Intermediate Algebra for Statistics & Finite Math
advertisement

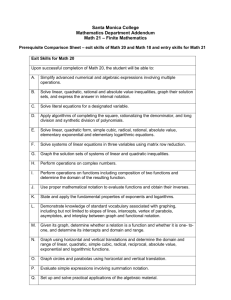
Santa Monica College Mathematics Department Addendum Math 18 – Intermediate Algebra for Statistics & Finite Math Prerequisite Comparison Sheet – exit skills of Math 31 and entry skills for Math 18 Exit Skills for Math 31 Upon successful completion of Math 31, the student will be able to: A. Solve linear, quadratic, and literal equations, and systems of equations and linear inequalities. B. Graph linear equations and inequalities C. Factor polynomials at an elementary level. D. State and apply the quadratic formula. E. Add, subtract, multiply and divide polynomials, square roots and rational expressions F. Simplify complex fractions, square roots and exponential expressions. G. Solve introductory level equations with rational and radical expressions. H. Translate and solve algebraic word problems in a single variable I. Given the description of a graph of a line, write an equation of the line. J. Define and use properties of equality and inequality K. Recognize and use common mathematical language to describe mathematical processes in either written or verbal form. L. Apply units of measurements in the solution of algebraic applications as appropriate : Entry Skills for Math 18 Prior to enrolling in Math 18 students should be able to 1. Perform basic operations on polynomials. .2. Factor general trinomials at an elementary level 3. Solve linear equations in a single variable over the rationals Santa Monica College Page 2 of 5 Entry Skills for Math 18 4. Solve second degree polynomial equations in a single variable over the rationals by factoring 5. Simplify square roots. 6. Solve first degree linear inequalities in a single variable 7. Solve applications involving equations in a single variable. 8. Solve linear systems of two equations in two variables 9. Graph first degree equations/ inequalities in one and two variables 10. Given the description of a graph of a line, write the equation of the line Santa Monica College Page 3 of 5 Santa Monica College Student Learning Outcomes Date: Fall 2009 Course Name and Number: Math 18 Intermediate Algebra for Statistics and Finite Mathematics Student Learning Outcome(s): Individual faculty members will develop and reports on assessments for SLOs. 1. Given a multi-step application problem, students will apply algebraic concepts and vocabulary to formulate an appropriate equation, inequality, or system of equations or inequalities, solve this mathematical problem, and interpret the answer. 2. Given equations such as linear, quadratic, logarithmic and exponential, students will solve for the indicated variable Demonstrate how this course supports/maps to at least one program and one institutional learning outcome. Please include all that apply: 1. Program Outcome(s): The student will demonstrate an appreciation and understanding of mathematics in order to develop creative and logical solutions to various abstract and practical problems. As a result of learning about the the basic structure and manipulation of mathematical functions, students will analyze and solve abstract and practical problems. 2. Institutional Outcome(s): As a result of studying instructor feedback given during lecture, or written on homework and exams, students will evaluate information critically and present solutions in a clear and logical manner. Santa Monica College Page 4 of 5 Comparison of Math 20 with Math 18 It is important for instructors to distinguish that Math 20 and Math 18, while both titled “Intermediate Algebra”, serve two different populations. The statement of intent submitted to the SMC Curriculum Committee in fall 2008 when Math 18 was proposed as an alternative prerequisite for Math 21, Finite mathematics for Liberal Arts, and Math 52/54, Elementary Statistics, is quoted below. “It has become apparent that the foundational needs of students intending to continue onto Calculus or teaching mathematics differ from students whose goal is a terminal liberal arts or statistics math course. Intermediate Algebra, Math 20, serves as a launching group for both students. … “Math 20 will continue to serve those students planning to continue on to calculus, Math 41, Mathematics for Elementary School Teachers, or who are undecided. Math 18, Algebra for Statistics and Finite Mathematics, is a new 3-unit course that is a second course in high school algebra designed for students whose terminal math course is Math 21 (Finite Mathematics) or Math 54 (Elementary Statistics). This 3-unit course differs from the 5-unit course Math 20 in the target audience. Math 20 remains the more rigorous algebraic prerequisite for students who intend to take calculus or Math 41 (Mathematics for Elementary School Teachers). While Math 20 and Math 18 cover the same broad topics, the depth of the coverage in Math 18 is substantially reduced from that of Math 20. In exchange, the emphasis in Math 18 is on setting up and solving practical applications of the algebraic material, essential for success in the following terminal courses. It is critical that instructors teaching Math 18 recognize that while this course covers many, but not all, of the same topics as Math 20, it serves as the preprequisite for students who plan to complete their study of mathematics with Math 21, Finite Mathematics, or Math 54, Elementary Statistics. It is not meant to prepare students for the study of calculus. For this reason, instructors should note that Chapters 5 (polynomial functions), 6 (rational expressions), 7 (rational exponents, radicals and complex numbers) and 10 (conic sections) are not part of the curriculum for this course. Textbook: Martin-Gay, E. Intermediate Algebra. Upper Saddle River, 2009 A Sample Schedule for Math 18 This schedule assumes a standard meeting schedule of 1 hr 20 min with 2 class meetings per week. Session 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Text Section/Activity Text section/topic Chapter 1 Review of the Real Number System 2.1/2.3 Linear Equations in One Variable, Formulas and Problem Solving 2.4/2.5 Linear Inequalities and Problem Solving, Compound Inequalities 2.6/2.7 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities 3.2/3.3 Introduction to Functions, Graphing Linear Functions 3.4/3.5 The Slope of a Line, Equations of Lines Exam 1 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 4.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables 4.3 Systems of Linear Equations and Problem Solving Santa Monica College Page 5 of 5 Session 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Text Section/Activity 4.4 Solving Systems of Equations by Matrices 3.7/4.5 Graphing Linear Inequalities, Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities 8.1/8.2 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square & the Quadratic Formula 8.3 Solving Equations by Using Quadratic Methods 8.5 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs 8.6 Further Graphing of Quadratic Functions Exam 2 9.2 Inverse Functions 9.3 Exponential Functions 9.4 Logarithmic Functions 9.5 Properties of Logarithms 9.6 Common Logarithms, Natural Logarithms, and Change of Base 9.7 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Applications Exam 3 11.1/11.3 Sequences, Series 11.2 Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 11.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences Review