What`s Your Angle - Gaiser Middle School
advertisement

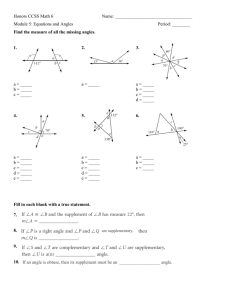
What’s Your Angle? Directions: Use the following information to answer questions 1 through 7. Sunlight strikes Earth at different angles due to the shape of Earth, as shown below. Sunlight Striking Earth Two students, Amy and Chris, wanted to know if the shape of Earth affects surface temperatures on Earth. They investigated this phenomenon with a model of the Earth-Sun system as described in the Earth-Sun Model. Question: What is the effect of the angle at which light strikes a wooden block on the surface temperature of that block? Hypothesis (prediction): As the angle that the light strikes the block increases to 90°, the block’s surface temperature will increase because the light will strike the block more directly. Materials: wooden block thermometer black paper lamp protractor meterstick stand and clamp timer What’s Your Angle? 1 Investigation Setup Earth-Sun Model Procedure: 1. Lay the thermometer on the wooden block. 2. Cover the lower end of the thermometer with black paper and attach the paper to the wooden block. 3. Tilt the block so the light beams will strike at a 15˚ angle as shown in the Investigation Setup diagram. 4. Record the starting temperature of the block’s surface. 5. Turn on the lamp. Record the temperature after 2.5 minutes and again after 5 minutes. 6. Turn off the lamp and wait 10 minutes for the thermometer to return to room temperature. 7. Repeat steps 3 through 6 using 30˚, 60˚, and 90˚ angles. Keep the lamp at the same distance from the wooden block for each condition. 8. Repeat steps 1 through 7 two more times as trials 2 and 3. Data: Angle Light Strikes Block vs. Block’s Surface Temperature Angle Light Strikes Block (degrees) Block’s Surface Temperature (degrees Celsius) Starting 2.5 minutes 5 minutes 15 26 31 36 30 27 35 41 60 28 38 46 90 28 46 56 Note: Temperatures are the averages of the three trials. 2 What’s Your Angle? 1 Which variable was the responding (dependent) variable in Chris and Amy’s investigation? o A. Surface temperature of the wooden block o B. Distance of the lamp from the wooden block o C. Color of the paper covering the wooden block o D. Angle that light beams strike the wooden block 2 Sunlight strikes Earth at different angles due to the shape of Earth as shown below. Sunlight Striking Earth At which location would shadows be longest at noon on a clear summer day? o A. Location A o B. Location B o C. Location C o D. Location D 3 Amy and Chris want to repeat their investigation with a different color paper over the thermometer. Which color would result in the lowest surface temperature of the block? o A. Red o B. Blue o C. White o D. Green 3 What’s Your Angle? 4 Predict the surface temperature of the wooden block if the block was set at a 45° angle for five minutes. In your prediction, be sure to: Predict the approximate surface temperature of the wooden block. Include data from the Angle Light Strikes Block vs. Block’s Surface Temperature table to support your prediction. 4 What’s Your Angle? 5 How could Amy and Chris change their Earth-Sun Model to more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun? Be sure to: Identify one change that could be made to the model. Explain how this change would more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun. Change: How this change would more accurately show how Earth is heated by the Sun: 5 What’s Your Angle? 6 Describe two energy transfers that happened in Chris and Amy’s investigation. In your description, be sure to: Identify the energy forms before and after each energy transfer. Describe where in the system each energy transfer happened. Use words, labeled pictures, and/or labeled diagrams in your response. One transfer: Another transfer: 6 What’s Your Angle? 7 Plan a new investigation to answer Chris and Amy’s new question printed in the box. In your plan, be sure to include: Hypothesis (prediction) of the investigation results Materials needed to perform the investigation Procedure that includes: logical steps to perform the investigation one controlled (kept the same) variable one manipulated (changed) variable one responding (dependent) variable how often measurements should be taken and recorded Question: How does the angle at which sunlight strikes Earth affect the length of shadows cast on the ground? Hypothesis (prediction): Materials: 7 What’s Your Angle? You may use the space below for a labeled diagram to support your procedure. Procedure : 8 Clean Water? Directions: Use the following information to answer questions 8 through 13. Darcie and Matt were hiking in the Cascade Mountains and ran out of clean water. The only water they could find was from a muddy stream. They designed and built the water cleaner system shown in the diagram below. Darcie and Matt used their scientific understanding of the water cycle around them in the design of their water cleaner system. Darcie and Matt made their water cleaner system from equipment found in their backpacks. They poured muddy water into the bottom of a large plastic bowl. They placed a metal cup into the middle of the muddy water in the plastic bowl. Then they stretched clear plastic wrap over the top of the plastic bowl. Finally they placed a rock on top of the plastic wrap causing the plastic wrap to sag in the middle. Their water cleaner system functioned with the energy input from sunlight. 9 Clean Water? 8 Which force caused the clean water to drop into the metal cup? o A. Electric o B. Magnetic o C. Frictional o D. Gravitational 9 Which of the following statements explains why Darcie and Matt should be more concerned about running out of water than running out of food? o A. The human body is able to obtain more nutrients from water than from food. o B. The human body is able to survive longer without food than without water. o C. The human body is made up of very little water. o D. The human body is made up of very little liquid. 10 If Darcie uses filter paper to filter the muddy water, which of the following parts of the muddy water will remain in the water once the water has been filtered? o A. Sand o B. Leaves o C. Insects o D. Bacteria 10 Clean Water? 11 Describe two human activities that could make the stream water muddy. In your description, be sure to: Identify two different human activities that may have made the stream muddy. Describe how each activity may have made the stream muddy. One human activity: Another human activity: 11 Clean Water? 12 Darcie and Matt realized that their Water Cleaner System was not cleaning as much water as they needed. They decided to redesign their water cleaner system to produce clean water faster than the original. They had the following four items available to use in their redesign: large pieces of aluminum foil metal pot large, black plastic bag white towel Use one or more of the materials listed to redesign the original Water Cleaner System. You may also use any of the original materials. Be sure to: Describe how you would use the material(s) to redesign the original Water Cleaner System. Explain how your redesign would clean water faster than the original Water Cleaner System. Use words, labeled pictures, and/or labeled diagrams in your response. 12 Clean Water? 13 Darcie and Matt used their scientific understanding of the water cycle around them in the design of their Water Cleaner System. Four processes that are part of the water cycle are listed below: 1. 2. 3. 4. Condensation Evaporation Precipitation Collection Explain how Darcie and Matt used each of these four water cycle processes in the design of their Water Cleaner System. In your explanation, be sure to: Identify a specific location in the Water Cleaner System that models each of the four water cycle processes listed above. Describe how each of the four water cycle processes is used in the design of their Water Cleaner System. Describe how each process occurs in the environment around Darcie and Matt. You may use words, labeled pictures, and/or labeled diagrams on the diagram below. How does the design use condensation? How does condensation happen in the environment? 70 Clean Water? How does the design use evaporation? How does evaporation happen in the environment? How does the design use precipitation? How does precipitation happen in the environment? How does the design use collection? How does collection happen in the environment? 71