Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template
advertisement

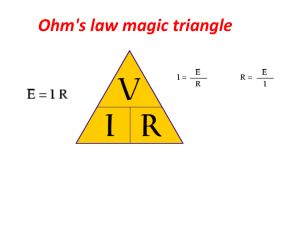
Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Ohm’s Law Author(s): Jim Caswell, Automotive Technology Colleen Stepanovich, Mathematics Lesson Objective: Lesson # 5 Phone Number(s): (570) 346-8471 X117 (570) 346-8471 X167 E-mail Address(es): jcaswell@ctc.tec.pa.us cstepanovich@ctc.tec.pa.us Student will demonstrate a working knowledge of Ohms law and how to manipulate the math formula to find an unknown variable of an electrical circuit. Supplies Needed: TEACHER NOTES (and answer key) THE "7 ELEMENTS" 1. Introduce the CTE lesson. Cletus installed super driving lights on a 12 Volt system. His 15 Amp fuse keeps blowing. He has 0.4 Ohms of resistance. Is the fuse properly rated for this light and how can you tell? 2. Assess students’ math awareness as it relates to the CTE lesson. (Continue introduction on items 1 and 2) 1. Review that voltage is electromotive force (E). Amperes is inductive force (I). Resistance is opposition a conductor has to the flow of current (R). 2. Ohm-unit of electrical resistance measurement. One ohm is the resistance that will allow one ampere to flow when pushed by one volt. Review of Georg OhmGerman physicist (1787-1854). 3. Show the student a simple multiplication problem. 1. Previous discussion/lesson of what voltage, amperes, and resistance is. 2. Resistance is measured in ohms. What is an ohm? Where did the name ohm come from? Why was it selected? Today we will discuss the concept Mr. Ohm developed regarding electrical circuits more familiarly called “Ohms Law”. 3. Do you know how to multiply? 2x3=6 4. 62=3 4. Do you know how to divide? 5. Do you know that a fraction is a division problem? Show the student a simple division problem. 5. Show a division problem as a fraction. 6 / 2 = 3 (Show as a fraction 6 over 2) 3. Work through the math example embedded in the CTE lesson. Our original question was: Cletus installed super driving lights on a 12 Volt system. His 15 Amp fuse keeps blowing. He has 0.4 Ohms of resistance. Is the fuse properly rated for this light and how can you tell? 1. E = IR I = E/R 1. Show the Ohm’s Law formula. R = E/I E/IR (Show as standard formula E over IR) E = Electromotive force (Volts) 2. I = Current (Amperes) R = Resistance (Ohms) 2. Demonstrate the Ohm’s Law formula by blocking the unknown variable to obtain the required math formula. 3. I = E/R I = 12/ 0.4 3. If E (Voltage) = 12 and R (Resistance) = 0.4, what is I (Amperes) equal to? I = 30 Amps Cletus needs a 30 Amp fuse to handle the lights. 4. Work through related, contextual math-in-CTE examples. Using Ohms Law calculate the following. 1. 1998 Ford F-150 needs 180 starting amps to crank the engine. What is the resistance if the voltage is 12v? 1. R = E/I R = 12/180 R .066 Ohms 2. If the resistance in the rear taillight is 1.8 ohms and the voltage equals 12 volts, what is the amperage? 2. I = E/R I = 12/1.8 I 6.66…Amps 3. A 100-amp alternator has 0.12 ohms of resistance. What must the voltage equal? 3. E = IR E = 100 (0.12) E = 12 Volts 5. Work through traditional math examples. 1. Demonstrate formulas by blocking the unknown variable to obtain the required math formula. It works for other mathematical formulas. Substitute each of the formulas below (A = LW, D = RT and GP = RT) to show students this concept. 2. The formula for area of a rectangle is A = LW where A is the area, L is the length and W is the width. Find the area of a rectangle that has a length of 8 ft and an area of 120 sq ft. 1. 2. A = LW You know the length and the area, block the unknown variable (the width) to obtain the formula. A/L = W 120 ft2/8ft = W 15 ft = W 3. The formula for distance is D = RT where D is the distance, R is the rate of speed in mph and T is the time in hours. If a car is traveling at an average speed of 55 mph and you travel 385 miles, how long did the trip take? 3. D = RT You know the rate and the distance, block the unknown variable (the time) to obtain the formula. T = D/R T = 385 miles/55 miles per hour T = 7 hours 4. The formula to calculate gross pay is GP = RT where GP is gross pay (pay before payroll deductions), R is the rate of pay per hour and T is the time in hours. A worker works 43 hours and his gross pay is $344. How much did he make per hour? 4. GP = RT You know the gross pay and the time, block the unknown variable (the rate) to obtain the formula. GP/T = R $344/43 = R $8 = R 6. Students demonstrate their understanding. 1. See attached worksheet (Ohm’s Law Worksheet). 1. See attached worksheet solutions (Ohm’s Law Worksheet Solutions). 7. Formal assessment. 1. See attached assessment sheet (Ohm’s Law Assessment) 1. See attached assessment solutions (Ohm’s Law Assessment Solutions).