(Heat Transfer) Study Guide
advertisement

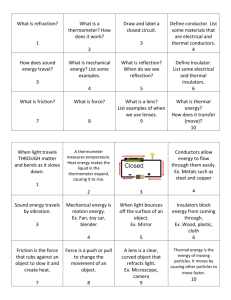
Science 5P3 Energy: Conservation & Transfer Study Guide Name: Date: Heat-the transfer of thermal energy from one piece of matter to another. Conduction- the transfer of thermal energy between things that are touching (particles of matter bumping into each other) Convection–the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of liquids or gases Hot air balloons, movement of boiling water, sea breeze and land breeze Land and Sea Breezes (High Pressure goes to Low Pressure) Low Pressure Air is warm and light because the warm land is heating up the air above it. High Pressure Air is cool and heavy because the cool water is cooling the air above it. When you are on the beach, during the day the sun heats the land and makes the air above it hot this air rises and pulls in air from the sea to replace it, this is a sea breeze. High Pressure Low Pressure Air is cool and heavy Air is warm and light because the cool land is because the warmer water is cooling the air above it. heating up the air above it. At night the land cools down and when it is colder than the sea (which remains almost the same temperature day and night) then hot air rises from the sea surface and it pulls in air form the land, this is a land breeze. Radiation-the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves bundles of energy that move through matter and through empty space (Sun rays, microwaves, rays from a fire, light rays from standing near a lamp) *Darker colors ABSORB more heat from radiation (why you feel hotter when you wear a black t-shirt on a sunny summer day) * White and light colors reflect (bounce off) sun’s rays so there is less absorption of radiation. –This is also why water takes longer to heat up because the ray’s are reflected off the water. Temperature-the measure of how warm something is a measure of the average energy of motion (kinetic energy) of the particles in matter Thermal Energy-the energy of the moving particles that make up all matter Electromagnetic energy-a form of energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic waves. Microwaves use electromagnetic waves. Transfer-movement of something from one location or condition to another Contract-to make smaller in size or number Solid-the state of matter that has a definite shape and takes up a definite amount of space Liquid-the state of matter that takes the shape of its container and takes up a definite amount of space. Gas-the state of matter that has no definite shape and takes up no definite amount of space A state of matter that has a fixed shape and volume such as ice. A state of matter that has a fixed volume but its shape changes to match the shape of its container such as water. A state of matter that does not have a fixed volume or shape such as water vapor. Heating-increasing the energy of an object, molecules move faster Cooling-reducing the energy of an object, molecules move slower *All objects have some thermal energy, colder objects just have less thermal energy. Freezing- process of changing from a liquid to a solid by removing heat energy. Water freezes at 32 °F or 0 °C Melting- process of changing a solid to a liquid. Ice melts at temperatures higher than 32 °F or higher than 0 °C. Boiling Point- temperature at which liquid changes to vapor. Water boils at 212 °F or 100 °C Environment- the natural surroundings of living things including biotic and abiotic factors (living and nonliving factors) Heat Exchange or Heat Transfer-the flow of heat from a warmer object to a cooler one. Additional Vocabulary Energy-the ability to make things move or change Potential energy – the energy an object has because of its place or its condition. Kinetic energy-the energy of motion or energy in use Insulator–a material that heat does not move through easily. (Styrofoam, Plastic) Conductor-a material through which heat can move easily. Eg: aluminum and stainless steel, copper. Ways in which heat energy is produced (made NOT transferred). Friction, Eg. Rubbing one’s hands together, rubbing a match against a rough surface. Combustion (burning) Eg campfire Pressure (pressing down) Eg Car sliding on an icy road Objects increase in size (expand) as they are heated and contract as they cool. The liquid or mercury in a thermometer is an example. As the temperature increases the mercury in the thermometer expands and “rises” up the thermometer. Another example: your feet swelling in the afternoon. *Adding heat energy to an object will warm or heat that object. *Removing heat energy from an object will cool or freeze that object. Conductors and insulators Heat travels through solid, liquids and gases. Solids are the best conductors, but some solids are better conductors than on others. Metal is a better conductor than wood. You can hold a wooden match stick without getting burned but if you grab a hot pan or pot without a potholder you may get burned due to conduction. Conductors: a material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it easily which speeds up the lost or gain of heat energy Insulators: a material that keeps thermal (heat energy) IN- slows down the transfer of heat and does not allow heat to pass easily. Convection Currents Warm liquids (water in a boiling pot) or gases rise (hot air balloon)