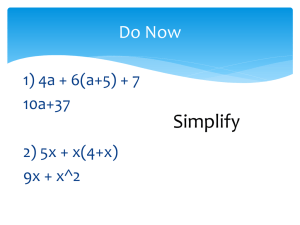
Unit 6 Equations and Inequalities
advertisement

MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 Unit Description Big Idea(s) What enduring understandings are essential for application to new situations within or beyond this content? Unit: 6 Title: Equations and Inequalities Suggested Length: 4 weeks Enduring Understandings Writing, solving, and understanding variables in mathematical expressions and equations. Enduring Skills Rubric measures competency of the following skills: Equivalence: A given equation can be represented in an infinite number of different ways that have the same solution (e.g., 3x – 5 = 16 and 3x = 21 are equivalent equations; they have the same solution, 7). Comparison: Numerical and algebraic expressions can be compared using greater then, less than, or equal. Operation Meanings & Relationships: Adding x is the inverse of subtracting x. Multiplying by x is the inverse of dividing by x. Variable: Letters are used in mathematics to represent generalized properties, unknowns in equations, and relationships between quantities. Relations & Functions: Mathematical relationships can be represented and analyzed using words, table, graphs, and equations. In mathematical relationships, the value for one quantity depends on the value of the other quantity. The graph of a relationship can be analyzed with regard to the change in one quantity relative to the change in the other quantity. Essential Question(s) What questions will provoke and sustain Curriculum and Instruction Equations & Inequalities: A solution to an equation is a value of the unknown or unknowns that make the equation true. Properties of equality and reversible operations can be used to generate equivalent equations and find solutions. Techniques for solving equations can be applied to solving inequalities, but the direction of the inequality sign needs to be considered when negative numbers are involved (7th grade). • How is an equation like a balance? How can the idea of balance help me solve an equation? • What strategies can I use to help me understand and represent 2015-2016 Page 1 of 7 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 student engagement while focusing learning? Standards real situations using equations and inequalities? How can I write, interpret and manipulate equations and inequalities? • How can I solve an equation? • How can I tell the difference between an expression, equation and an inequality? • How are the solutions of equations and inequalities different? • What does an equal sign mean mathematically? • How does a change in one variable affect the other variable in a given situation? • Which tells me more about the relationship I am investigating, a table, a graph or a formula? Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Students choose the appropriate algebraic representations for given contexts and can create contexts given equations or inequalities. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students represent a wide variety of real world contexts through the use of real numbers and variables in mathematical expressions, equations, and inequalities. Students contextualize to understand the meaning of the number or variable as related to the problem and decontextualize to manipulate symbolic representations by applying properties of operations. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students construct arguments using verbal or written explanations accompanied by expressions, equations, inequalities, models, graphs, and tables. 4. Model with mathematics. Students model problem situations in symbolic, graphic, tabular, and contextual formats. Students form expressions, equations, and inequalities from real world contexts and connect symbolic and visual representations. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. Students use number lines to graph equations and inequalities. Students use tables to organize information to write equations and inequalities. 6. Attend to precision. Students precisely define variables. 7. Look for and make use of structure. Students seek patterns or structures to model and solve problems using tables, and equations. Students seek patterns or structures to model problems using tables and inequalities. Students apply properties to generate equivalent expressions (i.e. 6 + 2x = 3 (2 + x) by distributive property) and solve equations (i.e. 2c + 3 = 15, 2c = 12 by subtraction property of equality, c = 6 by division property of equality). 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Students generalize effective processes for representing equations and inequalities based upon experiences. Students will be solving for equations. Standards for Mathematical Content 6.EE.5 Understand solving an equation or inequality as a process of Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 2 of 7 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 answering a question: which values from a specified set, if any, make the equation or inequality true? Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specified set makes an equation or inequality true. Supporting Standard(s) Which related standards will be incorporated to support and enhance the enduring standards? 6.EE.6 Use variables to represent numbers and write expressions when solving a real-world or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number, or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set. 6.EE.7 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers. 6.EE.8 Write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem. Recognize that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have infinitely many solutions; represent solutions of such inequalities on number line diagrams. 6.EE.9 Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. For example, in a problem involving motion at constant speed, list and graph ordered pairs of distances and times, and write the equation d = 65t to represent the relationship between distance and time. 6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. 6.NS.3 Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation. 6.NS.4 Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. For example, express 36 + 8 as 4 (9 + 2). 6.NS.7 Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. a. Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 3 of 7 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. For example, interpret –3 > –7 as a statement that –3 is located to the right of –7 on a number line oriented from left to right. 6.NS.8 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.RP.3 Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. a. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. 6.EE.1 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. 5th grade Standards 5.OA.1: Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols. Instructional Outcomes What must students learn and be able to do by the end of the unit? Curriculum and Instruction I am learning to…. Recognize solving an equation or inequality as a process of answering “which value from a specified set, if any, make the equation or inequality true?” Know that the solutions of an equation or inequality are the values that make the equation or inequality true. Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specified set makes an equation or inequality true. Recognize that a variable can represent an unknown number or any number in a specified set. Relate variables to context. Define inverse operation. Know how inverse operations can be used in solving one-variable equations. Apply rules of the form x + p = q and px = q, for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers, to solve real world and mathematical problems. (There is only one unknown quantity.) Develop a rule for solving one-step equations using inverse operations 2015-2016 Page 4 of 7 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 Essential Vocabulary What vocabulary must students know to understand and communicate effectively about this content? Curriculum and Instruction with nonnegative rational coefficients. Solve and write equations for real-world mathematical problems containing one unknown (Include whole numbers and decimals). Identify the constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem in order to set up an inequality. Recognize that inequalities of the form x >c or x < c have infinitely many solutions. Write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem. Represent solutions to inequalities or the form x > c or x < c, with infinitely many solutions, on number line diagrams. Define independent and dependent variables. Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another. (Ex., d=rt) Write an equation to express one quantity (dependent) in terms or the other quantity (independent). Analyze the relationship between the dependent variable and independent variable using tables and graphs. Relate the data in a graph and table to the corresponding equation. Essential Vocabulary Additive Inverse Constraint (for an inequality) Dependent Variable Equation Evaluate Independent Variable Inequality Inverse Operations Multiplicative Inverse Solution of an Equation Solution of an Inequality Substitution Variable Supporting Vocabulary Axis Equivalent Greater than (>) Less than (<) Rational number (nonnegative) 2015-2016 Page 5 of 7 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 6 Resources/Activities What resources could we use to best teach this unit? Resources/Activities https://www.georgiastandards.org/CommonCore/Common%20Core%20Frameworks/CCGPS_Math_6_6thGrade_Unit4.pdf The following website is a website with lessons to address CCSS: https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics Khan Academy – www.khanacademy.org IXL – www.ixl.com http://www.insidemathematics.org/common-core-resources/mathematicalcontent-standards/standards-by-grade/6th-grade http://www.mathchimp.com/6th-grade-math-resources Remember there are other sources in your school that may not be listed on this resources list due to variation in each individual school. If you have a good resource that you would be willing to share, please let Mendy Mills know so that she can share with other math teachers. Mendy.Mills@madison.kyschools.us Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 6 of 7 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 7 of 7