Graphing and function vocabulary: Math 97
advertisement

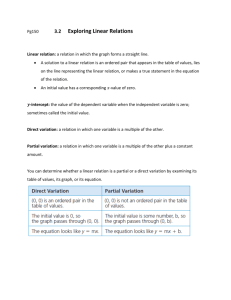
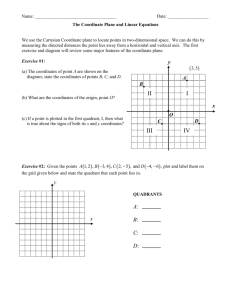
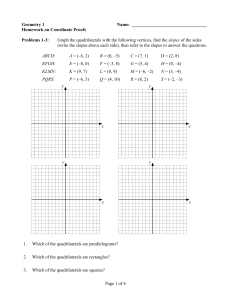
Graphing and function vocabulary: Math 99 Below is a list of words with which you should have a working knowledge. Be sure you have an understanding of each: use your textbook to assist you with this (all words are found in bold print throughout Chapters 3 and 7, are in the glossary, or were covered in class) Axes—two perpendicular number lines used to identify points in a plane Origin—the point on the graph where the two axes intersect: coordinates are (0,0) Coordinates (first and second)—the numbers in an ordered pair: the x-coordinate (measured on horizontal axis) is first, the y-coordinate (measured on vertical axis) is 2nd Ordered pairs—a pair of numbers that designate a particular point on a plane. The order is significant! Interpolation—process of estimating a value between given values Extrapolation—the process of estimating a value that goes beyond the given data Graph (both as a verb, “to graph something” and as a noun, “construct a graph”)—as a verb, “to graph” is to create a picture or diagram of the possible solutions to an equation. As a noun, “a graph” is a picture or diagram that displays data Linear—refers to something that relates to a straight line. Linear Equations are equations that, when graphed, form a straight line. Algebraically, they have no terms of higher degree than 1. Dependent and Independent variables—The dependent variable is generally the yvariable, b/c it’s value depends on the x-variable chosen. The x-variable is generally independent, b/c it can be chosen at random. Intercepts (x and y)—the x-intercept is where the graphed equation crosses the x-axis (y-coord is always 0): the y-intercept is where the graphed equation crosses the y-axis (x-coord is always 0) Rate—a ratio that indicates how two quantities change with respect to each other. Slope—The ratio of the rise to the run for any two points on a line Slope-intercept equation—of the form y=mx+b, gives info about the slope and the yintercept of a line. Parallel—lines that extend indefinitely and never intersect: their slopes are the same Perpendicular—lines that intersect at right angles: their slopes are opposite reciprocals of one another (the product of their slopes is -1) Function—a correspondence that assigns to each member of some set called the domain exactly one member of a set called the range. Domain of function—the set of all first coordinates of the ordered pairs in a function. Range of function—the set of all 2nd coordinates of the ordered pairs in a function. Relation—a correspondence between the domain and range such that each member of the domain corresponds to at least one member of the range. Piecewise function—a function that is defined by different equations for various parts of its domain Linear function—a function that graphs to a non-vertical straight line Non-linear function—a function whose graph is not a straight line