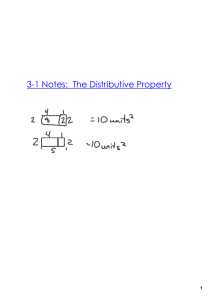
Equations and Problem Solving (wkbk p30)
advertisement

Fold here Equations and Problem Solving 2.5 Solve each formula in terms of the given variable. 1. 5d – 2g = 9; g 2. 4xy + 3 = 5z; y 3. d(a – b) = c; a 4. 5 1 (b c); b 2 2 5. The formula A = 2h(l + w) give the lateral area (A) of a rectangle solid with length (l), width (w), and height (h). Find h if A=37.4ft2, l- 4.3ft, and w = 6.7 ft. Like terms – have exactly the same variable factors. The coefficient does not matter. Use any of the following symbols to show the like terms below: O 3x -5x2 -7x2y3 3z 4y x2y xy2 -2x Examples 1. 6x – 2 = x +13 2. 4p – 10 = p + 3p – 2p 3. 3(x-4) = 3x – 12 4. 9x + 3x – 10 = 3(3x+x) SOLVING EQUATIONS WITH VARIABLES ON BOTH SIDES 2.4 *Solving equations with variables on both sides is a great way to solve real-life situations such as cost comparisons. STEPS 1. Combine like terms on each side of the equation (equal sign). Hint: Use the Distributive Property to get rid of parentheses. 2. Combine like terms across the equation/equal sign. Hint: Use the Addition or Subtraction Property of Equality. Sample A Sample B Sample C 6(w – 5) = 3w + 12 18x + 6 = 3(6x + 1) 3(x + 8) + 5x = 2(12 + 4x) 6w – 30 = 3w + 12 18x + 6 = 18x + 3 8x +24 = 24 + 8x 3. Isolate the variable (get the variable alone). Hint: Use the Multiplication or Division Property of Equality. 4. Simplify Fold here Distributive Property: For every real number a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac (b + c)a = ba + ca a(b – c) = ab – ac (b – c)a = ba – ca Example: 1. 3(4m – 7) 2. (3 – 8x)(-1) COMBINING LIKE TERMS/DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY 1.7 Turn this page upside down before copying. 1. Addition Property Of Equality Subtraction Property Of Equality For every real number a, b, and c, For every real number a, b, and c, If a = b, then a + c = b + c. If a = b, then a – c = b – c. x–3=–8 2. b – 13 = – 24 1. m + 5 = 8 2. 9 + y = 11 1. 72 + 4 – 14 c 2. -13 = 2b – b – 10 3. 5 (y – 3) = 19 4. x/6 – 7 2/3 5. ¼(g – 16) = 7 SOLVING MULTI- STEP EQUATIONS 2.3 Turn this page upside down before copying. STEPS FOR SOLVING A MULTI-STEP EQUATION 1. Clear the equation of fractions and decimals. 15 = -3(x – 1) + 9 -2y + 5 + 5y = 14 2. Use the Distributive Property to remove parentheses on each side. Skip (no parentheses) 3. Combine Like Terms on each side. 4. Undo addition or subtraction. 5. Undo multiplication or division. Fold here 1. 3. Multiplication Property of Equality Division Property of Equality For every real number a, b, and c, For every real number a, b, and c, If a = b, then ac = bc. If a = b, then a b . m 5 6 2. d 20 5 3 x 15 8 SOLVING ONE-STEP EQUATIONS c 1. 3f = 12 2. -8 = 5y 3. -7k = 9 c 2.1 STEPS FOR SOLVING 2-STEP EQUATIONS 1. Use the Addition or Subtraction Property of Equality to get the term with a variable alone on one side of the equation. x 15 12 9 3x – 2 = 4 2. Use the Multiplication or Division Property of Equality to write an equivalent equation in which the variable has a coefficient of 1. 1. 3. 10 m 2 4 x 5 1 12 SOLVING TWO-STEP EQUATIONS 2. – a – 5 = -8 4. 8 – 3y = 14 2.2