Short Answer
advertisement
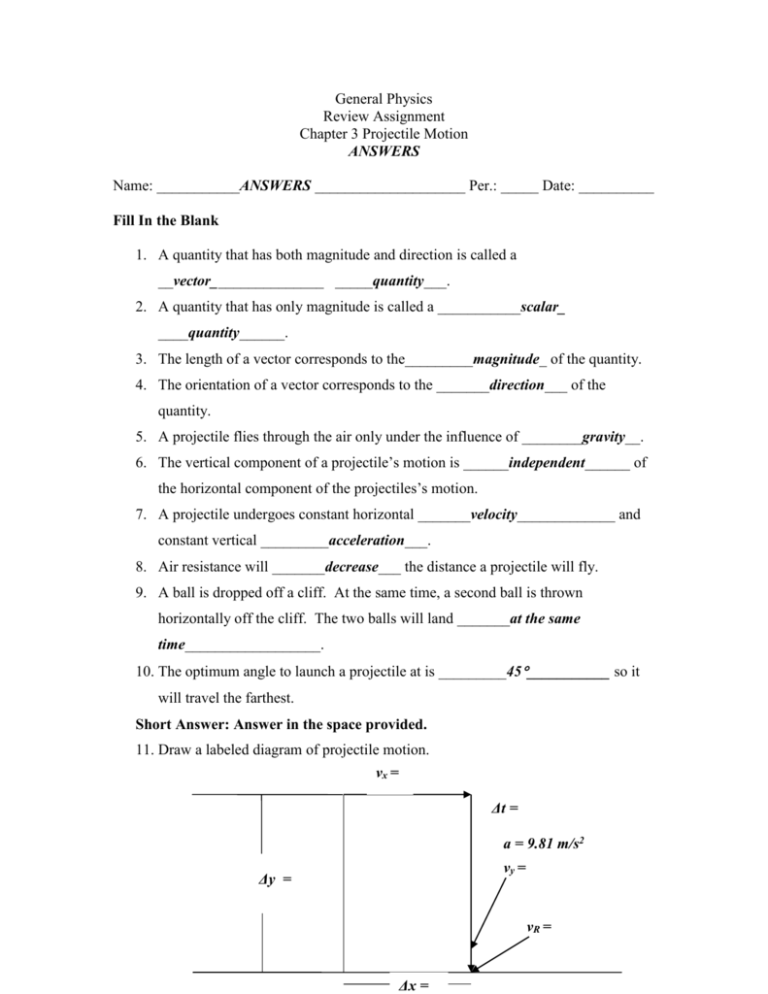
General Physics Review Assignment Chapter 3 Projectile Motion ANSWERS Name: ___________ANSWERS ____________________ Per.: _____ Date: __________ Fill In the Blank 1. A quantity that has both magnitude and direction is called a __vector_______________ _____quantity___. 2. A quantity that has only magnitude is called a ___________scalar_ ____quantity______. 3. The length of a vector corresponds to the_________magnitude_ of the quantity. 4. The orientation of a vector corresponds to the _______direction___ of the quantity. 5. A projectile flies through the air only under the influence of ________gravity__. 6. The vertical component of a projectile’s motion is ______independent______ of the horizontal component of the projectiles’s motion. 7. A projectile undergoes constant horizontal _______velocity_____________ and constant vertical _________acceleration___. 8. Air resistance will _______decrease___ the distance a projectile will fly. 9. A ball is dropped off a cliff. At the same time, a second ball is thrown horizontally off the cliff. The two balls will land _______at the same time__________________. 10. The optimum angle to launch a projectile at is _________45___________ so it will travel the farthest. Short Answer: Answer in the space provided. 11. Draw a labeled diagram of projectile motion. vx = Δt = a = 9.81 m/s2 vy = Δy = vR = Δx = Vx = horizontal velocity Vy = vertical velocity VR = overall velocity (usually velocity when it lands) Δt = time of flight (how long it takes to land) Δ x = horizontal displacement (where it lands) Δy = vertical displacement (how tall the cliff, etc. is) a = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2) 12. Compare vectors and scalars and give an example of each. a. Both vectors and scalars have magnitude, but vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Scalars have only magnitude. Velocity is and example of a vector, while speed is an example of a scalar. 13. What is a projectile? Give an example of a projectile. a. A projectile is an object that flies through the air or space under the influence of gravity. It has both horizontal and vertical motion. The horizontal and vertical motion are independent of each other. An example of a projectile is a car going off a cliff. Problem Solving: Show all your work in the space provided. Be sure to draw a diagram for each problem. Assume no air resistance. 14. Henry accidentally falls out of a helicopter that is traveling horizontally at 45 m/s. He plunges into the water below 5.00 seconds later. What horizontal distance did he travel while falling? Solve algebraically. Equation: Δx = vxΔt Answer: Δx = 230 m ON TEST, YOU WOULD SHOW DIAGRAM AND 5-BOX 15. Judith jumps horizontally from the top of a building that is 25.0 m high. She hopes to reach a swimming pool that is at the bottom of the building. The edge of the pool is 18 m horizontally from the edge of the building, and the pool is 22 m wide. If she is to reach the center of the pool, what must her jumping speed be? Solve algebraically. Plan: Find Δt, then vx Answers: Δt = 2.26 seconds, vx = 13 m/s ON TEST, YOU WOULD SHOW DIAGRAM AND 5-BOXES 16. Draw a vector that represents 7535 km/hr west. Your answer is individual. You must show: Compass Scale Domino calculation Vector of correct length 17. A skier travels 3 m west, turns and travels 4 m south. What is his final displacement? Solve algebraically and graphically Algebraically: Use Pythagorean Theorem, R = 5m ON TEST, YOU WOULD SHOW DIAGRAM AND 5-BOX Graphically: Must include Compass Scale Dominoes for all calculations Length of resultant from diagram Final displacement, angle measurement and direction (~ 5 m at 53 southwest)