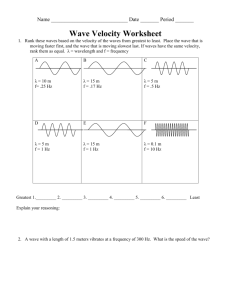
wave fig
advertisement
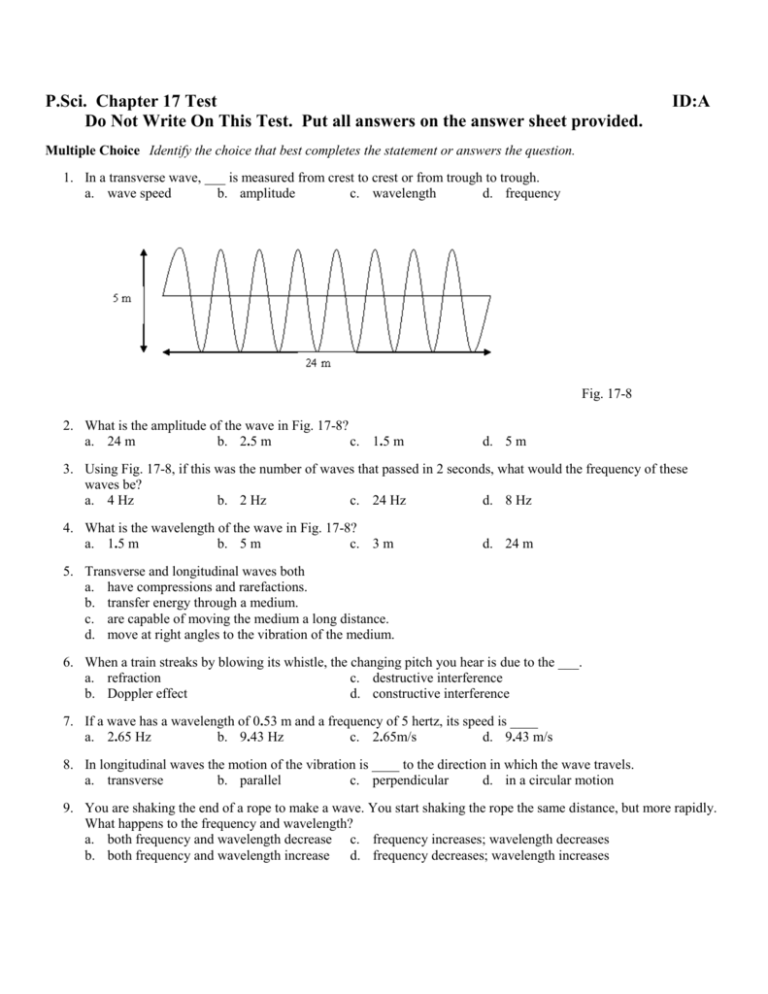
P.Sci. Chapter 17 Test Do Not Write On This Test. Put all answers on the answer sheet provided. ID:A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In a transverse wave, ___ is measured from crest to crest or from trough to trough. a. wave speed b. amplitude c. wavelength d. frequency Fig. 17-8 2. What is the amplitude of the wave in Fig. 17-8? a. 24 m b. 2.5 m c. 1.5 m d. 5 m 3. Using Fig. 17-8, if this was the number of waves that passed in 2 seconds, what would the frequency of these waves be? a. 4 Hz b. 2 Hz c. 24 Hz d. 8 Hz 4. What is the wavelength of the wave in Fig. 17-8? a. 1.5 m b. 5 m c. 3 m d. 24 m 5. Transverse and longitudinal waves both a. have compressions and rarefactions. b. transfer energy through a medium. c. are capable of moving the medium a long distance. d. move at right angles to the vibration of the medium. 6. When a train streaks by blowing its whistle, the changing pitch you hear is due to the ___. a. refraction c. destructive interference b. Doppler effect d. constructive interference 7. If a wave has a wavelength of 0.53 m and a frequency of 5 hertz, its speed is ____ a. 2.65 Hz b. 9.43 Hz c. 2.65m/s d. 9.43 m/s 8. In longitudinal waves the motion of the vibration is ____ to the direction in which the wave travels. a. transverse b. parallel c. perpendicular d. in a circular motion 9. You are shaking the end of a rope to make a wave. You start shaking the rope the same distance, but more rapidly. What happens to the frequency and wavelength? a. both frequency and wavelength decrease c. frequency increases; wavelength decreases b. both frequency and wavelength increase d. frequency decreases; wavelength increases Figure 17-3 10. What is the difference between wave A and wave B in Figure 17-3? a. Wave B has an amplitude that is one half the amplitude of wave A. b. Wave B has a wavelength that is 4 times that of wave A c. Wave A has a wavelength that is 3 times that of wave Bs d. Wave A has an amplitude that is one half the amplitude of wave B 11. What is the difference between wave C and wave D in Figure 17-3? a. Wave C has a frequency half that of wave D; Therefore, the wavelength in wave D is one half that of wave C. b. Wave D has a frequency twice that of wave C; Therefore, the wavelength in wave D is one half that of wave C. c. Wave C has a frequency twice that of wave D; Therefore, the wavelength in wave C is one half that of wave D. d. Wave D has a frequency half that of wave C; Therefore, the wavelength of wave C is half that of wave D 12. Which wave causes the medium to vibrate only in a direction perpendicular to the wave’s motion? a. a surface wave c. a longitudinal wave b. a transverse wave d. none of the above 13. In which medium does sound travel the fastest? a. cast iron b. salt water c. fresh water d. air 14. ___ is the unit that measures wave frequency? a. m/s b. hertz c. d. decibel 15. A sound wave is an example of a a. surface wave. b. longitudinal wave. c. standing wave. d. transverse wave. 16. An ambulance siren sounds different as it approaches you than when it moves away from you. What scientific term would you use to explain how this happens? a. rarefaction b. the Doppler effect c. diffraction d. ultrasound 17. A ___ is the material through which a mechanical wave travels. a. transverse wave b. medium c. logitudinal wave d. wavelength 18. A light wave bends as it passes from the air into water. This is called ____ a. diffraction b. rarefaction c. reflection d. refraction 19. Suppose two waves collide and the temporary combined wave that results is smaller than the original waves. What term