & animals do with the CO2 produced when glucose breaks down? EXHALE IT 16. What do plants do with the CO2 produced during cellular respiration? RECYCLE IT TO PHOTOSYNTHESIS (CHLOROPLAST) 17. What do we do with the H2O produced when glucose breaks down? RELEASE IT (PERSPIRATION, EXHALE, URINATE) OR RE-USE TO REHYDRATE CELLS 18. What do plants do with the H2O they produce during cellular respiration? RECYCLE TO PHOTOSYNTHESIS (CHLOROPLAST) OR RELEASE TO AIR BY TRANSPIRATION 19. How many ATP’s of energy are produced from one molecule of glucose? 40 20. Name 5 ways we use this energy. BREATHING, WALKING, RUNNING, DIGESTING FOOD, PUMPING BLOOD, ALL BODY MOVEMENTS, AND FOR ALL CELL ACTIVITIES/CHEMICAL REACTIONS. 21. Name the 4 stages of cellular respiration. GLYCOLYSIS, CONVERSION OF PYRUVATE, KREBS’ CITRIC ACID CYCLE, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN PER 2 22. What does glycolysis mean? SPLITTING OF GLUCOSE 23. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? CYTOPLASM 24. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 2 PYRUVIC ACID MOLECULES (2 PYRUVATE) 25. Does glycolysis need/require O2? NO 26.Is glycolysis an anaerobic or aerobic process? ANAEROBIC 27. How many ATP’s does it take to begin glycolysis? 2ATP’S 28. Where do these ATP’s that start glycolysis come from? CYTOPLASM 29. How many total ATP’s (gross ATP production) are produced during glycolysis? 4ATP’S 30. Are the conversion of pyruvate, Kreb’s citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain aerobic or anaerobic processes? AEROBIC – NEEDS OXYGEN 31. Where does the conversion of pyruvate, Kreb’s citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain occur in the cell? MITOCHONDRIA 32. What’s the function of the Electron Transport Chain? PRODUCES 34 ATPs & FORMS 12 WATER MOLECULES 33. Name the 2 hydrogen acceptor molecules involved in cellular respiration. NAD & FAD 34. Three ATP’s worth of energy is stored in the hydrogen acceptor. NADH2 35. Two ATP’s worth of energy is stored in the hydrogen acceptor. FADH2 36. How many ATP’s are produced in glycolysis? 4ATP’S 37. How many ATP’s are produced during the Kreb’s citric acid cycle? 2ATP’S 38. How many ATP’s are produced via the electron transport chain? 34 ATP’S 39. Name the 6 carbon molecule produced in the Krebs cycle. CITRIC ACID 40. What substance bonds with the de-energized hydrogen ions at the bottom of the electron transport chain? OXYGEN What is formed when these 2 molecules combine? WATER 41. What does fermentation mean? ANAEROBIC METABOLIC BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC MOLECULES. 42. Name the 2 types of fermentation. ALCOHOL FERMENTATION LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION 43. What organisms carry out alcohol fermentation? YEAST 44. Equation for alcohol fermentation. 2ATP 2NAD IN 2NAD OUT BACK TO GLYCOLYSIS GLUCOSE 2 PYRUVIC ACID 2 ETHYL ALCOHOL + 2CO2 OUT 4ATP 2NADH2 2NADH DROP OFF HYDROGEN 45. Does alcohol fermentation require oxygen? NO – ANAEROBIC PROCESS 46. Why does bread dough rise? CARBON DIOXIDE GAS RELEASED BY THE YEAST CELLS DURING ALCOHOL FERMENTATION 47. What happens to the alcohol in bread dough? EVAPORATES DURING THE BAKING/COOKING PROCESS 48. What organisms carry out lactic acid fermentation? HUMAN/ANIMAL MUSCLE CELLS 49. After we exercise strenuously our muscles are sore. Why? LACTIC ACID BUILDS UP IN THE MUSCLE CELLS. 50. Equation for lactic acid fermentation. 2ATP 2NAD IN 2NAD OUT BACK TO GLYCOLYSIS GLUCOSE 2 PYRUVIC ACID 2 LACTIC ACID OUT 4ATP 2NADH2 2NADH2 DROP OFF HYDROGEN 51. Does lactic acid fermentation require oxygen? NO – ANAEROBIC PROCESS 52. Does cellular respiration require oxygen? YES - AEROBIC PROCESS 53. How often does cellular respiration occur in our bodies? ALL THE TIME Table 2 – Answer the following questions in the appropriate box. Animals Plants How do these organisms obtain the oxygen they need for cellular respiration? How do these organisms get the glucose they need for cellular respiration? How do these organisms get the water they need for cellular respiration? What do these organisms do with the water made during cellular respiration? What do these organisms do with the carbon dioxide made during cellular respiration? What do these organisms do with the 40 ATPs made during cellular respiration? Breathe it in/ inhale from the air. From the air, it enters pores in the leaf called stomata; or recycle from photosynthesis From the foods they eat. Photosynthesis produces glucose. Drink it. Absorb water from soil thru roots. Reuse it in cytoplasm, blood plasma, tissue fluid; exhale some every time we breathe out or talk; excrete it as urine. Reuse some for photosynthesis, to form more cytoplasm, & in the water vacuole to maintain shape of cell; excess water leaves thru the stomata (transpiration). Exhale it. Recycle to photosynthesis Use for all cellular activities. Use for all cellular activities.