Solutions
advertisement

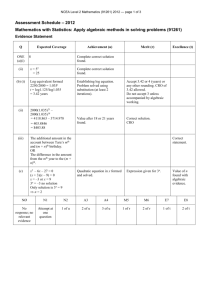
1. Determine whether solutions exist for each of the following quadratic equations. Where they do find the solution(s). Firstly determine whether solutions exist using the following criteria: Two solutions b2 4ac 0 2 One solution b 4ac 0 2 No solution b 4ac 0 Secondly find the solution where possible using the formula: x (i) b b 2 4ac 2a x2 2x 0 a=1, b=-2, c=0 b2 4ac 22 410 4 0 two solutions exist b b 2 4ac 2 4 2 2 2a 21 2 22 x 2 2 22 x 0 2 x (ii) 3x 6x 1 0 Multiply out the quadratic 3x 2 3x 6 0 Divide across by 3 x2 x 2 0 a=1, b=-1, c=-2 b2 4ac 12 41 2 9 0 two solutions exist b b 2 4ac 1 9 1 3 2a 21 2 1 3 x 2 2 1 3 x 1 2 x (iii) 9 x 2 24 x 16 0 a=9, b=-24, c=16 b2 4ac 242 4916 576 576 0 x b b 2 4ac 24 0 24 1.33 2a 29 18 one solution (iv) 3x 2 2 x 3 0 a=3, b=2, c=3 b2 4ac 22 433 4 36 32 0 no solution (v) 2 x 2 11x 21 0 a=2, b=11, c=-21 b2 4ac 112 42 21 121 168 289 0 two solutions b b 2 4ac 11 289 11 17 2a 22 4 11 17 11 17 x 1.5 x 7 4 4 x (vi) 2 x 2 x 10 0 a=-2, b=1, c=10 b2 4ac 12 4 210 81 0 two solutions b b2 4ac 1 81 1 9 2a 2 2 4 1 9 1 9 x 2 x 2 .5 4 4 x 2 A firms demand function for a good is given by P = 107-2Q and their total cost function is given by TC = 200+3Q . i) Obtain an expression for total revenue profit in terms of Q Total Revenue = P.Q TR = (107-2Q)*Q = 107Q-2Q2 Profit = TR-TC Profit = 107Q-2Q2-200-3Q = -2Q2+104Q-200 ii) For what values of Q does the firm break even Firm breaks even where Profit = 0 -2Q2+104Q-200 = 0 a = -2, b=104, c=-200 Q 104 Q 2, Q 50 1042 4 2 200 104 2 2 10816 1600 104 96 4 4 iii) Illustrate the answer to (ii) using sketches of the total cost function, the total revenue function and the profit function 2000 TC / TR / Profit 1500 Proft = 1150 1000 500 TC TR 0 0 10 30 20 40 Q = 26 50 Profit Profit -500 Note: Break even where Profit = 0 or TR=TC. iv) From the graph estimate the maximum profit and the level of output for which profit is maximised Maximum profit at max point on profit curve. Max profit = 1150 at Q = 26 3. What is the profit maximising level of output for a firm with the marginal cost function MC = 1.6Q2-15Q+60 and a marginal revenue function MR = 280-20Q? Profit is maximised where MR=MC 280-20Q = 1.6Q2-15Q+60 1.6Q2+5Q-220=0 a=1.6, b=5, c=-220 Q 5 52 41.6 220 5 21.6 25 1408 5 37.85 3.2 3.2 Q 10.27, Q 13.39 Profit maximising level of output is Q = 10.27 (can’t have negative output) Q 60 4. The demand function for a good is given as Q = 130-10P. Fixed costs associated with producing that good are €60 and each unit produced costs an extra €4. i) Obtain an expression for total revenue and total costs in terms of Q TR = P.Q Q = 130-10P 10P = 130-Q P = 13-Q/10 TR = (13-Q/10)*Q = 13Q-0.1Q2 TC = FC+VC TC = 60+4Q ii) For what values of Q does the firm break even Firm breaks even where TR = TC 13Q-0.1Q2=60+4Q -0.1Q2+9Q-60=0 a=-0.1, b=9, c=-60 Q 9 92 4 0.1 60 9 81 24 2 0.1 0.2 9 7.55 0.2 Q 7.25, Q 82.75 iii) iv) Obtain an expression for profit in terms of Q and sketch its graph Use the graph to confirm your answer to (ii) and to estimate maximum profit and the level of output for which profit is maximised Profit = TR-TC Profit = 13Q-0.1Q2-60-4Q=-0.1Q2+9Q-60 200 Profit 150 Profit Max Profit = 143 100 Profit 50 Q 0 0 -50 -100 10 Break Even Q = 7.25 20 30 40 50 Profit Max Q = 45 60 70 80 Break Even Q = 82.75 90