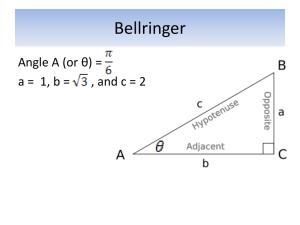
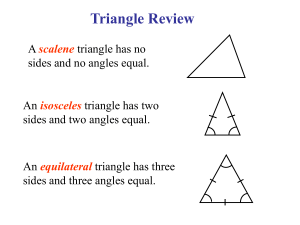
TRIANGLES on Sketchpad: Covering and Surrounding 6
advertisement

Shapes and Designs: Investigation 2.1, Triangles In the Triangles lesson on Sketchpad, students will explore different properties of triangles. They look at the perimeter and the area in order to find that triangles with differing perimeters can have the same area, as long as the base and height remain constant. By dragging the vertices of a triangle in Sketchpad, students can see the infinite number of triangles that have the same base and height. Also, students explore the different positions of the height in a triangle: the height of a triangle can be found inside, outside, or along one side of a triangle. They also investigate the fact that all triangles will always have three different heights. VOCABULARY: Height: The height is a segment that starts at a vertex of the triangle and is perpendicular to the base. Since all triangles have three bases, all triangles have three heights. Base: The base of the triangle is the side that is perpendicular to the height. Right Angle: Angle of 90 degrees. Obtuse Angle: Angle more than 90 degrees. Acute Angle: Angle less than 90 degrees. LAUNCH: Begin by asking students: Do you think two different triangles can have the same perimeter? Do you think two different triangles can have the same area? If students do not bring up the idea of base and height in this discussion, briefly review the vocabulary, telling them that these ideas will help them answer the questions. Depending on the students’ familiarity with Sketchpad, or on their ability to follow the directions on the worksheet, you may want to show students how to find the perimeter and area of a triangle. EXPLORE: As you walk around the room, pose questions to the students such as: Tab: Perimeter vs. Area. After students have concluded that the triangles have the same area, ask what they see in common with the triangles (or do they have the same area by coincidence?) Have them move certain points on the triangles as you guide them to see that both the base and height are always staying the same length. Tab: Where is the height? Focus not only on words like “inside” or “outside” the triangle, but also direct students to the angles of the triangle. Right, acute, and obtuse angles are also a way of determining where the height of the triangle will fall. Tab: Three heights of a triangle. After looking at the three different heights, ask students if any triangle would have three heights. Could all three heights be the same length? When? When would two heights be the same length? SUMMARIZE: With about ten minutes left, gather students in a group around a community computer or projector. For the tab Perimeter vs. Area, ask students why they thought the three triangles had the same area. Once base and height has been suggested, demonstrate (by moving points on the sketch that would move the base and then the height of one of the triangles) how the base and height of all three triangles remain the same. For the tab Where is the height?, students may say that the triangle was “inside” when the top point was above the base, and vice versa. This is correct, but also demonstrate how by looking at the angle of the triangle, you can determine where the height will fall. For the tab Three heights of a triangle, ask students how many triangles could have three heights. Could a triangle have more than three heights? Discuss why sometimes some students only see one height when they look at a triangle.