The Properties of Graphs of Exponential Functions
advertisement

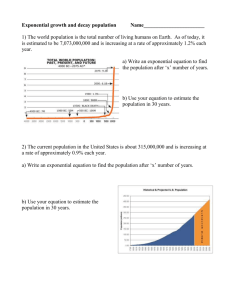
Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ The Properties of Graphs of Exponential Functions Part A- Reflections in the x-axis Graph the exponential y 2 x by completing the following chart: x y 10 y 9 8 -3 7 -2 6 -1 5 0 4 1 3 2 2 1 3 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 1. What is the y value where the graph seems to level off?____________________ This line is called the horizontal asymptote. 2. Does the graph produce a growth curve or a decay curve?__________________ 3. What is the focal point of this curve?_____________________ x Graph the following function, y (2 x ) y x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -3 -2 -2 -3 -1 -4 0 -5 1 -6 2 -7 3 -8 Does the graph produce a growth curve or a decay curve?_________________ What is the focal point of this curve?_____________ -9 -10 y 4. Make a statement connecting the sign of the coefficient of 2 x and the look of the graph. *This graph is said to be a reflection in the x-axis of the y 2 x graph. 1 Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Part B- Reflections in the y-axis Graph the exponential y 2 x by completing the 10 y following chart: 9 x y 8 -3 7 -2 6 -1 5 0 4 1 3 2 2 3 1 x -4 -3 -2 -1 5. Does the graph produce a growth curve or a decay curve?__________________ 6. What is the focal point of this curve?_____________________ x Graph the following function, y 2 x y 1 10 2 3 4 y 9 -3 8 -2 7 -1 6 0 5 1 4 2 3 3 2 1 x Does the graph produce a growth curve or a decay -4 curve?_________________ What is the focal point of this curve?_____________ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 7. Make a statement connecting the sign of the coefficient in front of the x term of 2 x and the look of the graph. *This graph is said to be a reflection in the y-axis of the y 2 x graph. 2 Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Part C- Vertical Stretches Complete the table of values for y 2 x and 10 y 1 y 2 x below, and draw both graphs on the right. 3 9 x 1 y2 y 2x 8 3 x y x -3 -3 -2 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 7 y 6 5 4 3 2 1 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 1. How are the two graphs alike? (shape, growth/decay, steepness, etc.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. How are they different? (focal point, etc.) ______________________________________________________________________________ Complete the table of values for 3 y 2 x and y 2 x below, and draw both graphs on the right. 10 y 9 y2 x x y 3y 2 x x y 8 7 -3 -3 6 -2 -2 5 -1 -1 4 0 0 3 1 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 This factor of change between the y-values of 1 y 2 x and y 2 x is known as a vertical stretch. In this case, we have a vertical stretch of 3. 3 1 3 y 2 x has a vertical stretch of from y 2 x 3 3 3 4 Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Part D- Horizontal Stretches Complete the table of values for y 2 x and 10 y y 2( x / 2) below, and draw both graphs on the right. y 2x y 2( x / 2) 9 x x 8 y y -3 -3 7 -2 -2 6 -1 -1 5 0 0 4 1 1 3 2 2 2 3 3 1 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 3. How are the two graphs alike? (shape, growth/decay, focal point, etc.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. How are they different? (steepness, etc.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Complete the table of values for y 22 x and y 2 x 10 y below, and draw both graphs on the right. y 2x y 22 x x x 9 8 y -3 -3 -2 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 y 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 x -4 This factor of change between the y-values of x ( x / 2) is known as a horizontal y 2 and y 2 stretch. In this case, we have a horizontal stretch of 2. y 22 x has a horizontal stretch of ½ from y 2 x 4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Part E- Vertical Translation Complete the table of values for ( y 3) 2 x and y 2 x below, and draw both graphs on the right. y 2x x y -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 10 ( y 3) 2 x x y -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 1. What is the focal point of ( y 3) 2 x ? __________________________________ 2. What is the horizontal asymptote of ( y 3) 2 x ? 2 1 x -4 _______________________________________________ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 Complete the table of values for ( y 2) 2 x and y 2 x below, and draw both graphs on the right. (Remember to make it calculator-friendly). x y2 ( y 2) 2 x x y x y -3 -3 -2 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 3. What is the focal point of ( y 2) 2 x ? __________________________________ 4. What is the horizontal asymptote of ( y 2) 2 x ? 7 y 6 5 4 3 2 1 x -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 -1 -2 -3 _______________________________________________ This change to the graph is called a vertical translation. The graph ( y 3) 2 x has a vertical translation of 3. This means that the graph is vertically translated +3 units from the basic exponential form. The graph ( y 2) 2 x has a vertical translation of -2. This means that the graph is vertically translated -2 units from the basic exponential form. 5. What happens to the number in the brackets with the y term to get the vertical translation? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5 4 Date:________________________ Part F- Horizontal Translations Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Complete the table of values for y 2( x 2) and y 2 x below, and draw both graphs on the right. x y2 y 2( x 2) x y x y -3 -5 -2 -4 -1 -3 0 -2 1 -1 2 0 3 1 10 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 ( x 2) 1. What is the focal point of y 2 ? __________________________________ 1 x -4 ( x 1) Complete the table of values for y 2 and y x below, and draw both graphs on the right x y2 y 2( x 1) x y x y -3 -2 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 2 10 y 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2. What is the focal point of y 2( x 1) ? __________________________________ 2 1 3. What do you notice about y 2( x 1) in comparison to y 2 x ? -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 _______________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Has the shape of the graph changed? __________________________________ 5. What are the coordinates of the focal point of y 2( x 1) ? __________________________________ 6. This change to the graph is called a horizontal translation. The graph y 2( x 2) has a horizontal translation of –2 (i.e., the graph is translated horizontally –2 units from the basic exponential form). 6 x 4 Date:________________________ Part G- Mapping Rules Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ The Mapping Rule allows us to easily get a table of values for a transformed exponential function without doing all of the mathematical computations The mapping rule that would represent this comparison is between the basic exponential y b x and 1 ( xh) 1 the transformed exponential ( y k ) b c would be ( x, y ) (()cx h, ()ay k ) where: a Vertical stretch = a Horizontal stretch = c Vertical translation = +k Horizontal translation = +h There is a reflection in the x-axis if there is a negative in front of “a” There is a reflection in the y-axis if there is a negative in front of “c” Example : Find the mapping Rule of the following exponential ( y 2) 3( x 3) Vertical stretch = 1 Horizontal stretch = 1 Vertical translation = -2 Horizontal translation = -3 Reflection= No Mapping Rule: x, y x 3, y 2 Part H- Finding the focal point To find the focal point of a transformed exponential, we simply use the mapping rule to transform the focal point of y b x (0,1) Example : Find the focal point of the following exponential ( y 2) 3( x 3) Mapping Rule: x, y x 3, y 2 Focal point: 0,1 0 3, 1 2 3,1 7 Date:________________________ Block:__________ Name:____________________________________ Part I – Practice For each exponential function: 1) State the transformations 2) The Mapping Rule. 3) Focal point 3) Create one table of values for the basic exponential and a second table of values for the given function (use the mapping rule). 1 ( x 1) 1 15 y A) ( y 2) 3 2 2 10 5 x -10 -5 5 10 -5 B) 2( y 1) 23( x 2) 5 y x -10 -5 5 -5 -10 -15 8 10