best describes this interaction? a. constructive interference c. standing wave formation b. destructive interference d. diffraction 20. You shake the end of a rope to make a wave. You start shaking the rope a greater distance but at the same speed. How are the wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed affected? a. they all decrease b. wavelength, frequency, and speed remain the same; amplitude increases c. wavelength and frequency decrease, speed increases, and amplitude remains the same d. wavelength and frequency increase and speed and amplitude remain the same 21. To what is amplitude related? a. the amount of energy carried by the wave b. the maximum displacement from the rest position c. neither A nor B d. both A and B 22. Waves in a rope are transverse waves because the medium’s vibration is ____ to the direction in which the wave travels. a. longitudinal b. perpendicular c. parallel d. in a circular motion A B 23. Which of the above waves is a longitudinal wave? a. B b. both A and B c. neither A nor B d. A 24. A wave has a speed of 28.8 m/s and a frequency of 4.8 hertz. What is its wavelength? a. 6 mm/s b. 138.24 mm/s c. 6 m d. 138.24 m 25. Which type of mechanical wave needs a source of energy to produce it? a. a transverse wave c. a longitudinal wave b. a surface wave d. all of the above 26. In which medium would sound travel the slowest? a. air b. cast iron c. salt water 27. To find amplitude, measure a. from a crest to the rest position. b. from a trough to the rest position. d. fresh water c. neither A nor B d. either A or B Figure 17-1 28. Consider the properties of a wave—wave speed, amplitude, wavelength, period, and frequency. Which two properties could you determine the numerical values of by using only the information given in Figure 17-1? a. wavelength & frequency d. wave speed & frequency b. period & frequency e. amplitude & wavelength c. wave speed & period Matching Match the parts of the diagrams with the correct terms below them. 29. amplitude 30. trough 31. wavelength 32. crest 33. rarefaction 34. compression 35. wavelength True/False Indicate whether the statement is true (A) or false (B). 36. To compare the energy of different waves, measure the wavelength of the waves. 37. Sound waves cannot travel through solids. 38. As the frequency of sound waves increases, the wavelength of the sound waves decreases. 39. Reflection is the bending of a wave as it enters a new medium at an angle. 40. Two waves cannot occupy the same space at the same time. 41. Constructive interference produces a larger wave than the two original waves. 42. The energy of a mechanical wave depends on the amplitude of the wave. 43. Sound waves travel faster in a liquid than in a gas because the particle in a liquid are closer together. 44. Diffraction is the bending of a wave as it moves around an obstacle or passes through a narrow opening. 45. Refraction is when a wave bounces off a surface that it cannot pass through. P.Sci. Chapter 17 Test Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: C 2. ANS: B 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: C 5. ANS: B 6. ANS: B 7. ANS: C 8. ANS: B 9. ANS: C 10. ANS: A 11. ANS: B 12. ANS: B 13. ANS: A 14. ANS: B 15. ANS: B 16. ANS: B 17. ANS: B 18. ANS: D 19. ANS: B 20. ANS: B 21. ANS: D 22. ANS: B 23. ANS: A 24. ANS: C 25. ANS: D 26. ANS: A 27. ANS: D 28. ANS: B MATCHING 29. ANS: E 30. ANS: C 31. ANS: D 32. ANS: B 33. ANS: B 34. ANS: A 35. ANS: C TRUE/FALSE 36. ANS: F 37. ANS: F 38. ANS: T 39. ANS: F 40. ANS: F 41. ANS: T 42. ANS: T 43. ANS: T ID:A 44. ANS: T 45. ANS: F STA: SPS9.a STA: SPS9. STA: SPS9.d STA: SPS9.d STA: SPS9.e STA: SPS9.d STA: SPS9.b STA: SPS9.b STA: SPS9.a STA: SPS9.b