Chapter 21
advertisement

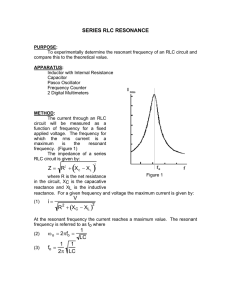
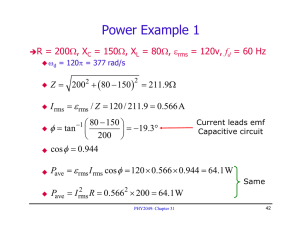
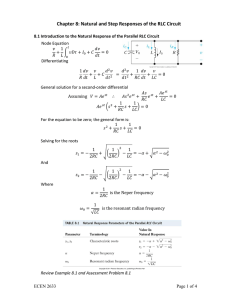
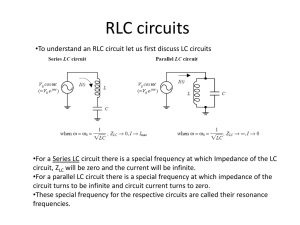
March 26, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion Spring ‘09 Conceptual Review: Chapter 21 A . RMS Current & Voltage 1. What is the definition of rms current/voltage? B. RLC Series AC Circuits 1. In an RLC circuit, rms voltages across each element are measured to be VR = 100 V, VL = 200 V and VC = 100 V. Calculate the rms voltage across the AC source & the phase angle. 2. Describe the asymptotic behaviors of current and phase angle when the AC frequency approaches zero or infinity. C. Power in AC Circuits 1. Express power factor in terms of resistance and impedance in an AC circuit. 2. An rms emf of 100 V is applied to an AC series circuit with R = 100 Ω, XL = 200 Ω and XC = 100 Ω. What is the power output? D. Resonance in RLC Series Circuits 1. If the frequency of an AC source is larger than the resonance frequency, does the applied voltage lead the current or lag behind current? 2. In RLC circuit in a radio is in resonance with AM 1500 KHz. If the radio station is changed to AM 750 KHz, by what factor must the capacitance be multiplied to achieve resonance again? E. Transformer 1. Explain why the voltage is stepped up in power plants before the electricity is sent to cities. F. Properties of Electromagnetic Wave 1. In what direction does an electromagnetic wave propagate with respect to the associated E and B fields? 2. A small spherical particle of radius r and density ρ is suspended by a vertical laser beam. What is the intensity of the laser beam if the particle perfectly absorbs the beam? March 26, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion – Spring ‘09 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 21) 1. An AC voltage source, with a peak output of 120 V, results in dissipation of energy in a resistor at rate of 100 W. What is the value of the resistance? (Rms Voltage & Current) a. 144 b. 120 c. 100 d. 72 2. An AC series circuit has 12.0 resistance, 15.00 inductive reactance and 10.00 capacitive reactance. If an effective (rms) emf of 120 V is applied, what is the effective (rms) current value? (Impedance in RLC Series Circuit) a. 5.31 A b. 9.23 A c. 10.8 A d. 26.0 A 3. A resistor, inductor, and capacitor are connected in series, each with an effective (rms) voltage of 65 V, 140 V, and 80 V, respectively. What is the magnitude of the phase angle in this circuit? (Phase Angle in RLC Series Circuit) a. 22 b. 28 c. 37 d. 43 4. The power dissipated in an AC series circuit increases as the phase angle approaches what value? (Power Factor) a. zero b. 45 c. 90 d. 180 5. What is the average power dissipation in an RLC series circuit in which R = 100 , L = 0.1 H, and C = 10 µF driven at resonance by a 100-V (rms) source? (Resonance in RLC Series Circuits) a. 100 W b. 500 W c. 1 000 W d. 2 W 6. An ideal transformer consists of a 500-turn primary coil and a 2 000-turn secondary coil. If the current in the secondary is 3.00 A, what is the primary current? (Transformer) a. 0.750 A b. 1.33 A c. 12.0 A d. 48.0 A 7. What is the maximum value of the electric field E at 1.0 m from a 100-W light bulb radiating in all directions? (µ0 = 4 107 Tm/A, c = 3.00 108 m/s) (Energy Carried by Electromagnetic Waves) a. 77 V/m b. 2 000 V/m c. 4 000 V/m d. 6 000 V/m 8. What value of inductance should be used in a series circuit with a capacitor of 1.8 103 F when designed to radiate a wavelength of 35 m? a. 3.8 mH b. 2.6 102 mH Answers: 1-d 2-b 3-d 4-a (c = 3.00 108 m/s) (Resonance Frequency in LC Circuits) c. 3.8 103 mH 5-a 6-c 7-a d. 1.9 104 mH 8-d