Geometry: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Unit Plan
advertisement

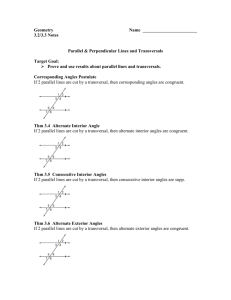
Geometry: Unit 3 – Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Unit Title: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Course: Geometry Grade Levels: 10, 11, 12 Time Frame: 15 fifty minute class periods Designer: Cheryl Maddox Link to State Standards MA1 - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division; other number sense, including numeration and estimation; and the application of these operations and concepts in the workplace and other situations MA2 - geometric and spatial sense involving measurement (including length, area, volume), trigonometry, and similarity and transformations of shapes MA4 - patterns and relationships within and among functions and algebraic, geometric and trigonometric concepts MA5 - mathematical systems (including real numbers, whole numbers, integers, fractions), geometry, and number theory (including primes, factors, multiples Link to MAP Benchmarks I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VIII. Problem Solving Communication Reasoning Connections Number Sense Geometric and Spatial Sense Patterns and Relationships Brief Summary of Unit Students will study the angles formed when two lines are cut by a transversal. Students will be introduced to several theorems and postulates related to parallel and perpendicular lines. What enduring understandings are desired? Students will understand that: Pictures are a useful tool to help set up algebraic expressions. Parallel and perpendicular lines are a fundamental part of our world. What essential questions will guide this unit and focus teaching? What are the relationships of the angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal? Can I find angle measures just by knowing certain properties? How will I ever use these ideas? What key knowledge and skills will students acquire as a result of this unit? Students will know: Key terms: parallel lines, perpendicular lines, skew lines, parallel planes, transversal, corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, same-side interior angles, converse The relationships between angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal The angle relationships necessary to show two lines are parallel Students will be able to: Determine whether lines are parallel, perpendicular or skew Use properties of angles to set up algebraic equations Identify corresponding angles, alternate interior and exterior angles, and same-side interior angles Find missing angle measurement by applying theorems and postulates Show two lines are parallel by applying theorems and postulates Performance Task After Unit 4 Other forms of assessment: What will be assessed? Mathematical understanding, reasoning, accuracy of work, and presentation of the solution will be assessed. How will evidence be collected? 20 point quizzes: Homework quizzes will be given one per week to assess understanding of homework 50 point quizzes: To test student's understanding of smaller portions of the unit. Test: A test will be given at the end of the unit. Assignments: The students will be given an assignment after each lesson. Other: Each student will be expected to keep a geometry notebook consisting of lesson notes, theorems, postulates, homework and corrections. What type of assessment will be used? Selected response Academic prompt Questions and Answer Constructed Response Observation Work Sample Description of the assessment 75% from 20 point quizzes, 50 point quizzes and unit test 25% from daily checks and homework scores By what criteria will the student responses be evaluated? Homework will be graded in class each day by stating answers out loud. Students will analyze their mistakes and make corrections. Homework quizzes will be graded on mathematical reasoning, accuracy and presentation of work. Unit Test will be graded on mathematical reasoning, accuracy and presentation of work. Notes, theorems and postulates will be checked periodically for completion and accuracy. Learning Experiences and Instruction Where is the unit going? Post essential questions Complete vocabulary terms to be used throughout the unit. Hook the student Begin discussion on where in the classroom and in their homes do we see parallel and perpendicular lines. Discuss jobs that involve parallel and perpendicular lines (physical therapist, bicycle designer, etc). Discuss the "How will you use these ideas" section at the beginning of chapter 3 Parallel lines are not seen in all types of geometry. Equip the student, explore the subject Explore the concepts of parallel and perpendicular lines and how they form angles with certain relationships by learning how to draw a 3-dimensional box. Use the box to discuss parallel, perpendicular and skew lines. Equip the students with the knowledge of properties, theorems and postulates involving parallel and perpendicular lines. Discover relationships among pairs of angles when two lines are cut by a transversal. Use notebook lines to form parallel lines and draw in a transversal. Use a protractor to measure and make conjectures about pairs of angles. Learn how to construct parallel and perpendicular lines using only a straight edge and a compass. Identify transformations using the graphing boards – specifically translations. Rethink and revise opportunities After each lesson, there will be an assignment that reinforces the concepts demonstrated in that lesson. In addition to completing the current assignment, the students are expected to correct the previous assignment hey evaluated that class period. At the end of the unit, students will reflect upon the essential question by way of a class discussion. Evaluate performance and progress The students will maintain a geometry notebook consisting of lesson notes, examples, theorems, postulates, assignments, corrections and vocabulary. Students will participate in a review game of Jeopardy before the unit test. Students will complete quizzes and a unit test over the material covered in unit 3.