Chapter 17 Review
advertisement

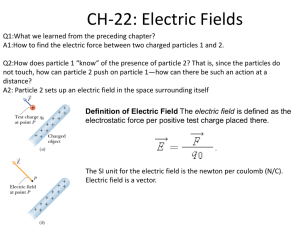
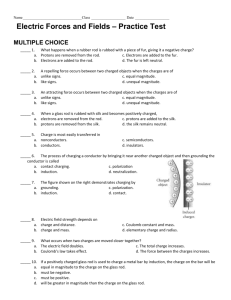
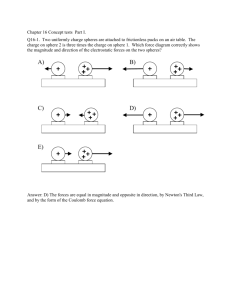
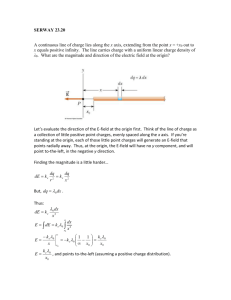
Review Chapter 17 [Physics] 1. What sentence best characterizes electron conductors? a. They have low mass density b. They have high tensile strength c. They have electric charges that move freely d. They are poor heat conductors 2. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge? a. Protons are removed from the rod b. The fur is also negatively charged c. The fur is left neutral d. Electrons are added to the rod 3. An attracting force occurs between two charged objects when a. charges are of unlike signs b. charges are of like signs c. charges are of equal magnitude d. charges are of unequal magnitude 4. A repelling force occurs between two charged objects when a. charges are of unlike signs b. charges are of like signs c. charges are of equal magnitude d. charges are of unequal magnitude 5. Which sentence best characterizes electric insulators? a. Charges on their surface do not move b. they have high tensile strength c. Electric charges move freely on them d. They are good heat conductors 6. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk and becomes positively charged, a. electrons are removed from the rod b. protons are added to the silk c. protons are removed from the silk d. the silk remains neutral 7. Which of the following transfers charge most easily? a. nonconductors b. conductors c. semiconductors d. insulators 8. If a positively charged glass rod is used to charge a metal bar by induction, a. the charge on the bar will be equal in magnitude to the charge on the glass rod b. the charge on the bar must be negative c. the charge on the bar must be positive d. the charge on the bar will be greater in magnitude than the charge on the glass rod 9. The process of charging a conductor by bringing it near another charged object and then grounding the conductor is called a. charging by conduction b. charging by polarization c. neutralization d. charging by induction 10. Electric charge is a. found only in a conductor b. conserved c. found only in insulators d. not conserved 11. Unlike insulators, conductors can be charged by a. grounding b. induction c. polarization d. conduction 12. A surface charge can be produced on insulators by a. grounding b. induction c. polarization d. contact 13. When a charged body is brought close to an uncharged body without touching it, a(n) _____ charge may result on the uncharged body. When a charged body is brought into contact with an uncharged body and then is removed, a(n) _____ charge may result on the uncharged body. a. negative, positive b. positive, negative c. induced, residual d. residual, induced 14. A balloon has a negative charge of 3.5 μC. How many excess electrons are on the balloon? a. 3.5 x 10 -6 b. 2.2 x 10 13 c. 3.9 x 10 -16 d. 3.8 x 10 24 15. What determines the direction of the force between two charges? a. the signs of the charges b. the magnitude of the charges c. the distance between the charges d. Coulomb’s law 16. Which of the following statements concerning electric field lines is false? a. Electric field lines cannot cross each other. b. Electric field lines must begin at a positive charge and end at a negative charge. c. Electric field lines are always tangent to the direction of the electric force. d. Electric field lines do not actually exist. 17. Two parallel plates are oppositely charged. The left plate is negative and the right plate is positive. In which direction does the electric field point? a. right b. left c. cannot be determined 18. As an electric field becomes stronger, the field lines should be drawn _____. a. thicker b. thinner c. closer together d. farther apart Problems: 1. What is the electric force between an electron and a proton that are separated by a distance of 1.0 x 10-19 m? Fe k c 19 q1q2 1.602 10 19 9 1.602 10 = 2.3 x 1010 N 8 . 99 10 19 2 r2 1 10 2. What is the electric force between a proton and an alpha particle (charge 2e) that are separated by a distance of 3.0 x 10-6 m? Fe k c 19 q1q2 2 1.602 10 19 9 1.602 10 = 4.1 x 10-17 N 8 . 99 10 6 2 r2 3.0 10 3. What is the electric force between an electron and a potassium nucleus (charge 19e) that are separated by a distance of 5.2 x 10-10 m? 1.6 x 10-8 N 4. Find the electric force between two charges of +40.0 x 10-9 C and +60.0 x 10-9 C separated by a distance of 30.0 cm. 2.4 x 10-4 N 5. Calculate the net charge on a substance consisting of a combination of 7.0 x 10 13 protons and 4.0 x 1013 electrons. (7.0 x 1013 x 1.602 x 10-19) + (-4.0 x 1013 x 1.602 x 10-19) = 4.8 x 10-6 C 6. The dome of a Van de Graaff generator receives a charge of 2.0 x 10-4 C. The radius of the dome is 1.0 m. Find the magnitude of the electric field strength at the following locations: a. inside the dome zero b. at the surface of the dome r = 1.0 so E= 8.99x109(2.0 x 10-4 C)/1.02 = 1.8x106 N/C The charge is considered to be at the center, therefore r = 1.0m c. 4.0 m from the center of the dome r = 1.0 so E= 8.99x109(2.0 x 10-4 C)/1.02 = 1.8x106 N/C 1.12 x 105 N/C 7. A Van de Graaff generator is charged so that the electric field at its surface is 3.0 x 10 4 N/C. What is the electric force on a proton released at the surface of the generator? 4.8 x 10 -15 N 8. Thunderstorms can have an electric field of up to 3.4 x 10 5 N/C. What is the magnitude of the electric force on an electron in such a field? 5.45 x 10-14 N 9. Identify the charges on the objects in the following configurations.