Acceleration on ramp revised 2012
advertisement

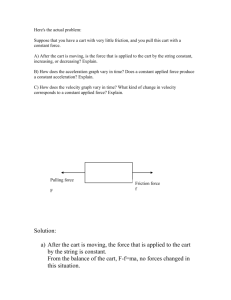
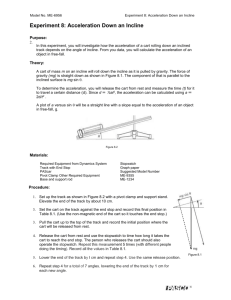
Acceleration Lab The purpose of this activity is to determine the velocity and acceleration of a cart rolling down a track. You will also need to compare your acceleration results to theoretical values (to check if the physics is working!). Here is what you will be assessed on: 1.8 The ability to synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error. To carry out this investigation you will use a motion sensor and a cart on a track. 1. Set up a ramp with the cart going down and determine the angle of the ramp relative to the horizontal. Draw a sketch and show your ramp and show your calculations here: The angle θ of my ramp is: ________________ HYPOTHESIS: The theoretical value of what the acceleration should be can be determined with the following equation: a(on a ramp) = sinθ * 9.8m/s2 . Find the theoretical value of acceleration and show your work below: The cart should accelerate at ___________ based on the theoretical value above. 2. In the first part of this investigation you will release a cart at the top of the track and graph its POSITION as it rolls down the track using your GLX. Before you actually collect data, predict what the position time graph will look like by sketching it in the space available below. Label the sketch “Prediction of Position – down ramp” 3. Use the GLX to collect data while the cart rolls down the incline. Try to start the GLX as soon as you release the cart and stop the collection just as the car reaches the bottom of the incline. If you are not successful the first time, try again. When you have been successful in collecting the data, copy your data into the graph above and label it ACTUAL POSITION DATA. Describe the motion of the cart here (tell the story). 4. Use the tangent tool on your GLX to determine the highest velocity reached by the cart (remember, velocity is the slope of a d vs t graph). Record it in the space below. vmax=_________________________________ 5. Why did you use a tangent to find velocity on this graph??___________________________________________________________. SAVE YOUR DATA AT THIS POINT 6. Set up your GLX to collect both d-t and v-t on two graphs shown in the same screen. Repeat step 3. Sketch your data below. 7. What does the shape of the velocity time graph tell you about the acceleration? (ie. Is the acceleration constant or not constant? Explain using the results of your graph and using the language of physics.) 8. Acceleration is defined as a = v/t. a = v/t is simply the slope of the velocity time graph above. Use the smart tool on your GLX to find 2 points on your velocity vs time graph. In the space below, write your two points down and then determine the slope of the portion of the graph, which represents the acceleration. What is the value of the acceleration? a = __________________________ 9. What if you were to make the incline steeper of your ramp steeper, how do you think the graph would change? Why would it do this? (Hint: if the angle of the ramp was 90 degree (ie straight down), what would be the value of the acceleration?). 10. State your results: The acceleration of the cart on the ramp is: ____________. 12. Find the % error between your actual results and what the theoretical results should be. Show your work in the space below. 13. Account for any sources of error and EXPLAIN HOW YOU WOULD IMPROVE THE EXPERIMENT TO REDUCE THE ERROR.