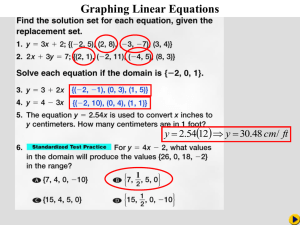
First Quarter apply necessary test-taking strategies in different
advertisement
Syllabus: Algebra 1 Course Number: 212 September 2010 J. O’Connor Course: Algebra 1 (212) Grade Level: Freshwomen First Quarter Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter 687286548 apply necessary test-taking strategies in different situations (recognizing key words, guess & check, process of elimination) identify and use variables and expressions identify and use patterns and sequences use order of operations to simplify numerical expressions create and use stem- and-leaf plots solve open sentences for given values identify and use identity and inequality properties, distributive. commutative, and associative properties use operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide) with integers and rational numbers simplify simple square roots making a table measurement write equations, inequalities for verbal expressions solve equations using +, -, *, / solve multi-step equations solve equations with variable on both sides solve formulas for a given variable recognize and write ratios solve proportions using proportional reasoning to arrive at an answer making and interpreting graphs applying probability and odds to real-world situations solve problems involving percents (money applications) use direct and inverse variation to solve problems explore the coordinate plane and graph ordered pairs identify domain, range, and inverse of a relation use mapping, tables, graphs to show relations graph linear equations using tables, slope and y- intercepts use TI -83 calculator to find ordered pairs to graph in a line calculate slope of a line graphically and algebraically apply concept of slope to real-life problems write linear equations in slope-intercept point-slope and standard forms writing equations from patterns and working backwards to solve a problem write linear equations in various forms solve systems of equations using graphing, substitution and elimination use TI-83 calculator to solve systems of equations and to graph lines organize data applying inequalities in science prepare for and take a comprehensive Exam presentation skills (public speaking, recognizing important information to convey) 1 22-Aug-10 At the end of Chapter 1, the student will be able to... • translate verbal expressions into mathematical expressions and vice versa • solve problems by looking for a pattern • use the order of operations to evaluate real number expressions • display and interpret data on a stem-and-leaf plot • solve open sentences by performing arithmetic operations • use the properties of identity and equality • determine the multiplicative inverse of a number • use the distributive property to simplify expressions • interpret graphs in real-world settings • sketch graphs for given functions At the end of Chapter 2, the student will be able to... • state the coordinate of a point on a number line • graph integers on a number line • interpret numerical data from a table • display and interpret statistical data on a line plot • find the absolute value of a number • add and subtract integers • compare and order rational numbers • find a number between two rational numbers • add and subtract rational numbers • simplify expressions that contain rational numbers • multiply rational numbers • divide rational numbers • find square roots • classify numbers • graph solutions of inequalities on number lines • translate verbal sentences and problems into equations or formulas and vice versa At the end of Chapter 3, the student will be able to... • solve equations by using addition and subtraction • solve equations by using multiplication and division • solve equations involving more than one operation • solve problems by working backwards • find the complement and supplement of an angle • find the measure of the third angle of a triangle given the measures of the other two angles • solve equations with the variable on both sides • solve equations containing grouping symbols • solve equations and formulas for a specified variable • find and interpret the mean, median, and mode of a set of data 687286548 2 22-Aug-10 At the end of Chapter 4. the student will be able to... • collect data to determine ratios • solve proportions • find the unknown measures of the sides of two similar triangles • use trigonometric ratios to solve right triangles • solve percent problems • solve problems involving simple interest • solve problems involving percent of increase or decrease • solve problems involving discounts or sales tax • find the probability of a simple event • find the odds of a simple event • solve mixture problems • solve problems involving uniform motion • solve problems involving direct and indirect variation At the end of Chapter 5. the student will be able to... • graph ordered pairs on a coordinate plane • solve problems by making a table • use a graphing calculator to graph relations • identify the domain, range, and inverse of a relation • show relations as sets of ordered pairs, tables, mappings, and graphs • use a graphing calculator to investigate relations and determine the ranges when the domains are given • determine the range for a given domain • graph the solution set for the given domain • use a graphing calculator to graph linear relations and functions • graph linear equations • determine whether a given relation is a function • find the value of a function for a given element of the domain • use a graphing calculator to calculate measures of variations • calculate the range, quartiles, and interquartile range of sets of data At the end of Chapter 6, the student will be able to... • find the slope of a line, given the coordinates of two points on the line • write the linear equation im point-slope form • write linear equations in standard form • graph and interpret points on a scatter plot • draw and write equations for best-fit lines, and make predictions by using those equations • solve problems by using models • determine the x- and y-intercepts of linear graphs from their equations • write equations in slope-intercept form • write and solve direct variation equations • graph a line given any linear equation • determine if two lines are parallel or perpendicular by their slopes • write equations of lines passing through a given point, parallel or perpendicular to the graph of a given equation 687286548 3 22-Aug-10 At the end of Chapter 7, the student will be able to... • solve inequalities by using addition and subtraction • solve inequalities by using multiplication and division • solve inequalities involving more than one operation • find the solution set for a linear inequality when replacement values are given for the variables • solve problems by making diagrams • solve compound inequalities and graph their solution sets • solve problems that involve compound inequalities • find the probability of a compound event • solve open sentences involving absolute value and graph the solutions • use a graphing calculator to display and interpret data on box-and-whisker plots At the end of Chapter 8, the student will be able to... • solve systems of equations by graphing • determine whether a system of equations has one solution, no solutions, or infinitely many solutions by graphing • solve systems of equations by the substitution method • organize data to solve problems • solve systems of equations by the elimination method • use a graphing calculator to solve systems of equations At the end of Chapter 9, the student will be able to... • multiply monomials • simplify expressions involving powers of monomials • solve problems by looking for a pattern • simplify expressions involving quotients of monomials • simplify expressions containing negative exponents • use a graphing calculator to express numbers in scientific notation and standard notation • find the degree of a polynomial • arrange polynomials so that the powers of the variables are in ascending or descending order • add and subtract polynomials • multiply a polynomial by a monomial • simplify expressions involving polynomials • use the FOIL method to multiply two binomials • multiply any two polynomials by using the distributive property • use patterns to find (a + b)2, (a - b)2, and (a + b)(a - b) In Chapter 10, the student will be able to... • find the prime factorization of integers • find the greatest common factors (GCF) for sets of monomials • use the GCF and the distributive property to factor polynomials • identify and factor binomials that are the differences of squares • identify and factor perfect square trinomials 687286548 4 22-Aug-10 In Chapter 12, the student will be able to... • simplify rational expressions • multiply rational expressions • divide rational expressions • add and subtract rational expressions with like denominators In Chapter 13, the student will be able to... • simplify square roots • simplify radical expressions EXAM TEMPLATE for Algebra 1 (Course # 212) Semester Exams will test mastery of skills appropriate to the course, problems that require the application of previously learned concepts and real-world applications. Students will also be expected to apply their knowledge to previously unseen applications. The test will consist of: • Multiple choice items • Skill based problems to be completed manually and/or by using a graphing calculator • Open-ended questions • Word problems involving real-world applications • Short answers involving explanations of procedures and/or facility with mathematical vocabulary 687286548 5 22-Aug-10