MS20 Laboratory: Waves on the Oceans
advertisement

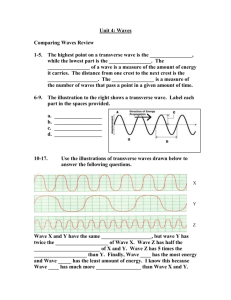
MS 20 Introduction To Oceanography Waves Team Number: Team Leader: Team Members: Section Time: A. Determining shallow-water wave speed as a function of depth TABLE A: DEPTH TIME IN SECONDS a 1 cm b Average CALCULATED VELOCITY THEORETICAL VELOCITY L/T from equation 6 31.3 cm/s 2 cm 3 cm 4 cm On the following graph, plot measured wave speed (solid line) against theoretical wave speed (dashed line). Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 1 of 8 The gravity on Mars is about one fourth that on Earth (2.5 m/s2 instead of 9.8 m/s2). If there were an ocean on Mars in the past, would you expect a wave traveling through shallow water to move faster or more slowly than on the Earth? Explain your answer. You have a deep-water wave moving onto shore with a with a wave speed of 12.5 meters per second. The period of the wave is S seconds. At what water depth will this wave begin to first interact with the sea bed? Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 2 of 8 B. Determining the period of a standing wave TABLE B: DEPTH TIME IN SECONDS/10 a b PERIOD THEORETICAL PERIOD (average of a & b) from equation X 10 cm 15 cm 20 cm The formula for the period of a standing wave is similar to the formula for a shallow water wave, the only difference being the factor of two. Make a sketch below to show why two basin lengths are needed to determine the standing wave period. You live on a narrow lake, 2000 m long and 40 m deep. What would be the period of the standing wave in the lake in seconds? Show your work. Make a sketch of the lake from the side, and indicate where on this lake would you experience maximum water-level fluctuations? Maximum horizontal currents? Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 3 of 8 C. Determining the period of a standing wave TABLE C: Internal wave Surface wave WAVE SPEED WAVE HEIGHT d1 h1 d2 h2 Theoretical wave speed Why is there such a large difference between the wave height of the internal wave and the surface wave ? If two fluids were closer in density than those used in this experiment, would you expect larger or smaller internal waves given the same input of energy? Explain! D. Ripple marks in sediment Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 4 of 8 D1: Fine grained ripple pattern D2: Coarse grained ripple pattern Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 5 of 8 Where are the maximum horizontal currents on the aquarium bottom? Minimum? (hint: maximum displacement of the sand indicates high currents) How do the ripple forms relate to the horizontal currents. (hint: examine wave length and wave height) Observe the ripple patterns and comment on the relationship between the creation of ripple forms and grain size. (hint: the currents are exactly the same in the two aquaria.) Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 6 of 8 E. Relationship between wavelength and water depth What do you observe happening to the wave speed as the waves approach the shoaling area? What do you observe happening to the wavelengths as the waves move from the deeper to shallower areas? Would waves of a longer length be slowed down further offshore than shorter waves? Explain. F. Refraction of waves How does the angle of the wave change as the waves move from deeper water into shallower water. Explain why this happens. Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 7 of 8 G. Wave interference The figure below shows two wave trains from two different storms passing through one another. For each of the waves (A and B) identify the period and maximum and minimum wave heights and enter the data on the figure below. Also plot the resultant wave. Revised on 2/6/2016 Page 8 of 8