Math 030 - Section 5.2
advertisement
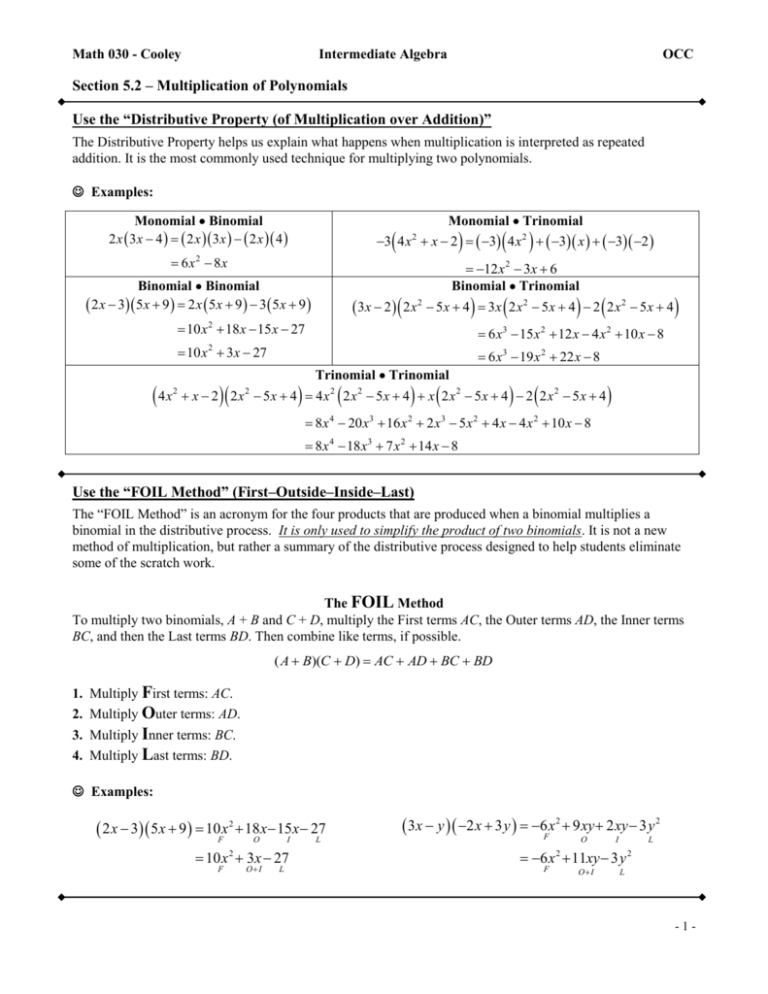
Math 030 - Cooley Intermediate Algebra OCC Section 5.2 – Multiplication of Polynomials Use the “Distributive Property (of Multiplication over Addition)” The Distributive Property helps us explain what happens when multiplication is interpreted as repeated addition. It is the most commonly used technique for multiplying two polynomials. Examples: Monomial Binomial 2 x 3 x 4 2 x 3 x 2 x 4 Monomial Trinomial 6 x 8x 2 12 x 2 3x 6 Binomial Trinomial Binomial Binomial 2 x 3 5x 9 2 x 5x 9 3 5x 9 3x 2 2 x 2 5 x 4 3x 2 x 2 5 x 4 2 2 x 2 5 x 4 10 x 2 18 x 15 x 27 6 x3 15 x 2 12 x 4 x 2 10 x 8 10 x 3x 27 6 x3 19 x 2 22 x 8 2 4x 2 3 4 x x 2 3 4 x 2 3 x 3 2 2 Trinomial Trinomial x 2 2 x 5x 4 4 x2 2 x2 5x 4 x 2 x2 5x 4 2 2 x2 5x 4 2 8 x 4 20 x3 16 x 2 2 x3 5 x 2 4 x 4 x 2 10 x 8 8 x 4 18 x3 7 x 2 14 x 8 Use the “FOIL Method” (First–Outside–Inside–Last) The “FOIL Method” is an acronym for the four products that are produced when a binomial multiplies a binomial in the distributive process. It is only used to simplify the product of two binomials. It is not a new method of multiplication, but rather a summary of the distributive process designed to help students eliminate some of the scratch work. The FOIL Method To multiply two binomials, A + B and C + D, multiply the First terms AC, the Outer terms AD, the Inner terms BC, and then the Last terms BD. Then combine like terms, if possible. ( A B)(C D) AC AD BC BD 1. Multiply First terms: AC. 2. Multiply Outer terms: AD. 3. Multiply Inner terms: BC. 4. Multiply Last terms: BD. Examples: 2 x 3 5 x 9 10Fx 2 18O x 15I x 27 L 10 x 3x 27 2 F O I L 3x y 2 x 3 y 6Fx 2 9 xy 2 xy 3 y 2 O I L 6 x 11xy 3 y 2 F O I 2 L -1- Math 030 - Cooley Intermediate Algebra OCC Section 5.2 – Multiplication of Polynomials Use “Special Products” or Formulas “Special Products” or Formulas are used to help us simplify some commonly encountered mathematical structures involved with polynomial multiplication. The formulas represent what happens after the polynomial multiplication process takes place and like terms are collected. The Square of a Binomial (a.k.a. Binomial Squared) a b a 2ab b 2 a b a 2 2ab b2 2 2 2 Why it Works: a b 2 a b 2 a b a b a 2 ab ab b 2 a 2 2ab b 2 F I L a b a b a ab ab b 2 a 2 2ab b 2 F O I L Examples: 3x 7 y 3x 2 3x 7 y 7 y 9 x 2 42 xy 49 y 2 2 2 2 2a 3 2a 2 2a 3 3 4a 2 12a 9 2 (These result is a perfect-square trinomial). The Product of a Sum and Difference of Two Terms (a.k.a. Product of Two Conjugates) a b a b a O 2 2 2 Why it Works: ab b2 a 2 b2 a b a b aF2 ab O I L Examples: 2 b 3x 4 y 3x 4 y 3x 4 y 2 2 2 9 x 2 16 y 2 (This results in a Difference of Two Squares). Exercises: Multiply, and if possible, simplify 1) 6(5 x 4 ) 2) 2 x3 4 x 3) 3uv 2 (5u 2v7 ) 4) 3x(x 5) 5) ( x 7)( x 7) 6) ( x 3)( x 3) 7) (3 x)(6 2 x) 8) x 12 x 15 -2- Math 030 - Cooley Intermediate Algebra OCC Section 5.2 – Multiplication of Polynomials Exercises: Multiply, and if possible, simplify 9) ( x 2 3)( x 1) 10) (4 x 1)(2 x 7) 11) (c 9)2 12) ( y 4)( y 4) 13) (5t 3)(5t 3) 14) (3a 2)(3a 2) 15) ( x 5)2 16) (5 2t 3 ) 2 17) (3 p 2 p)(3 p 2 p) 18) (5 x 2 2)(3x 3 8) 19) ( x 2)( x 2 x 7) 20) ( x 2 5 x 1)( x 2 x 3) 21) (4 x 2 5x 3)( x 2 2 x 4) 22) (t 5)2 (t 4)(t 4) -3-