Lab XX: Waves on a String – The Sonometer
advertisement

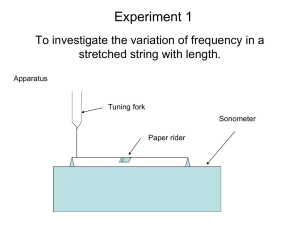
Newbury Park High School - Physics Lab: Waves on a String – The Sonometer Purpose: Derive experimentally a formula for the fundamental frequency of vibration of a string as a function of the length of the string and the tension on the string, and the linear density of the string. Leveling Knob Pick-Up Coil Tension Arm Left Hand Bridge Part I: Length vs. Frequency, Tension and Linear Density held constant. Procedures: 1. Put the yellow wire on the sonometer, adjust the knob on the left side until the tension arm is level. (See fig.1) 2. Adjust the black bridges so that the left one is set at 10 cm and the right hand one is set at 75 cm. This gives a length of 75-10 or 65 cm. 3. Make sure the pick-up coil is about in the center of the wire. 4. Using the plastic loop put a 1 kg mass on the tension hanger on slot 5 (furthest from the wire). 5. Turn the oscilloscope on. Once it finishes its automatic calibration procedure turn on the frequency counter. To do this, press the “selector” lever down 4 times until the word “Freq” appears at the upper left of the screen. (See fig. 2) 6. Readjust the knob on the left to level the tension arm if needed. 7. Pluck the string to set it vibrating. Read the frequency on the oscilloscope. To get the best reading, let the vibrations settle down for a second or two before taking the reading. Repeat this several times and take an average of the frequency readings and record them on your data table. 8. Move the right hand black bridge 5 cm to the left to 70 cm and repeat the steps to take a frequency reading. 9. Continue to vary the length by moving the right hand bridge in increments of 5 cm until you have taken 8 readings. Newbury Park High School - Physics Selector Lever Slot # 5 Right Hand Bridge Tension Hanger Arm Part II: Tension vs. Frequency, length and linear density constant. Procedures: 1. Return the right hand black bridge to the 75 cm mark. 2. The 1 kg mass should be on the # 5 slot on the tension hanger. Again make sure the tension hanger is level. 3. Pluck the string as before and record the average frequency of the wire. 4. Move the 1 kg mass to the #4 slot on the tension hanger. Readjust the knob on the left to level the hanger. 5. Pluck the string as before and record the average frequency of the wire. 6. Continue in this manner, moving the mass to subsequent hanger slots for a total of 5 readings (one for each slot). Part III: Linear Density vs. Frequency, length and tension constant. Procedures: 1. With the 1 kg mass on the # 5 slot, and the bridges set to 10 cm and 75 cm pluck the wire as before and record the frequency. 2. Using the micrometer, measure and record the diameter of the wire. Take several measurements, each at a different spot on the wire. Measure the diameter with the 1 kg mass on the #5 slot. 3. Change wires and repeat steps 1 and 2. Continue this until all five wires have been tested. Newbury Park High School - Physics Calculations and Analysis: 1. Using Excel, create the following graphs. Length vs. Frequency, Tension vs. frequency, and Linear Density vs. Frequency. In each case, frequency is on the y axis. 2. Insert a trendline, and trendline equation for each graph. 3. Using the exponents from each graph, derive (experimentally) the formula… freq = kLxTyz Where k = a constant x, y, and z are the exponents from the trendline equations. 4. Calculate a percent error for each exponent. 5. Calculate the value of the constant k for your equation. Do this by entering various data points, and taking an average. Calculate a percent error for k. The actual equation is… Frequency 1 Tension 2Length Linear Density Finding Linear Density () Wire diameter (measured): 0.590mm Radius = 0.295mm Density of Steel (look up): 7800 kg/m3 Consider 1.00 m of wire… 1.00m Linear Density kg m Volume of wire = (R2)(1.00m) = [(0.295mm)(1m/1000mm)]2(1.00m) =2.73x10-7m3 mass of 1.00 m wire = density x volume = (7800 kg/m3)(2.73x10-7 m3) = .002132 kg/m This is the linear density (), the mass per meter of the wire.