math-alg1-leq-1
advertisement

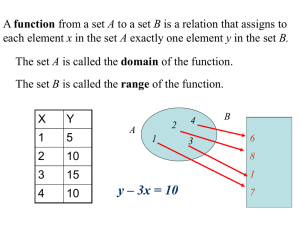
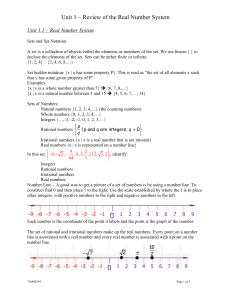
Unit 1 Real Number System UEQ: How do we use the properties of rational and irrational numbers and extend the properties of exponents to rational exponents? Lesson 1: Integer Exponents Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Learning Goals for this Lesson: Standards: MAFS.912.N-RN.1.1, MAFS.912.NRN.1.2, MAFS.912.N-RN.2.3, MAFS.912.N-Q.1.1 Students Will Know: Students Will Be Able To: That the sum and product of two rational numbers Find the sums and products of rational and is a rational number and an irrational number. That irrational numbers. Recognize that the sum of a the product of a nonzero rational number and an rational number and a irrational number is irrational number is a irrational number. irrational. Recognize that the product of nonzero rational number and a irrational number is irrational. Lesson Essential Question: How do the properties of rational and irrational numbers determine their sums and products? Activating Strategy: Have the students evaluate each expression on the processing side of their cornell notes. We will go over the answers to the questions in Learning Activity 2. 1) 2) 3) Key Vocabulary to Preview and Vocabulary Strategy: Zero exponent, negative exponent, base, power, rational number, irrational number, integer, whole number, natural number Lesson Instruction: Learning Activity 1: Introduce Vocabulary: base, power, exponent, zero exponent, negative exponent (in the numerator and in the denominator). Show and model examples of each vocabulary term. Assessment Prompt for LA 1: Quick Write: Have the students write in their cornell note books the answer to the following questions: (answer must be written in at least three complete sentences) What is the difference between a negative exponent in the Graphic Organizer: Cornell Notes Guided Notes: Exponents and Radicals Graphic Organizer: Properties of Exponents numerator and a negative exponent in the denominator? What happens to the solution when the negative exponent is in the numerator or in the denominator? Differentiation: Learning Activity 2: Model and Explain to students how to simplify expressions that have a zero and negative exponents. But FIRST REVIEW how to solve an expressions that uses an exponent. For example: = means 7 x 7 not 7 x 2. Review the student’s answers to the Activating Strategy. Common Error: Assignment: Textbook Pages 392397 Workbook Pages 321326 Students forget that the exponent wants the number to be multiplied by itself not the number that is in the exponent. Zero – Exponent: any number raised to the power of zero will ALWAYS equal 1. Negative Exponent: (negative number in the numerator) set the expression equal to 1 and divide by the base/exponent, and change the exponent to a positive value. (negative number in the denominator) set the expression equal to 1 and multiply by the base exponent and change the exponent to a positive value. See examples 1 and 2 on text book page 393. Work book practice problems on page 324. Assessment Prompt for LA 2: Collaborative Pairs: one student will simplify , the other student will simplify . The first student will explain how they got their answer to the other student and vis versa. If a student disagrees with the other student’s answer, they must work together to find the correct solution. Differentiation: Learning Activity 3: Model and Explain to the students how to evaluate expressions with zero and negative exponents. Common Error: When evaluating an expression using exponents you not only have to simplify the expression you also have to find the solution to the expression. Remember: any number with an exponent of zero will ALWAYS be 1. NO MATTER THE NUMBER. Negative Exponents are another story. KNOW: if the negative exponent is in the numerator the solution will be a fraction. If the negative exponent is in the denominator then the solution will be a whole number. For example: and x=2 Step 1: put the expression into a fraction . Remember to change the negative exponent to a positive value. Step 2: Substitute the value of 2 into the expression for the value of x. Step 3: Simplify the expression denominator of the expression. = 2 x 2 which is 4. Place the 4 in the Step 4: The solution is See example 3 on page 393 in the text book. Assessment Prompt for LA 3: Collaborative Pairs: one student will evaluate the expression the other student will evaluate the expression where p = 2, where p is = 3. The first student will explain how they got their answer to the other student and vis versa. If a student disagrees with the other student’s answer, then they will work together to find the correct solution to the problem. Practice Assignment: TB: 395-397 Basic: #12-23 Advanced: # 43-65 Extra Credit: # 86-93 Quick Check Homework: 24,28,34,42,52,77 Differentiation: Learning Activity 4: Model and Explain to the students how to simplify more complex expressions with zero and negative exponents. Expressions with more than one variable or part will require multiple steps to find the solution. For example: The expression reads 3 times . Since the expression is NOT in parenthesis the negative exponent is only associated with the y variable/ IF the expression has parenthesis then the negative exponent would be associated with the 3y. To Simplify . Step 1: Separate the expressions into pieces. 3 x . Step 2: Since the value of 3 is positive then it stays the same, but since the y has a negative exponent then it will be set equal to 1 and divide by the variable and negative exponent. (change the negative exponent to a positive exponent). Then combine the expression with 3. 3x Solution is See example 4 on page 394 in the text book. Assessment Prompt 4: Think-Ink-Pair-Share: Students will see the following expression on the board and they must list the steps on how to simplify the expression. Then they will share and compare with steps with the other student (partner). Differentiation: Learning Activity 5: Introduce the Properties of Exponents: refer to page 331 in their work books to see the chart for properties of exponents. Model and Explain how each property works. Provide the students with the Properties of Exponents worksheet from them to complete the examples and practice problems. “Foldable or Graphic Organizer that you can use. See attached.” Assessment Prompt 5: Think-Ink-Pair-Share: Provide the students with the following list of expressions. Have the students name which property of exponents they need to use to simplify the expression, and they have them simplify the expressions. Once the students have completed the activity they will share their answers with their partner. If one student does not agree with the other student’s answer then they must work together to find the correct solution. Differentiation: Summarizing Strategy: Ticket Out The Door: Have the students choose three exercises from page 395 numbers 37-42, write each expression in words and then show two different ways to evaluate each expression.