AP_Physics_Assignments_files/AP Lesson 19 HW Key
advertisement
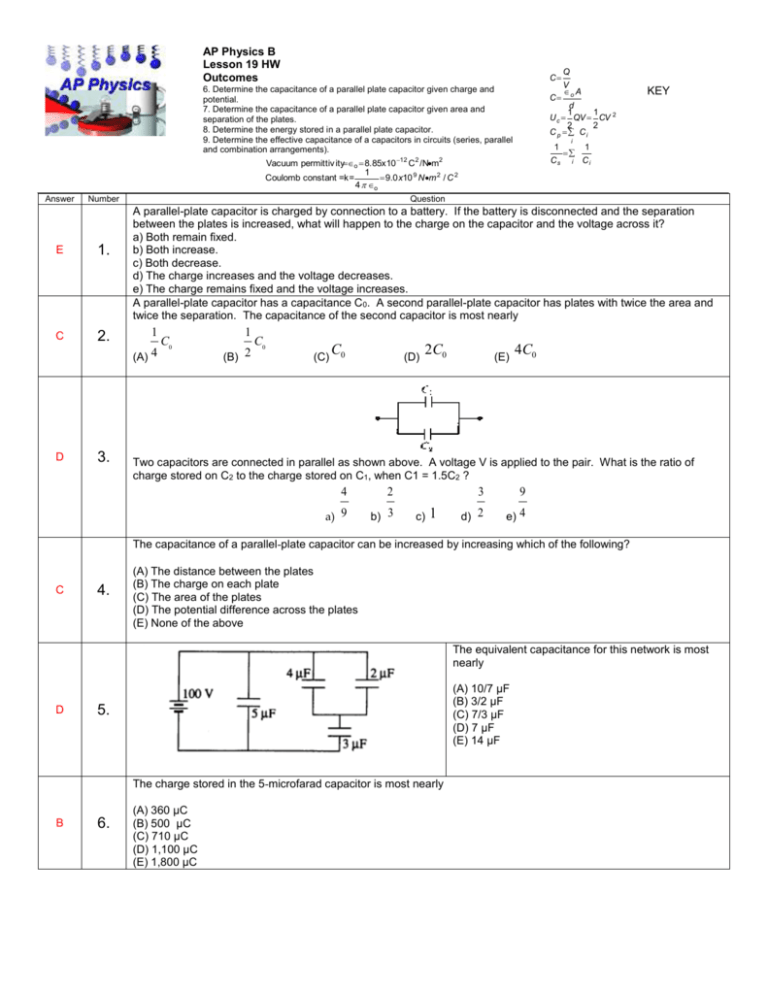
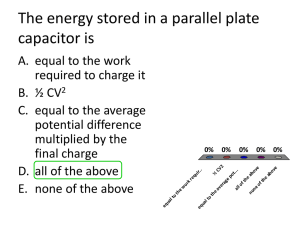
AP Physics B Lesson 19 HW Outcomes C 6. Determine the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor given charge and potential. 7. Determine the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor given area and separation of the plates. 8. Determine the energy stored in a parallel plate capacitor. 9. Determine the effective capacitance of a capacitors in circuits (series, parallel and combination arrangements). C Number E 1. C 2. i 1 1 Cs i Ci Question A parallel-plate capacitor is charged by connection to a battery. If the battery is disconnected and the separation between the plates is increased, what will happen to the charge on the capacitor and the voltage across it? a) Both remain fixed. b) Both increase. c) Both decrease. d) The charge increases and the voltage decreases. e) The charge remains fixed and the voltage increases. A parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance C0. A second parallel-plate capacitor has plates with twice the area and twice the separation. The capacitance of the second capacitor is most nearly 1 (A) 4 D 3. KEY d 1 1 U c QV CV 2 2 2 C p Ci Vacuum permittiv ityo 8.85x10 12 C 2 /Nm2 1 Coulomb constant =k= 9.0x10 9 Nm 2 / C 2 4 o Answer Q V o A C0 1 (B) 2 C0 (C) C0 (D) 2C0 (E) 4C0 Two capacitors are connected in parallel as shown above. A voltage V is applied to the pair. What is the ratio of charge stored on C2 to the charge stored on C1, when C1 = 1.5C2 ? 4 2 a) 9 b) 3 c) 1 3 9 d) 2 e) 4 The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor can be increased by increasing which of the following? C 4. (A) The distance between the plates (B) The charge on each plate (C) The area of the plates (D) The potential difference across the plates (E) None of the above The equivalent capacitance for this network is most nearly D (A) 10/7 µF (B) 3/2 µF (C) 7/3 µF (D) 7 µF (E) 14 µF 5. The charge stored in the 5-microfarad capacitor is most nearly B 6. (A) 360 µC (B) 500 µC (C) 710 µC (D) 1,100 µC (E) 1,800 µC Two parallel conducting plates, separated by a distance d, are connected to a battery of emf is correct if the plate separation is doubled while the battery remains connected? B 7. E 8. . Which of the following a) The electric charge on the plates is doubled. b) The electric charge on the plates is halved. c) The potential difference between the plates is doubled. d) The potential difference between the plates is halved. e) The capacitance is unchanged. A 4µF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 100 V. The electrical energy stored in the capacitor is The total capacitance of several capacitors in parallel is the sum of the individual capacitances for which of the following reasons? A 9. (A) same. (B) (C) (D) (E) The charge on each capacitor depends on its capacitance, but the potential difference across each is the The charge is the same on each capacitor, but the potential difference across each capacitor depends on its capacitance. Equivalent capacitance is always greater than the largest capacitance. Capacitors in a circuit always combine like resistors in series. The parallel combination increases the effective separation of the plates. Free Response 2002B5B. Two parallel conducting plates, each of area 0.30 m 2, are separated by a distance of 2.0 x 10-2 m of air. One plate has charge +Q; the other has charge -Q. An electric field of 5000 N/C is directed to the left in the space between the plates, as shown in the diagram above. (a) Indicate on the diagram which plate is positive (+) and which is negative (-). (b) Determine the potential difference between the plates. b) V=Ed 100V = (5000N/c) • (2x10-2 m) (c) Determine the capacitance of this arrangement of plates. c) C= eo A/d = 8.85x10-12 (0.3m2 /2x10-2m) = 1.33x10-10 F An electron is initially located at a point midway between the plates. (d) Determine the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the electron at this location and state its direction. d) F=Eq = (5000N/c)•(1.6x10-19 C) = 8 x10-16N (e) If the electron is released from rest at this location midway between the plates, determine its speed just before striking one of the plates. Assume that gravitational effects are negligible. e) V2=Vo2+2ax V=√2ax a=F/m v=√2xF/m v= √2 (8x10-16N)(0.1)/9.1x10-31) v= 4.2 x106 m/s