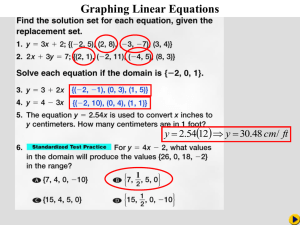
Exponents
advertisement
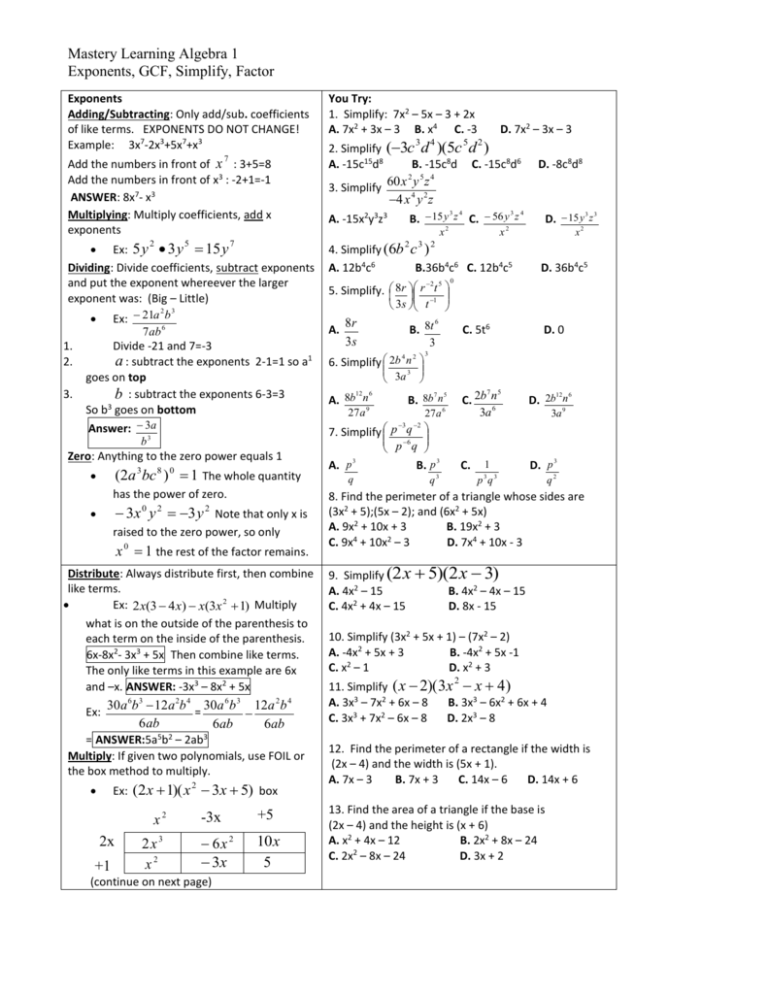
Mastery Learning Algebra 1 Exponents, GCF, Simplify, Factor Exponents Adding/Subtracting: Only add/sub. coefficients of like terms. EXPONENTS DO NOT CHANGE! Example: 3x7-2x3+5x7+x3 7 Add the numbers in front of x : 3+5=8 Add the numbers in front of x3 : -2+1=-1 ANSWER: 8x7- x3 Multiplying: Multiply coefficients, add x exponents Ex: 5 y 3 y 15 y Dividing: Divide coefficients, subtract exponents and put the exponent whereever the larger exponent was: (Big – Little) 2 3. 7 2 3 Ex: 21a b 7ab 6 1. 2. 5 3 Answer: 3a b3 4 5 D. 7x2 – 3x – 3 2 2. Simplify (3c d )(5c d ) A. -15c15d8 B. -15c8d C. -15c8d6 2 3. Simplify D. -8c8d8 5 4 60x y z 4 x 4 y 2 z A. -15x2y3z3 3 4 3 4 B. 15 y z C. 56 y z x2 2 x 3 3 D. 15 y z 2 x2 3 2 4. Simplify (6b c ) A. 12b4c6 B.36b4c6 C. 12b4c5 2 5 5. Simplify. 8r r t D. 36b4c5 0 1 3s t A. Divide -21 and 7=-3 a : subtract the exponents 2-1=1 so a1 goes on top b : subtract the exponents 6-3=3 So b3 goes on bottom 8r 3s 6 B. 8t 4 2 6. Simplify 2b n 3 3a 12 C. 5t6 D. 0 3 6 3 7 5 B. 8b n A. 8b n 27 a 9 27 a 6 7 C. 2b n 3a 6 5 12 6 D. 2b n 3a 9 7. Simplify p q 6 3 Zero: Anything to the zero power equals 1 2 p q 3 B. p 3 q 3 A. p has the power of zero. 8. Find the perimeter of a triangle whose sides are (3x2 + 5);(5x – 2); and (6x2 + 5x) A. 9x2 + 10x + 3 B. 19x2 + 3 C. 9x4 + 10x2 – 3 D. 7x4 + 10x - 3 3x y 3 y Note that only x is raised to the zero power, so only 0 2 2 x 0 1 the rest of the factor remains. q C. 3 D. p (2a 3bc 8 ) 0 1 The whole quantity You Try: 1. Simplify: 7x2 – 5x – 3 + 2x A. 7x2 + 3x – 3 B. x4 C. -3 1 p q3 3 q2 Distribute: Always distribute first, then combine 9. Simplify (2x 5)(2x 3) like terms. A. 4x2 – 15 B. 4x2 – 4x – 15 2 2 Ex: 2 x(3 4 x) x(3x 1) Multiply C. 4x + 4x – 15 D. 8x - 15 what is on the outside of the parenthesis to 10. Simplify (3x2 + 5x + 1) – (7x2 – 2) each term on the inside of the parenthesis. 2 B. -4x2 + 5x -1 6x-8x2- 3x3 + 5x Then combine like terms. A. -4x + 5x + 3 C. x2 – 1 D. x2 + 3 The only like terms in this example are 6x 2 3 2 and –x. ANSWER: -3x – 8x + 5x 11. Simplify (x 2)(3x x 4) 3 2 A. 3x – 7x + 6x – 8 B. 3x3 – 6x2 + 6x + 4 30a 6b 3 12a 2b 4 30a 6 b 3 12a 2 b 4 Ex: = C. 3x3 + 7x2 – 6x – 8 D. 2x3 – 8 6ab 6ab 6ab = ANSWER:5a5b2 – 2ab3 Multiply: If given two polynomials, use FOIL or the box method to multiply. Ex: (2 x 1)( x 2 3x 5) box x2 2x +1 2x 3 x2 -3x +5 6x 2 3x 10 x 5 (continue on next page) 12. Find the perimeter of a rectangle if the width is (2x – 4) and the width is (5x + 1). A. 7x – 3 B. 7x + 3 C. 14x – 6 D. 14x + 6 13. Find the area of a triangle if the base is (2x – 4) and the height is (x + 6) A. x2 + 4x – 12 B. 2x2 + 8x – 24 2 C. 2x – 8x – 24 D. 3x + 2 Mastery Learning Algebra 1 Exponents, GCF, Simplify, Factor Rewrite the contents of the box and then 4 xy2 6 xy 8x 2 y 146. 