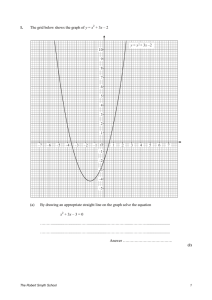
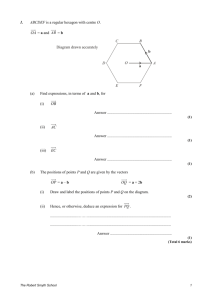
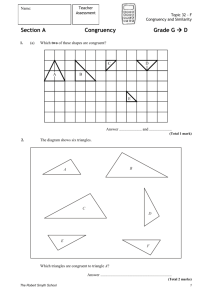
1. Two sides of a square are shown on the grid. (a) Write down the
advertisement

1. Two sides of a square are shown on the grid. y 4 A 3 B 2 1 O 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 x –1 –2 –3 (a) C Write down the coordinates of A. Answer ( ……………………. , ……………………. ) (1) (b) Write down the coordinates of C. Answer ( ……………………. , ……………………. ) (1) (c) Draw two more lines to complete the square ABCD. (1) (d) M is the mid-point of AC. Work out the coordinates of M. Answer ( ……………………. , ……………………. ) (2) (Total 5 marks) The Robert Smyth School 1 2. The points P, Q and R are plotted on the grid to form a triangle. y 6 Q 5 4 3 R 2 1 P 0 0 (a) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 x 8 What is the mathematical name given to triangle PQR? Answer ......................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Mark the mid-point of PQ on the grid. Label it M. (1) (ii) Write down the coordinates of M. Answer (............................, ...............................) (1) (Total 3 marks) 3. The diagram shows the positions of A (2, 5) and B (4, 1). y 6 A 4 2 B x –4 The Robert Smyth School –2 0 2 4 2 Find the coordinates of M, the mid-point of the line AB. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Answer................................................................................................................................... (Total 2 marks) 4. A line AB is shown on the grid. y 7 6 5 A 4 P 3 2 1 B 0 0 (a) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 x Mark the mid-point of AB. Label it M. (1) (b) Write down the coordinates of M. Answer ( ................. , .................) (1) (c) Draw a line through the point P, parallel to the line AB. (1) (Total 3 marks) The Robert Smyth School 3 5. The triangle ABC is shown on a centimetre grid. y 5 B 4 3 2 1 0 (a) A 0 1 2 C 3 4 5 6 x Find the coordinates of the midpoint of BC. ..................................................................................................................................... Answer ( ..............................., ..............................) (2) (b) Find the area of the triangle ABC. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Answer ..................................................................cm2 (2) (c) Show, on the grid below, how two triangles congruent to triangle ABC can be put together to form an isosceles triangle. (2) (Total 6 marks) The Robert Smyth School 4 1. (a) (2, 3) B1 If both reversed ie (3, 2) and (–3, 6) SC1 (b) (6, –3) B1 (c) 2 correct lines ± 2 mm meeting at (1, –2) Condone broken lines B1 (d) Look for answer (4, 0) If (4, 0) not seen, award M1 for position (4, 0) ± 2 mm clearly marked If both reversed in (a) and (b) and (0,4) in (d) SC1 M1 A1 [5] 2. (a) Isosceles B1 (b) (i) Point marked on diagram Condone missing label if point is clear B1 (ii) (2,3) B1 ft [3] 3. (– 2 + 4) / 2 oe M1 or (5+1) / 2 (1,3) A1 [2] 4. (a) Mid-point indicated at (4,2) 2mm; letter M not necessary (b) (4, 2) (c) Correct line through P At least 3cm long; check whether the line, if produced, would go within 2mm of (5, 4) and (9,2) B1 B1ft B1 [3] 5. 05 –42 or 2 2 M1 or evidence of good use of grid 2.5, –1 A1 Take one or other value correct as evidence for the M1 SC1 for (–1, 2.5) [2] 6. (a) (4, 2.5) or (x4, y2.5) B1 for each B1 if wrong way B2 (b) ½×2×3 M1 The Robert Smyth School 5 (c) 3 cm2 A1 Correct 2 triangles to 2mm accuracy B1 if triangles correct orientation but not touching along common side B1 any 2 congruent triangles B1 any isosceles triangle B2 [6] The Robert Smyth School 6