Physics Worksheet: Friction and Newton's Laws
advertisement

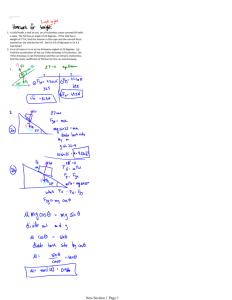
Name Date Pd UNIT V: Worksheet 4 1. Suppose a hanging 1.0 kg lab mass is attached to a 4.0 kg block on the table. Fnet = ma a = Fnet m a. If the coefficient of kinetic friction, µk is 0.20., what is the acceleration of the block? Fn = +40N Fg-block =-40N Fapplied = Fg –mass = 10N Ff = 0.20(+40N) = 8N Fnet = Ff + Fapplied = -8N + 10N = +2N = 5.0kg(a) a = +0.2m/s2 b. What would be the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction, µs, in order for the block to remain motionless? Fnet = Ff + Fapplied = -10N + 10N = 0N so 10N=µs40N µs= 0.25 2. A block weighing 300. N is moved at constant speed over a horizontal surface by a force of 50. N applied parallel to the surface. a. Construct a force diagram for the block. ©Modeling Workshop Project 2006 1 Unit V ws4 v3.0 b. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? c. What would be the acceleration of the block if k = 0? 3. A 100. N force is applied to a 50. kg crate resting on a level floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. a. Draw a force diagram to represent this situation. b. What is the acceleration of the crate? ©Modeling Workshop Project 2006 2 Unit V ws4 v3.0 4. In the situation described above, the coefficient of static friction, s = 0.25. Is the 100. N force sufficient to cause the crate to accelerate? Draw a force diagram, then explain why or why not. No. The force applied would be 100.N and the force of static friction would be 125N. Therefore the minimum force is not present to begin moving the object. 5. A 10 kg block is allowed to slide down a ramp with k = 0.15. a. What is the value of the frictional force opposing the block's slide down the ramp? b. What is the acceleration of the block? ©Modeling Workshop Project 2006 3 Unit V ws4 v3.0