14. Simplify combine like terms. 2 xy 2 x 3 6 x 2 10 x x 2 3x 5 Like A. 2xy – 3 + 4x B. 2y – 3 + 4x 2 2 D. 2xy – 3 + 4x2 terms in this example are 6x and x as C. 2y – 3 + 4xy well as 10 x and 3x . 15. Find the area of a square whose side is 3x4 3 2 ANSWER: 2 x 5 x 7 x 5 A. 12x4 B.9x16 C. 12x6 D. 9x8 GCF CALCULATOR: [MATH]->NUM 9: gcd( Type 2 numbers with ‘,’ between. If there are more than two then pair each number together. Then find the greatest common factor between your answers. Ex: Find the GCF of 12, 18, 36 gcd(12, 18)=6 gcd( 12, 36) =12 gcd( 18, 36)= 18 so GCF = 6 Variables: Take the smallest exponent of each variable. Ex: a12bc 4 , a 6 b 3 c 2 , a 9 b 5 c 6 6 ANSWER: a bc 2 158. Factor Ax Bx C 1. When factoring a trinomial, factor out any GCF(number and/or variable) between all three terms. 2. Multiply the coefficient of the first term by the last term. 3. Find the factors of this multiplied number that add to the middle term CALCULATOR STEPS: Go to y= Y1= AC Y2= B - x 2 x 6 4 16. Find the GCF: 63x y & 18 x A. 3x6y9 B. 9x6y9 C. 3x3y4 3 y9 D. 9x3y4 17. Find the GCF: 60r3s2 & 15r2s & 27rs3 A.5r3s3 B. 5r3s3 C. 3rs D. 3r3s3 18. Find the GCF: 12x2y4 & 60x3y6 & 36x4y3z A. 12x2y3 B. 12x4y6z C. 6x2y3 D. 12x4y6z <Another way to see if something is a factor is to do 17 STO X ENTER. Then divide the (problem) by each (factor). If you get an integer then it’s probably a factor> 19. The area of a rectangle is given by the expression of x - 5x - 6. The length and width only have integral coefficients. Which of the following could represent the length of the rectangle? A. x – 6 B. x – 2 C. x – 3 D. x – 1 20. Factor completely: A. a(2a – 7)(a + 3) C. a(a + 3)(a – 7) 2a 3 a 2 21a B. a(2a+7)(a – 3) D. a(a – 3)(a + 7) [2nd] [Graph] (Table) Look where Y1 and Y2 are 1 21. Which is a factor of 10x2 + 29x - 21? the same. Let Bx be ‘x’x and ‘Y1’x A. 5x + 3 B. 5x – 3 4. Rewrite as Ax2 + xx + Y1x + C. C. 2x – 7 D. 10x + 7 5. Solve by grouping. * Example: 2 x 5 x 3 x 3 2 1. x(2 x 5 x 3) 2. Factors of 6 that add to 5 3. 1, 6 2, 3 ** 4. (2x2 + 2x) + (3x + 3) 5. 2x(x + 1) + 3(x + 1) (2x + 3)(x + 1) 5. ANSWER: x( x 1)( 2 x 3) 2 22. Factor completely: 4 x 24 x A. (2x – 10)(2x – 2) B. 4(x – 5)(x – 1) C. 4(2x -10)(x – 1) D. (2x – 10)(x + 1) 2 20