Chapter 12
advertisement

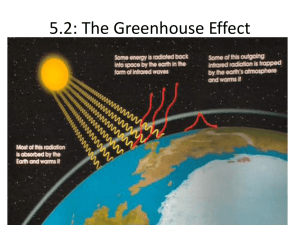
Chapter 12 Anthropogenic Climatic Changes 2. How does the greenhouse effect work and why is it not solely a natural process? Answer: The greenhouse effect works because certain atmospheric gases, known as greenhouse gases, transmit incoming shortwave radiation from the sun but do not easily transmit outgoing longwave radiation. This counter-radiation is responsible for keeping the earth at habitable temperatures. The greenhouse effect is not solely a natural process because humans are increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. As greenhouse gas concentrations increase more radiation will be directed back toward the earth’s surface, resulting in warmer surface temperatures. It is important to remember that the greenhouse effect is a natural process that is being enhanced by human activity. 4. What is the most abundant greenhouse gas and at what wavelengths is it most effective? Answer: Water vapor is by far the most abundant and important greenhouse gas. The concentration of atmospheric water vapor varies from nearly 0 to 4 percent of the mass of the lower atmosphere. Water vapor is particularly effective at absorbing longwave radiation from the earth’s surface at wavelengths between 5 and 8 micrometers. 6. What are the sources of atmospheric methane? Answer: Methane is released to the atmosphere through several processes. Anaerobic decomposition in wetlands accounts for 23 percent of the atmospheric CH4 on a global basis. The flooding of rice fields account for 20 percent of the total and anaerobic digestive processes of animals account for 16 percent. Biomass burning, anaerobic digestion by termites, landfills, fossil fuel combustion, and biological oceanic processes are believed to account for the remaining sources of atmospheric methane. 8. What country is the world’s leading emitter of greenhouse gases, and which are projected to be the leading countries in the future? Answer: The United States is currently the world’s leading emitter of greenhouse gases, accounting for 25 percent of the world’s total. Newly industrializing countries, particularly China, India, and Brazil, are projected to be the world’s leading emitters of greenhouse gases in the foreseeable future. 10. Why are urban areas warmer than their surrounding rural environments? Answer: Urban areas are warmer than their surrounding rural environments for several reasons. The urban environment has less evapotranspiration of water from soil and plants than rural areas due to a lack of vegetation. More sensible heating can occur in the urban area as compared to surrounding areas due to the combined effects of less shading by trees and increased rainfall runoff. The buildings and streets in an urban area store energy during the daytime and release it at night. This delays the cooling of urban areas and makes evening temperatures significantly warmer than the surrounding countryside. Another factor for the urban heat island effect is the additional energy gained from waste heat that is released into the atmosphere due to the intense concentration of human activity. 12. What are the major arguments that environmentalists use to defend their position that the anthropogenic greenhouse effect is a major problem that must be solved? Answer: The majority of climate scientists agree that increasing greenhouse concentrations are the primary cause of the observed recent warming and that global warming is a major problem that needs immediate attention. Greenhouse gases are efficient absorbers and radiators of energy and the recent trends of increasing greenhouse emissions are very similar to the increasing temperature trends. Most scientists agree that the recent warming is due, at least in part, to increasing greenhouse gas emissions. Climate scientists also note that the effects of global warming are largely unknown and that the impacts of increased emissions may be felt for several decades even if emissions were to end immediately. Furthermore, environmentalists argue that greenhouse gas concentrations should be reduced because they are non-renewable resources that cause pollution, regardless of their impacts on global warming. These findings support the environmentalist’s position that the anthropogenic greenhouse effect is a major problem that must be solved. 14. How has the hockey stick temperature curve shaped the global warming debate in recent years? Answer: The hockey stick temperature curve refers to the shape of the global temperature curve for the last 1,000 years reconstructed by proxy evidence, historical and instrumental records. The curve shows relatively stable temperatures from about AD 1000 to about 1900, forming the shaft of the hockey stick. The last 100 years show abrupt warming that the authors attribute to greenhouse gas emissions. While this temperature curve is controversial it has become an important part of a report published in 2001 by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change to show that global warming is a major concern. 16. What did studies of the atmosphere in the absence of jet contrails reveal about global dimming in the days following September 11, 2001? Answer: Atmospheric studies in the days following September 11, 2001 revealed that the absence of jet contrails due to the grounding of all U.S. flights was associated with an increase in the daily temperature ranges of approximately 1 Co (2 Fo) in the United States. These results support the notion that aerosols, including jet contrails, have been masking the effects of global warming, at least during the daytime hours. It is now widely believed that the decreasing trend in shortwave radiation receipt between 1961 and 1990 is real, and that increasing atmospheric pollution and aerosols during this time caused at least some of this trend. 18. What factors cause California to have severe problems from photochemical pollution? Answer: California has severe problems from photochemical pollution due to the influence of the Hawaiian high and the coastal mountain range. The eastern sides of subtropical anticyclones support strong sinking motions and very stable atmospheres. California is located on the eastern side of the Hawaiian high that strengthens and expands during the summer, creating a persistent inversion near the coast. The coastal mountain ranges also contribute to sinking motions by confining sinking motions in the atmosphere to the coastal zone. Automobile exhaust and other pollutants are confined to this narrow zone, where 20 million people live. The abundant sunshine in the summer combined with stable atmospheric conditions make photochemical pollution a severe problem in southern California. 20. What are the criteria pollutants? Of these, which are primary pollutants? Answer: Criteria pollutants are pollutants that are sufficiently widespread and dangerous in the United States that they should be monitored at the federal level. Sulfur oxides, carbon monoxide, particulates, lead, nitrogen oxides, and photochemical oxidants are considered criteria pollutants. Primary pollutants are solids, liquids or gases that are emitted directly by human activities. Among the criteria pollutants, all with the exception of tropospheric ozone and some types of sulfur oxides and particulates are primary pollutants. 22. What danger does carbon monoxide pose if inhaled? Answer: Carbon monoxide is (CO) unstable in the free atmosphere and always attempts to bond with another atom or molecule when emitted. Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, attempts to deliver diatomic oxygen to body organs and tissues. If CO is inhaled, it may outcompete hemoglobin for this oxygen and starve the brain, heart, and other vital organs of oxygen. 24. How does industrial smog form? Answer: Industrial smog forms when chemical reactions occur between sulfur dioxide and particulates in the presence of fog. The biggest danger with industrial smog is that the particulates are very dangerous to the respiratory system. Notable industrial fog episodes include Donora, Pennsylvania, in 1948 and London in 1952. 26. What primary pollutants are the major contributors to acid rain, and how does the distribution of these pollutants differ? Answer: Acid rain occurs when sulfuric dioxide and nitrogen oxides (primary pollutants) are deposited on the surface. The most common form of acid rain results from the emission of sulfur dioxide in humid environments. The highest concentrations of sulfur dioxide pollution in the atmosphere are found in coalintensive industries in the eastern United States and western Europe. Nitrogen oxides are found more problematic in the “freeway cities” of the southern and western United States. Acid rain has not been as severe a problem to the United States as was initially anticipated. 28. What are the advantages and disadvantages of mitigation as a strategy in combating anthropogenic climatic change? Answer: Mitigation is the attempt to decrease the risk associated with a threat. Mitigation strategies are aimed at minimizing the impact of a threat. Successful mitigation strategies include building sea walls to combat the risk of coastal land loss from sea level rise and introducing new hybrid crops that are more resistant to drought. Although mitigation strategies may be successful, they are sometime criticized for being expensive and not “getting to the root of the problem.”