Year 11 Physics Formulae Booklet (Foundation Tier)
advertisement

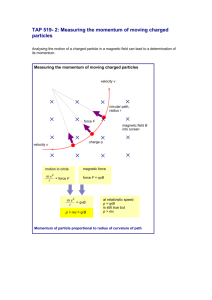
Year 11 P2 Additional Physics Foundation Tier Formulae Booklet 1 P2 1 Motion 1. Distance-time graphs: The slope of the graph = speed of the object. d d = distance (m) s = speed (m/s) t = time (s) s x t 2. Velocity-time graphs: An upwards slope on the graph = acceleration A downwards slope on the graph = deceleration (will be a negative number) v-u a x t v = final velocity (m/s) u = initial velocity (m/s) a = acceleration (m/s2) t = time (s) The area under the line = distance travelled (m) You will need to section your graph into rectangles and/or triangles. Remember! Area of a rectangle = height x base Area of a triangle = ½ height x base P2 2 Speeding up & Slowing down 1. Resultant force F m x a F = force (N) m = mass (kg) a = acceleration (m/s2) 2. Stopping distance Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance 3. Weight Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) 2 P2 3 Work, energy and momentum 1. Work done Work done = energy transferred W F x D W = work done (J) F = force (N) D = distance moved in the direction of the force (m) (Note the similarity to the equation used to calculate gravitational potential energy in year 10!) 2. Momentum momentum = mass x velocity P P = momentum (kgm/s)) M = mass (kg) V = velocity (m/s) M x V total momentum before = total momentum after 3.Conservation of momentum in an explosion Remember the momentum of an explosion before = 0 Therefore, total momentum after explosion = 0 So: (mass of A x velocity A) = - (mass of B x velocity of B) P2 5 Current electricity 1 Resistance Resistance = potential difference current V Rx I R = resistance = (ohms, ) V = potential difference (volts, V) I = current (amperes, A) 2 Resistance in a series circuit Add up the resistance of all the components in a series circuit. 3 3 Current Is a rearrangement of the resistance equation: current = potential difference resistance P2 6 Mains electricity 1 Power of an appliance power = energy transformed time ET Px t ET = energy transformed (joules, J) P = power (watts, W) T = time (secs) 2 Power supplied power supplied = current x potential difference P P = power supplied (watts, W) V = potential difference (volts, V) I = current (amperes, A) Vx I P2 7 Nuclear Physics 1 Radioactive decay -emission = atomic number (Z) down 2, mass number (A) down 4 -emission = atomic number (Z) up 1, mass number (A) stays same -emission = atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) both stay same Learn these formula triangles and equations and you can’t go wrong! Remember before you start the exam write all the formula triangles down in the front so that you can look back at them. In foundation tier you will not be expected to rearrange equations. Just use them in the format in which they are given to you! 4