Test 3 Answer is Here!!!!!
advertisement

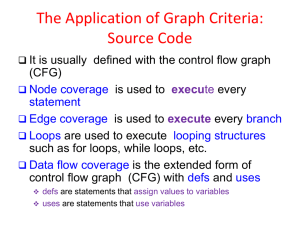
Chapter 9.
1. Use node<int> pointers for parts (a) and (b)
node<int> *p, *q, *r, *s;
After executing the instructions, display the order of the nodes.
p = new node<int>(10);
q = new node<int>(5);
r = new node<int>(7, p);
s = new node<int>(3, q);
p->next = s;
The correct answer: 7 10 3 5
2. What is the runtime efficiency for deleting the last node in a singly
linked list when a pointer to the rear of the list is not maintained?
The correct answer: O(n)
3. Assume the declaration
node<int> *p, *q, *r;
After executing the following statements, what is the order of the data
values in the resulting list?
p = new node<int> (12);
q = new node<int>(5);
r = new node<int>;
r->nodeValue = p->nodeValue + 3;
p->next = r;
r->next = q;
The correct answer: 12 15 5
4. The following function takes a pointer to the front of a singly linked
list.
template <typename T>
T f(node<T>* front)
{
node<T>* p = front;
while (p->next != NULL)
p = p->next;
return p->nodeValue;
}
Assume the linked list has the elements
5 -> 12 -> 8 -> 3 -> 7 -> 16 -> 10
front
The output from the statement "cout << f(front);" is ______
The correct answer: 10
5. Assume the linked list of integers is ___
6 -> 2 -> 9 -> 3 -> 8
front
Declare the pointers
node<int> *p = front->next, *q;
After executing the following statements, the list is ____
q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
delete q;
Your answer: 6 -> 2 -> 3 -> 8
front
6. Assume arr is an array of integers with the elements {7, 9, 6, 8, 4}.
After using the following declarations and the for-loop, give the order
of elements in the resulting singly linked list.
node<int> *front = NULL;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
if (front == NULL || arri[i] < front->nodeValue)
front = new node<int>(arr[i], front);
else
front->next = new node<int>(arr[i], front->next);
The correct answer: 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9
front
7. Consider a linked list with the following nodes containing character
data.
TJTKAJD
front
After executing the loop, what is the resulting value of n?
int n = 0;
node<char> *p = front;
while (p != NULL)
{
n++;
p = p->next;
}
The correct answer: 7
8. Does the following criteria indicate that a doubly linked list is empty?
header->next == header->prev
Your answer: False
9. Which of the following statements inserts a copy of the last element
in a doubly linked list at the first location in the list?
Your answer: insert(header->next, header->prev->nodeValue);
10. The list iterator for begin() and end() correspond to the dnode
pointers ________ respectively.
The correct answer: header->next and header
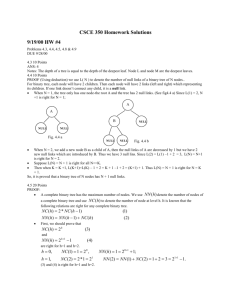
Chapter 10
1. Use the following representation of a binary tree.
8
19
30
14
50
25
7
12
25
18
10
1
3
8
The depth of the tree is _____
The correct answer: 5
2. Use the following representation of a binary tree.
8
19
30
14
50
25
7
12
25
18
10
1
3
8
The number of leaf nodes is _____
35
35
The correct answer: 6
3. Use the following representation of a binary tree.
8
19
30
14
50
25
7
12
25
18
35
10
1
3
8
From the LRN (postorder) scan of the nodes, identify the first 3 and the last three
nodes that are visited.
Your answer: 10 1 7 . . . 25 30 8
4. The algorithm to determine the depth of a tree is most easily handled using
______________.
Your answer: either LRN or RLN scan
5. A complete binary tree with 10 nodes has ______ leaf nodes.
The correct answer: 5
6. Use the following list of elements to build the binary search tree of integer nodes.
list: {20, 35, 18, 6, 40, 52, 10, 15, 25}
The number of nodes at level 2 in the tree is _____
Your answer: 3
7. Use the following list of elements to build the binary search tree of integer nodes.
list: {20, 35, 18, 6, 40, 52, 10, 15, 25}
When inserting value 8 in the binary search tree, the path of nodes from the root
contains the values _______
The correct answer: {6, 10, 18, 20}
8. In a RLN scan of a binary search tree, the first node visited has the ___________.
Your answer: largest value
9. A binary search tree uses stnode objects that contain the parent field. This field is
used for _____. Select the best response.
The correct answer: the insert(), erase(), and iterator ++ and -- operations
10. Trace the code in function f() for a binary tree with integer values. .
int f(tnode<int> *t)
{
int sl, sr;
if (t == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
sl= f(t->left);
sr= f(t->right);
return t->nodeValue + sl + sr;
}
}
What is the return value for the following binary tree?
30
50
10
15
50
40
5
25
The correct answer: 225